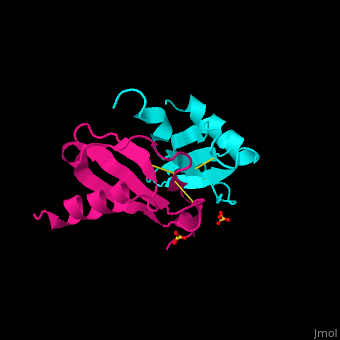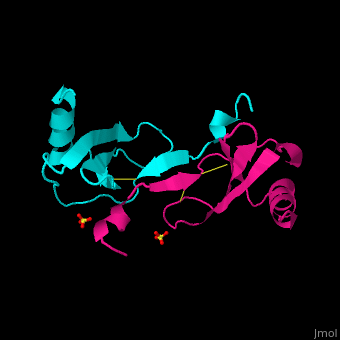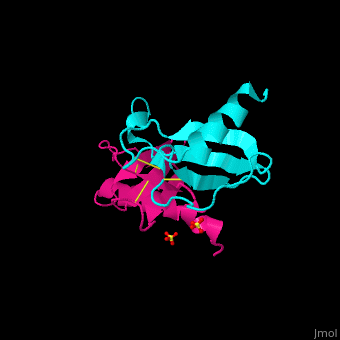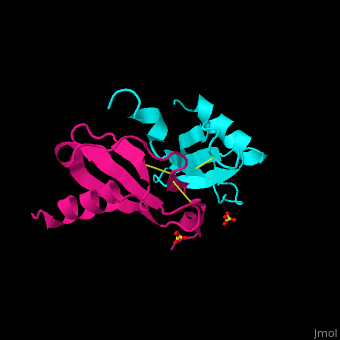Monocyte chemoattractant protein
From Proteopedia
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function and Structure == | == Function and Structure == | ||
| - | ''' | + | Human synthetic '''monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP)''' belongs to the superfamily of chemokines, which are proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The gene for CCL2 is on chromosome 17 in region 17q11.2-q12. The superfamily can be subdivided into 4 smaller groups, depending on the N-terminal arrangement of the cysteines. The CCL2<ref>PMID:8170963</ref> is also known as '''chemokine (C-C motif) ligand''' or: |
| - | - | + | - MCP1 |
- small inducible cytokine A2 (SCYA2) | - small inducible cytokine A2 (SCYA2) | ||
- MCAF | - MCAF | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
It exists as a monomer or a dimer, even though the homodimer form is preferred. | It exists as a monomer or a dimer, even though the homodimer form is preferred. | ||
The structure of the monomer is made of <scene name='72/721520/Ligand_binding_on_ccl2/2'>3 Beta sheets and 1 alpha helix</scene>. | The structure of the monomer is made of <scene name='72/721520/Ligand_binding_on_ccl2/2'>3 Beta sheets and 1 alpha helix</scene>. | ||
| + | *'''MCP-1''' regulates migration and infiltration of monocytes/macrophages<ref>PMID:19441883</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''MCP-3''' activates all types of leukocytes<ref>PMID:11781181</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''MCP-4''' is a potent chemoattractant for monocytes and eosinophils and stimulates histamine release from basophils<ref>PMID:8955214</ref>. | ||
== Ligands == | == Ligands == | ||
The known ligands for CCL2 are <scene name='72/721520/Ligand_binding_on_ccl2/1'>Potassium and PO4</scene>. The potassium binds to the S33 and S34 of the monomer and PO4 binds to F15 and N17. | The known ligands for CCL2 are <scene name='72/721520/Ligand_binding_on_ccl2/1'>Potassium and PO4</scene>. The potassium binds to the S33 and S34 of the monomer and PO4 binds to F15 and N17. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 45: | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | * Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 | + | * Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 1 or C-C motif chemokine 2 or CCL2 |
**[[1dok]], [[1dol]] – hMCP-1 (mutant) - human<br /> | **[[1dok]], [[1dol]] – hMCP-1 (mutant) - human<br /> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 54: | ||
**[[4zk9]] – hMCP-1 + chemokine binding protein<br /> | **[[4zk9]] – hMCP-1 + chemokine binding protein<br /> | ||
**[[4r8i]] – hMCP-1 + RNA<br /> | **[[4r8i]] – hMCP-1 + RNA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7so0]], [[8fj0]] – hMCP-1 + evasin<br /> | ||
| - | * Monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 | + | * Monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 or CCL8 or C-C motif chemokine 8 |
| + | **[[7s5a]] – hMCP-2 <br /> | ||
**[[1esr]] – hMCP-2 (mutant) <br /> | **[[1esr]] – hMCP-2 (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | * Monocyte chemoattractant protein 3 | + | * Monocyte chemoattractant protein 3 or C-C motif chemokine 7 or CCL7 |
**[[1ncv]], [[1bo0]] – hMCP-3 - NMR<br /> | **[[1ncv]], [[1bo0]] – hMCP-3 - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[4zkc]] – hMCP-3 + chemokine binding protein<br /> | **[[4zkc]] – hMCP-3 + chemokine binding protein<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7s58]], [[7s59]], [[7scu]] – hMCP-3 + evasin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8fk6]], [[8fk8]] – hMCP-3 + evasin<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8fj3]] – hMCP-3 (mutant) + evasin<br /> | ||
* Monocyte chemoattractant protein 4 | * Monocyte chemoattractant protein 4 | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Synthesis
The protein human CCL2 has been synthesized using a combination of solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and native chemical ligation (NCL). The thioester-peptide segment was synthesized using the sulfonamide safety-catch linker and 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) SPPS, and pseudoproline dipeptides were used to facilitate the synthesis of both CCL2 fragments. After assembly of the full-length peptide chain by NCL, a glutathione redox buffer was used to fold and oxidize the CCL2 protein. CCL2 was crystallized and the structure was determined by X-ray diffraction at 1.9-A resolution. This is probably one of the first crystal structures of a protein prepared using the sulfonamide safety-catch linker and NCL.
3D structures of Monocyte chemoattractant protein
Updated on 15-July-2024
References
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/CCL2 http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl?pdbcode=1DOK http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P13500#interaction http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3IFD
- ↑ Carr MW, Roth SJ, Luther E, Rose SS, Springer TA. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 acts as a T-lymphocyte chemoattractant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3652-6. PMID:8170963
- ↑ Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S, Sawaya BE. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): an overview. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Jun;29(6):313-26. PMID:19441883 doi:10.1089/jir.2008.0027
- ↑ Menten P, Wuyts A, Van Damme J. Monocyte chemotactic protein-3. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2001 Oct-Dec;12(4):554-60 PMID:11781181
- ↑ Garcia-Zepeda EA, Combadiere C, Rothenberg ME, Sarafi MN, Lavigne F, Hamid Q, Murphy PM, Luster AD. Human monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-4 is a novel CC chemokine with activities on monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils induced in allergic and nonallergic inflammation that signals through the CC chemokine receptors (CCR)-2 and -3. J Immunol. 1996 Dec 15;157(12):5613-26 PMID:8955214
- ↑ Ito Y, Ishiguro H, Kobayashi N, Hasumi H, Watanabe M, Yao M, Uemura H. Adipocyte-derived monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) promotes prostate cancer progression through the induction of MMP-2 activity. Prostate. 2015 Jul 1;75(10):1009-19. doi: 10.1002/pros.22972. Epub 2015 Apr 27. PMID:25917126 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pros.22972
- ↑ Lubkowski J, Bujacz G, Boque L, Domaille PJ, Handel TM, Wlodawer A. The structure of MCP-1 in two crystal forms provides a rare example of variable quaternary interactions. Nat Struct Biol. 1997 Jan;4(1):64-9. PMID:8989326
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Coline Perrin, Alexane Caignard, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman