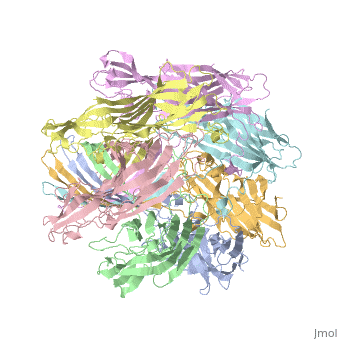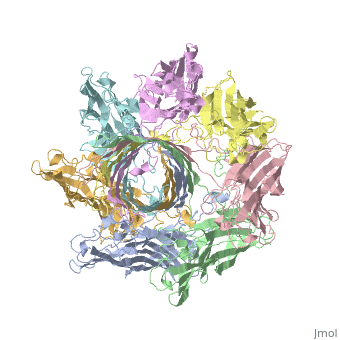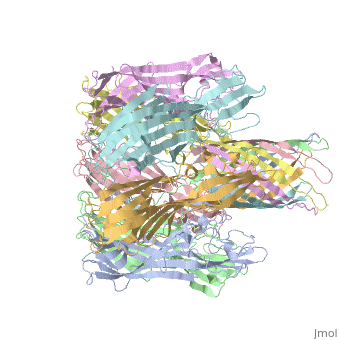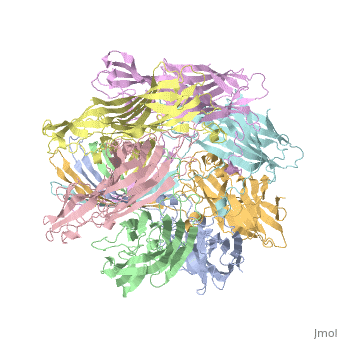We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Hemolysin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='7ahl' size='350' side='right' caption='α-hemolysin heptamer (PDB code [[7ahl]]).' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='7ahl' size='350' side='right' caption='α-hemolysin heptamer (PDB code [[7ahl]]).' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Hemolysin''' (HL) is exotoxin from bacteria which causes lysis of red blood cells<ref>PMID:20110774</ref>. | + | '''Hemolysin''' (HL) is exotoxin from bacteria which causes lysis of red blood cells<ref>PMID:20110774</ref>. |
| + | *'''alpha-hemolysin''' is a transmembrane pore-forming heptameric molecule<ref>PMID:8943190</ref>. See details for in [[Pore forming toxin, α-hemolysin]]. | ||
| + | *'''delta-hemolysin''' is a 26 amino acid peptide from the bacterium ''Staphylococcus'' exhibiting antimicrobial activity against'' Legionerlla'' <ref>PMID:19150639</ref>. | ||
| - | See details for α-hemolysin in [[Pore forming toxin, α-hemolysin]]. | ||
See details of hemolysin E in [[Molecular Playground/ClyA]]. | See details of hemolysin E in [[Molecular Playground/ClyA]]. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
HL acts as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of invasive infections<ref>PMID:12564994</ref>. | HL acts as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of invasive infections<ref>PMID:12564994</ref>. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | == 3D Structures of hemolysin == | ||
==3D Printed Physical Model of Hemolysin== | ==3D Printed Physical Model of Hemolysin== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
Shown below is a 3D printed physical model of Hemolysin. The model is shown in alpha carbon backbone format with each chain colored uniquely. | Shown below is a 3D printed physical model of Hemolysin. The model is shown in alpha carbon backbone format with each chain colored uniquely. | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:hemolysin1_centerForBioMolecularModeling.jpg|550px]] |
| - | [[Image:hemolysin2_centerForBioMolecularModeling.jpg]] | + | [[Image:hemolysin2_centerForBioMolecularModeling.jpg|550px]] |
====The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling==== | ====The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling==== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 25: | ||
The [http://cbm.msoe.edu MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling] uses 3D printing technology to create physical models of protein and molecular structures, making the invisible molecular world more tangible and comprehensible. To view more protein structure models, visit our [http://cbm.msoe.edu/educationalmedia/modelgallery/ Model Gallery]. | The [http://cbm.msoe.edu MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling] uses 3D printing technology to create physical models of protein and molecular structures, making the invisible molecular world more tangible and comprehensible. To view more protein structure models, visit our [http://cbm.msoe.edu/educationalmedia/modelgallery/ Model Gallery]. | ||
| + | == 3D Structures of hemolysin == | ||
| + | [[Hemolysin 3D structures]] | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | |||
| - | *α-hemolysin | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3anz]], [[7ahl]] – SaHL-α – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | ||
| - | A full page in Proteopedia exploring [[7ahl]] is found [[Pore_forming_toxin,_α-hemolsyin|here]].<br/> | ||
| - | **[[3m2l]], [[3m4d]], [[4p24]], [[4yhd]] - SaHL-α (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3m3r]], [[3m4e]] - SaHL-α (mutant) + β-cyclodextrin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4idj]], [[4u6v]] - SaHL-α + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *β-hemolysin | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3k55]] – SaHL-β)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3i5v]] - SaHL-β residues 35-330)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3i41]] - SaHL-β residues 35-330 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3i46]], [[3i48]] - SaHL-β residues 35-330 (mutant)<br /> + metal ion | ||
| - | |||
| - | *γ-hemolysin | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2qk7]] – SaHL-γ component A (mutant) +B (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3b07]] - SaHL-γ component A+B<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4p1x]] - SaHL-γ component B (mutant)+C<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4p1y]] - SaHL-γ component A + B (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *δ-hemolysin | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2kam]] – SaHL-δ - NMR | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Hemolysin | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3o44]] – VcHL residues 161-741 – ''Vibrio cholerae''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1xez]] – VcHL (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3a57]] – HL 2 – ''Vibrio parahaemolyticus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3hvn]] – HL (mutant) – ''Streptococcus suis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3fy3]], [[5keh]], [[5kf3]], [[4w8q]] – PmHL A residues 30-265 – ''Proteus mirabilis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5sz8]], [[5kkd]], [[4w8r]], [[4w8s]], [[4w8t]] - PmHL A residues 30-234 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1mt0]] – EcHL B ATP-binding domain – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5c21]], [[5c22]] - EcHL D residues 57-333 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2wcd]] – EcHL E residues 2-303 – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1qoy]], [[4pho]], [[4phq]] - EcHL E (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2oai]], [[2r8d]] – HL corc_hlyc domain – ''Xylella fastidiosa''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2r2z]] – HL residues 346-435 – ''Enterococcus faecalis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4wx3]], [[4wx5]] - HL – ''Grimontia hollisae''<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Alpha-toxin | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2wxt]], [[1ca1]] - CpAT + Cd + Zn – ''Clostridium perfringens''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1qm6]], [[1gyg]], [[1kho]] - CpAT + Zn <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2wy6]], [[2wxu]] – CpAT (mutant) + Ca + Cd + Zn<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1qmd]] - CpAT + Ca + Zn<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1olp]] - AT + Ca + Zn – ''Clostridium absonum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2vk9]] - AT – ''Clostridium novyi''<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
| + | [[Category:3D printer files]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mestre MB, Fader CM, Sola C, Colombo MI. Alpha-hemolysin is required for the activation of the autophagic pathway in Staphylococcus aureus-infected cells. Autophagy. 2010 Jan;6(1):110-25. PMID:20110774
- ↑ Song L, Hobaugh MR, Shustak C, Cheley S, Bayley H, Gouaux JE. Structure of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore. Science. 1996 Dec 13;274(5294):1859-66. PMID:8943190
- ↑ Verdon J, Girardin N, Lacombe C, Berjeaud JM, Héchard Y. delta-hemolysin, an update on a membrane-interacting peptide. Peptides. 2009 Apr;30(4):817-23. PMID:19150639 doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2008.12.017
- ↑ Nizet V. Streptococcal beta-hemolysins: genetics and role in disease pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 2002 Dec;10(12):575-80. PMID:12564994
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Mark Hoelzer, Wayne Decatur, Alexander Berchansky, Marius Mihasan