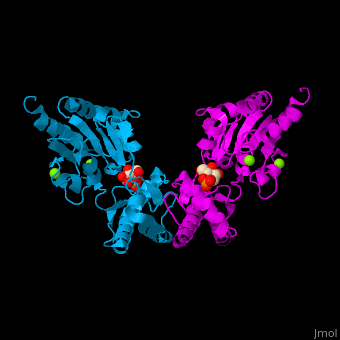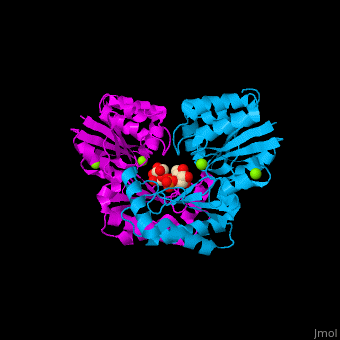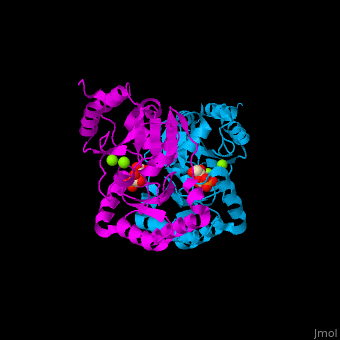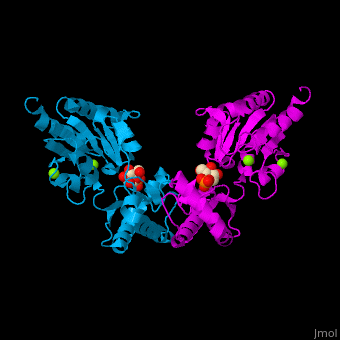Phosphomannomutase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human phosphomannomutase 1 complex with α-D-mannose-1-phosphate and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB entry [[2fue]])' scene='48/481638/Cv/1'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Phosphomannomutase''' (PMM) catalyzes the conversion of α-D-mannose 1-phosphate to D-mannose 6-phosphate. PMM participates in fructose and mannose metabolism. | '''Phosphomannomutase''' (PMM) catalyzes the conversion of α-D-mannose 1-phosphate to D-mannose 6-phosphate. PMM participates in fructose and mannose metabolism. | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | The PMM structure contains a <scene name='48/481638/Cv/ | + | The PMM structure contains a <scene name='48/481638/Cv/7'>core domain and a cap domain</scene>. It is known that in order for the substrate to bind, the cap must dissociate from the core domain and then re-associate to seal the active site from solvent molecules. The <scene name='48/481638/Cv/8'>active site of PMM is located at the interface of the core and cap domains of the molecule</scene><ref>PMID:16540464</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
*Phosphomannomutase | *Phosphomannomutase | ||
| - | **[[1k2y]] – PaPMM (mutant) – ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1k35]] – PaPMM<br /> | ||
**[[2amy]], [[2q4r]] – hPMM2 – human<br /> | **[[2amy]], [[2q4r]] – hPMM2 – human<br /> | ||
**[[2fuc]] – hPMM1 + Mg<br /> | **[[2fuc]] – hPMM1 + Mg<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6cfr]], [[6cfs]], [[6cft]], [[6cfu]] – hPMM1 (mutant) + Mg<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6cfv]] – hPMM1 + Mg + inosine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2fue]] – hPMM1 + α-D-mannose-1-phosphate + Mg<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7o0c]] – hPMM2 + Mg<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7o5z]] – hPMM2 (mutant) + Mg<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7o1b]], [[7o4g]], [[7o58]] – hPMM2 + α-D-glucose-1,6-bisphosphate + Mg<br /> | ||
**[[2i54]] – LmPMM + Mg – ''Leishmania Mexicana''<br /> | **[[2i54]] – LmPMM + Mg – ''Leishmania Mexicana''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3f9r]] - PMM + Mg – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | ||
**[[2i55]] - LmPMM + α-D-glucose-1,6-bisphosphate + Mg<br /> | **[[2i55]] - LmPMM + α-D-glucose-1,6-bisphosphate + Mg<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[3f9r]] - PMM + Mg – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> |
| + | **[[8b5v]] - PMM + Mg – ''Trypanosoma cruzi''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6i5x]] – PMM + Mg – ''Aspergillus fumigata''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1k35]] – PaPMM – ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1k2y]] – PaPMM (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[1p5d]], [[1p5g]] – PaPMM + α-D-glucose-1-phosphate<br /> | **[[1p5d]], [[1p5g]] – PaPMM + α-D-glucose-1-phosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4hjh]] - PaPMM + D-glucose-6-phosphate<br /> | **[[4hjh]] - PaPMM + D-glucose-6-phosphate<br /> | ||
**[[1pcj]], [[1pcm]] - PaPMM + α-D-mannose-1-phosphate<br /> | **[[1pcj]], [[1pcm]] - PaPMM + α-D-mannose-1-phosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5ue7]] - PMM – ''Candida albicans''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7myv]] – PMM + Mg – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | ||
*Phosphomannomutase/Phosphoglucomutase complex | *Phosphomannomutase/Phosphoglucomutase complex | ||
| Line 40: | Line 49: | ||
**[[2h5a]] - PaPMM/PGM + xylose-1-phosphate<br /> | **[[2h5a]] - PaPMM/PGM + xylose-1-phosphate<br /> | ||
**[[2f7l]] - PMM/PGM – ''Sulfolobus tokodaii''<br /> | **[[2f7l]] - PMM/PGM – ''Sulfolobus tokodaii''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3uw2]] – PMM/PGM PGM domain + phosphate – ''Burkholderia thailandensis'' | + | **[[3uw2]] – PMM/PGM PGM domain + phosphate – ''Burkholderia thailandensis''<br /> |
| + | **[[6mnv]] – XcPMM/PGM + Mg + CH2FG1P – ''Xanthomonas citri''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6n1e]] – XcPMM/PGM + Mg + methyl-glucose-6-phosphate <br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of phosphomannomutase
Updated on 28-August-2023
References
- ↑ Matthijs G, Schollen E, Pardon E, Veiga-Da-Cunha M, Jaeken J, Cassiman JJ, Van Schaftingen E. Mutations in PMM2, a phosphomannomutase gene on chromosome 16p13, in carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein type I syndrome (Jaeken syndrome). Nat Genet. 1997 May;16(1):88-92. PMID:9140401 doi:10.1038/ng0597-88
- ↑ Silvaggi NR, Zhang C, Lu Z, Dai J, Dunaway-Mariano D, Allen KN. The X-ray crystal structures of human alpha-phosphomannomutase 1 reveal the structural basis of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a. J Biol Chem. 2006 May 26;281(21):14918-26. Epub 2006 Mar 15. PMID:16540464 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M601505200