|
|
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | | | |
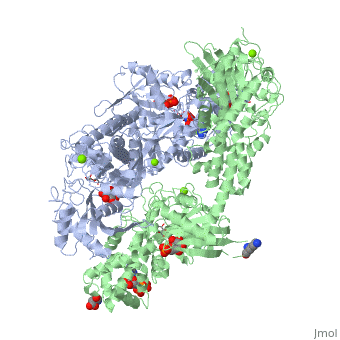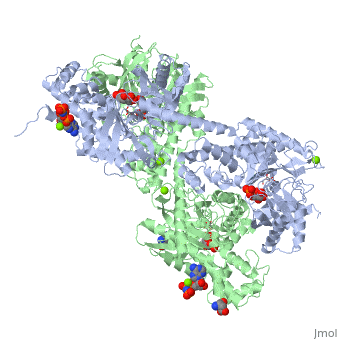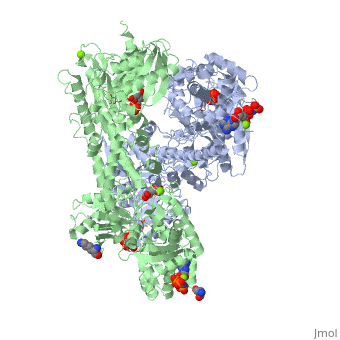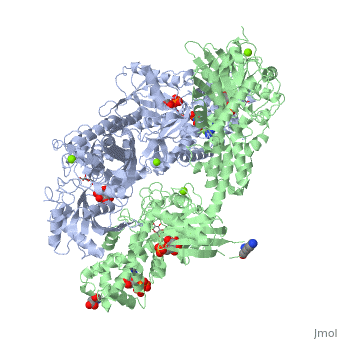
| | ==HUMAN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH ATP ANALOGUE AMP-PNP== | | ==HUMAN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH ATP ANALOGUE AMP-PNP== |
| - | <StructureSection load='1qha' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1qha]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.25Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='1qha' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1qha]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.25Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1qha]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1QHA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1QHA FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1qha]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1QHA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1QHA FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ANP:PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC+ACID-ADENYLATE+ESTER'>ANP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=G6P:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE'>G6P</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GLC:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE'>GLC</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.25Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hexokinase Hexokinase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=2.7.1.1 2.7.1.1] </span></td></tr>
| + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ANP:PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC+ACID-ADENYLATE+ESTER'>ANP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=G6P:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE'>G6P</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GLC:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE'>GLC</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1qha FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1qha OCA], [http://pdbe.org/1qha PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1qha RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1qha PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1qha ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1qha FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1qha OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1qha PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1qha RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1qha PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1qha ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Disease == | | == Disease == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HXK1_HUMAN HXK1_HUMAN]] Defects in HK1 are the cause of hexokinase deficiency (HK deficiency) [MIM:[http://omim.org/entry/235700 235700]]. HK deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease with nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia as the predominant clinical feature. | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HXK1_HUMAN HXK1_HUMAN] Defects in HK1 are the cause of hexokinase deficiency (HK deficiency) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/235700 235700]. HK deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease with nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia as the predominant clinical feature. |
| | + | == Function == |
| | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HXK1_HUMAN HXK1_HUMAN] |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 29: |
Line 31: |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | <div class="pdbe-citations 1qha" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | | <div class="pdbe-citations 1qha" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> |
| | + | |
| | + | ==See Also== |
| | + | *[[Hexokinase|Hexokinase]] |
| | + | *[[Hexokinase 3D structures|Hexokinase 3D structures]] |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Hexokinase]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Bolognesi, M]] | + | [[Category: Bolognesi M]] |
| - | [[Category: Deriu, D]] | + | [[Category: Deriu D]] |
| - | [[Category: Magnani, M]] | + | [[Category: Magnani M]] |
| - | [[Category: Rosano, C]] | + | [[Category: Rosano C]] |
| - | [[Category: Sabini, E]] | + | [[Category: Sabini E]] |
| - | [[Category: Glycolysis]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Kinase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Phosphotransferase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transferase]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Disease
HXK1_HUMAN Defects in HK1 are the cause of hexokinase deficiency (HK deficiency) [MIM:235700. HK deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease with nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia as the predominant clinical feature.
Function
HXK1_HUMAN
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
BACKGROUND: Hexokinase I sets the pace of glycolysis in the brain, catalyzing the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of glucose. The catalytic properties of hexokinase I are dependent on product inhibition as well as on the action of phosphate. In vivo, a large fraction of hexokinase I is bound to the mitochondrial outer membrane, where the enzyme adopts a tetrameric assembly. The mitochondrion-bound hexokinase I is believed to optimize the ATP/ADP exchange between glucose phosphorylation and the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation reactions. RESULTS: The crystal structure of human hexokinase I has been determined at 2.25 A resolution. The overall structure of the enzyme is in keeping with the closed conformation previously observed in yeast hexokinase. One molecule of the ATP analogue AMP-PNP is bound to each N-terminal domain of the dimeric enzyme in a surface cleft, showing specific interactions with the nucleotide, and localized positive electrostatic potential. The molecular symmetry brings the two bound AMP-PNP molecules, at the centre of two extended surface regions, to a common side of the dimeric hexokinase I molecule. CONCLUSIONS: The binding of AMP-PNP to a protein site separated from the catalytic centre of human hexokinase I can be related to the role played by some nucleotides in dissociating the enzyme from the mitochondrial membrane, and helps in defining the molecular regions of hexokinase I that are expected to be in contact with the mitochondrion. The structural information presented here is in keeping with monoclonal antibody mapping of the free and mitochondrion-bound forms of the enzyme, and with sequence analysis of hexokinases that differ in their mitochondria binding properties.
Binding of non-catalytic ATP to human hexokinase I highlights the structural components for enzyme-membrane association control.,Rosano C, Sabini E, Rizzi M, Deriu D, Murshudov G, Bianchi M, Serafini G, Magnani M, Bolognesi M Structure. 1999 Nov 15;7(11):1427-37. PMID:10574795[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Rosano C, Sabini E, Rizzi M, Deriu D, Murshudov G, Bianchi M, Serafini G, Magnani M, Bolognesi M. Binding of non-catalytic ATP to human hexokinase I highlights the structural components for enzyme-membrane association control. Structure. 1999 Nov 15;7(11):1427-37. PMID:10574795
|