|
Introduction and Background
The cytoskeleton brings structure to the cell, is integral in cell division, and aids in migration. One of the constitutive parts of the cytoskeleton are microtubules. Microtubules are polymerized from tubulin subunits that incorporate into a hollow cylindrical structure linked together by lateral and vertical hydrogen bonds. Each tubulin subunit is made from a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulin. Both alpha and beta tubulin are known to bind to GTP. However, only the beta subunit hydrolyzes GTP, which occurs once incorporated into microtubules. The beta tubulin hydrolysis of GTP to GDP is known to destabilize microtubules. Microtubules have polarity where one end of microtubule, called the plus end, has a greater affinity to add tubulin subunits than the other end, called the minus end. Microtubules are inherently dynamic, going through periods of depolymerization, known as catastrophe, and then return to polymerization, known as rescue. Microtubules can also go through a process called treadmilling, where the length of the microtubule does not change but the rate of polymerization at the plus end equals the rate of depolymerization at the minus end. There are a number of microtubule associated proteins (MAPs) that are known to regulate the dynamics of microtubules. Some examples of this include MAPTau, MAP2 and stathmin. See tubulin, tau.
Evolutionary conservation
Stathmin belongs to a gene family that have a characteristic stathmin-like domain spanning across eukaryotes. This family includes Stathmin-1, SCG10/stathmin-2, SCILP/stathmin-3, and RB3/stathmin-4. RB3 is alternatively spliced to form RB3, RB3', and RB3" [1]. SCG10 and SCLIP, are exclusively neuronal proteins, while RB3 is expressed mostly in the brain but some in the adrenal glands [2] [3]. Unlike the neuronal proteins, stathmin-1 is ubiquitously expressed in all cell types.
Function
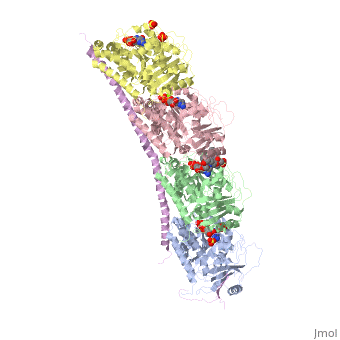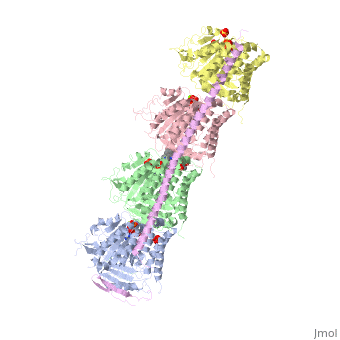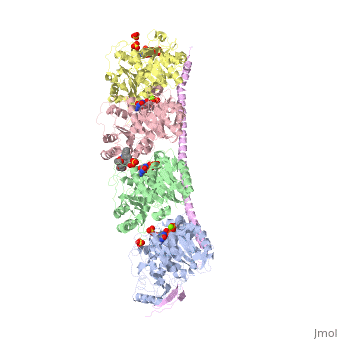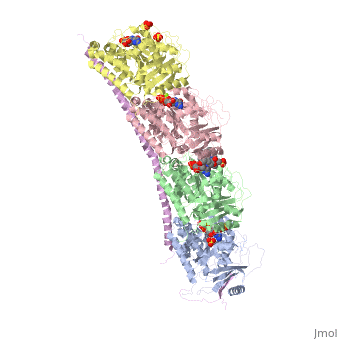
, also known as oncoprotein 18 or metablastin, is a 19kDa microtubule associated protein known to destabilize microtubules [4]. These proteins are cell cycle and developmentally regulated, known to play a role in proliferation, differentiation, and function of cells [5] [6]. Stathmin family proteins can bind to to inhibit polymerization or can bind to the microtubule to enhance the rate of catastrophe[7] The structure of stathmin-4, in 4eb6, is bound to two tubulin heterodimers. The tubulin dimers are bound to outside ligands. is a chemotherapeutic that binds to tubulin to prevent microtubule polymerization [8]. The tubulin subunits are bound to The beta subunits of tubulin are bound to GDP and each of the alpha subunits are bound to GTP and a Magnesium ion.
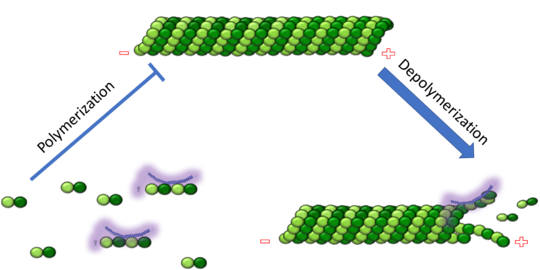 Figure 1. Adapted from Ruben 2004. Stathmin, in purple, can bind to tubulin dimers to prevent polymerization or to microtubules to increase the rate of catastrophe. Mitosis: Stathmin's role in the cell cycle progression is characterized. During interphase, microtubules are relatively stable. However during the onset of mitosis, stathmin is upregulated to increase the rate of catastrophe of microtubules, causing them to become more dynamic. Stathmin has also been shown to bind and sequester two tubulin heterodimers, reducing the amount of available tubulin to polymerize microtubules [9]. However, as mitosis progresses, microtubules must repolymerize to form the mitotic spindle. Stathmin is regulated during this process by phosphorylation [10] [11]. There are four known , serine 16, serine 25, serine 38, and serine 63 which are known to be a target of cyclin-dependent kinases [12] [13]. Stathmin overexpression prevents mitotic spindle formation where inhibition interferes with later stages in mitosis [14].
Migration: The cytoskeleton is a vital part of cell migration. Microtubules are needed to retract from the trailing edge to move the cell forward. Stathmin is thought to have a role in migration, allowing to microtubules to depolymerize to aid in movement. Stathmin has been show to be a part of the integrin alpha5 beta1/FAK/ ERK pathway [15]. Overexpression of stathmin increases motility of GN-11 neurons [16].
Differentiation: Stathmin family proteins expression are regulated during stages of development. They are regulated in early and late embryogenesis [17]. Stathmin is regulated in differentiating muscle cells, T lymphocytes, and oligodendryocytes [18] [19].
Structure
consistis of a coiled coil alpha helix in the C-terminal region and a mostly disordered N-terminal region that also has some beta strand properties. These different regions of the protein are known to have different functions.
 Figure 2. Stathmin structural domains related to amino acid sequence How does the structure relate to it's function?
The is known to increase tubulin catastrophe. This region helps destabilize the ends of the microtubule filaments by curving the tubulin dimers at the end, and disrupting lateral hydrogen bonds. The N-terminal region is known as the regulatory domain of the protein, because it is subject to most of the post-translational modifications. This region binds and caps alpha tubulin to accomplish this task [20]. The neuronal family members are known to contain an additional N-terminal domain to affect their localization [21]
The, also known as the interaction domain, is known to sequester tubulin heterodimers. This region is comprised of a . This region of stathmin is . Helix 10 of alpha tubulin is thought to be important for incorporation into microtubules [22]. All members of this protein family contain the C-terminal coiled coil domain. However, the binding affinity to tubulin differs from protein family members [23]
There are to stathmin-4 in this structure. The mutations at position 11 from an cysteine to an alanine and position 16 from a Phenylalanine to a Tryptophan.
Disease relevance
Cancer: Due to stathmin's role in mitosis and cell migration, it is not surprising that is has been implicated in many cancers and is an active target of cancer therapeutics. Stathmin is defined as an oncoprotein. Overexpression of stathmin has been shown to increase metastasis, worse prognosis, and increased chemoresistance [24] [25]. Stathmin levels are known to be increasesd in a number of cancers. Stathmin was seen to be upregulated in breast cancer tissue comparative with normal breast tissue [26]. Another study was done to show stathmin upregulation in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas [27]. Studies using a non-phosphorylatable stathmin mutant shows that cells arrest during mitosis [28].
Multiple Schlerosis: Stathmin expression has been linked to multiple sclerosis (MS) , a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by lack of motor control and numbness. MS is caused by loss of myelination on axons in the nervous system. Myelination of axons is performed by cells called oligodendrocytes. Stathmin is regulated in oligodendrocyte lineage, with progenitor cells containing larger amounts than differentiated oligodendrocytes. Brain tissue samples from people suffering from multiple sclerosis found that stathmin is up regulated later in the lineage of oligodendrocytes. The up-regulation of stathmin showed a more globular morphology of the cells. Oligodendrocyte ability to myelinate axons in the central nervous system was greatly reduced in these patients [29].
Links to available structures
- Stathmin SLD domain complex with tubulin
- 3ryf – rSTM + tubulin + GTP - rat
- 3hkb, 3ryc, 3ryi – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP
- 3ryh – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + phosphomethylphosphonic acid guanylate
- 3hkc, 3n2g, 3n2k – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + pyridine derivative
- 3hkd – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + pyrrolidine derivative
- 3hke – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + benzenesulfonamide derivative
- Stathmin SLD domain complex with tubulin and drugs
- 1sa0 – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + anti-gout drug
- 1sa1, 1z2b – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + anti-wart drug
- 5j2u – rSTM (mutant) + tubulin + GTP + GDP + anti-cancer drug
- 3du7 – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + phomopsine + anti-gout drug
- 3e22 – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + soblidotine + anti-gout drug
- 5lp6, 5kx5 – rSTM + tubulin + GTP + GDP + drug
- 3ut5 – rSTM (mutant) + tubulin + GTP + GDP + ustiloxine + anti-gout drug + Vinca tetrapeptide
- Stathmin SLD domain complex with tubulin and tubulin tyrosine ligase
- 4iij – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP
- 4ihj – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ADP
- 5jqg, 4wbn, 4i55 – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ATP derivative
- 4o2a – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ADP + inhibitor
- 4i50 – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + epothilone
- 4o4l, 5j2t, 5bmv, 5la6, 5jh7, 5jvd, 5fnv, 5c8y, 5ca0, 5ca1, 5cb4, 4yj2, 4yj3, 4x1i, 4x1k, 4x1y, 4x20, 4tuy, 4zol, 4tv8, 4tv9, 4o4j, 4o4l, 5i50, 4i4t, 4o4i, 4o2l, 5iyz, 5la6, 5m7e, 5m7g, 5m8d, 5m8g, 5xlt – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ATP derivative + anti-cancer drugs
- 4o2b – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ATP derivative + anti-gout drug
- 5lov, 5njh – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ATP derivative + azoamide
- 5lxs, 5lxt – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ATP derivative + discodermolide
- 5lyj, 5mf4 – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ATP derivative + natural product
- 5o7a – rSTM + tubulin + tubulin tyrosine ligase + GTP + GDP + ATP derivative + quinolin derivative
References
- ↑ Ozon S, Maucuer A, Sobel A. The stathmin family -- molecular and biological characterization of novel mammalian proteins expressed in the nervous system. Eur J Biochem. 1997 Sep 15;248(3):794-806. PMID:9342231
- ↑ Maucuer A, Moreau J, Mechali M, Sobel A. Stathmin gene family: phylogenetic conservation and developmental regulation in Xenopus. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16420-9. PMID:8344928
- ↑ Schubart UK, Banerjee MD, Eng J. Homology between the cDNAs encoding phosphoprotein p19 and SCG10 reveals a novel mammalian gene family preferentially expressed in developing brain. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):389-98. PMID:2776625
- ↑ Belmont LD, Mitchison TJ. Identification of a protein that interacts with tubulin dimers and increases the catastrophe rate of microtubules. Cell. 1996 Feb 23;84(4):623-31. PMID:8598048
- ↑ Jourdain L, Curmi P, Sobel A, Pantaloni D, Carlier MF. Stathmin: a tubulin-sequestering protein which forms a ternary T2S complex with two tubulin molecules. Biochemistry. 1997 Sep 9;36(36):10817-21. doi: 10.1021/bi971491b. PMID:9312271 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi971491b
- ↑ Howell B, Larsson N, Gullberg M, Cassimeris L. Dissociation of the tubulin-sequestering and microtubule catastrophe-promoting activities of oncoprotein 18/stathmin. Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jan;10(1):105-18. PMID:9880330
- ↑ Belmont LD, Mitchison TJ. Identification of a protein that interacts with tubulin dimers and increases the catastrophe rate of microtubules. Cell. 1996 Feb 23;84(4):623-31. PMID:8598048
- ↑ Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC. The clinical pharmacology and use of antimicrotubule agents in cancer chemotherapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Oct;52(1):35-84. PMID:1687171
- ↑ Jourdain L, Curmi P, Sobel A, Pantaloni D, Carlier MF. Stathmin: a tubulin-sequestering protein which forms a ternary T2S complex with two tubulin molecules. Biochemistry. 1997 Sep 9;36(36):10817-21. doi: 10.1021/bi971491b. PMID:9312271 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi971491b
- ↑ Marklund U, Osterman O, Melander H, Bergh A, Gullberg M. The phenotype of a "Cdc2 kinase target site-deficient" mutant of oncoprotein 18 reveals a role of this protein in cell cycle control. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30626-35. PMID:7982983
- ↑ Labdon JE, Nieves E, Schubart UK. Analysis of phosphoprotein p19 by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Identification of two proline-directed serine phosphorylation sites and a blocked amino terminus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3506-13. PMID:1737801
- ↑ Beretta L, Dobransky T, Sobel A. Multiple phosphorylation of stathmin. Identification of four sites phosphorylated in intact cells and in vitro by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20076-84. PMID:8376365
- ↑ Larsson N, Marklund U, Gradin HM, Brattsand G, Gullberg M. Control of microtubule dynamics by oncoprotein 18: dissection of the regulatory role of multisite phosphorylation during mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Sep;17(9):5530-9. PMID:9271428
- ↑ Larsson N, Segerman B, Gradin HM, Wandzioch E, Cassimeris L, Gullberg M. Mutations of oncoprotein 18/stathmin identify tubulin-directed regulatory activities distinct from tubulin association. Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):2242-50. PMID:10022911
- ↑ Lawler S, Gavet O, Rich T, Sobel A. Stathmin overexpression in 293 cells affects signal transduction and cell growth. FEBS Lett. 1998 Jan 2;421(1):55-60. PMID:9462839
- ↑ Giampietro C, Luzzati F, Gambarotta G, Giacobini P, Boda E, Fasolo A, Perroteau I. Stathmin expression modulates migratory properties of GN-11 neurons in vitro. Endocrinology. 2005 Apr;146(4):1825-34. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0972. Epub 2004 Dec , 29. PMID:15625246 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-0972
- ↑ Amat JA, Fields KL, Schubart UK. Distribution of phosphoprotein p19 in rat brain during ontogeny: stage-specific expression in neurons and glia. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991 Jun 21;60(2):205-18. PMID:1893566
- ↑ Filbert EL, Le Borgne M, Lin J, Heuser JE, Shaw AS. Stathmin regulates microtubule dynamics and microtubule organizing center polarization in activated T cells. J Immunol. 2012 Jun 1;188(11):5421-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200242. Epub 2012, Apr 23. PMID:22529300 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200242
- ↑ Liu A, Muggironi M, Marin-Husstege M, Casaccia-Bonnefil P. Oligodendrocyte process outgrowth in vitro is modulated by epigenetic regulation of cytoskeletal severing proteins. Glia. 2003 Dec;44(3):264-74. doi: 10.1002/glia.10290. PMID:14603467 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/glia.10290
- ↑ Howell B, Larsson N, Gullberg M, Cassimeris L. Dissociation of the tubulin-sequestering and microtubule catastrophe-promoting activities of oncoprotein 18/stathmin. Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jan;10(1):105-18. PMID:9880330
- ↑ Gavet O, Ozon S, Manceau V, Lawler S, Curmi P, Sobel A. The stathmin phosphoprotein family: intracellular localization and effects on the microtubule network. J Cell Sci. 1998 Nov;111 ( Pt 22):3333-46. PMID:9788875
- ↑ Howell B, Larsson N, Gullberg M, Cassimeris L. Dissociation of the tubulin-sequestering and microtubule catastrophe-promoting activities of oncoprotein 18/stathmin. Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Jan;10(1):105-18. PMID:9880330
- ↑ Charbaut E, Curmi PA, Ozon S, Lachkar S, Redeker V, Sobel A. Stathmin family proteins display specific molecular and tubulin binding properties. J Biol Chem. 2001 May 11;276(19):16146-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010637200. Epub 2001, Feb 15. PMID:11278715 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M010637200
- ↑ Jeon TY, Han ME, Lee YW, Lee YS, Kim GH, Song GA, Hur GY, Kim JY, Kim HJ, Yoon S, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kim JB, Oh SO. Overexpression of stathmin1 in the diffuse type of gastric cancer and its roles in proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2010 Feb 16;102(4):710-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605537. Epub 2010 Jan, 19. PMID:20087351 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605537
- ↑ Jiang L, Chen Y, Chan CY, Wang X, Lin L, He ML, Lin MC, Yew DT, Sung JJ, Li JC, Kung HF. Down-regulation of stathmin is required for TGF-beta inducible early gene 1 induced growth inhibition of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009 Feb 8;274(1):101-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.017. Epub, 2008 Oct 18. PMID:18930345 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.017
- ↑ Curmi PA, Nogues C, Lachkar S, Carelle N, Gonthier MP, Sobel A, Lidereau R, Bieche I. Overexpression of stathmin in breast carcinomas points out to highly proliferative tumours. Br J Cancer. 2000 Jan;82(1):142-50. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.1999.0891. PMID:10638981 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.1999.0891
- ↑ PMID: 23229199>
- ↑ Gavet O, Ozon S, Manceau V, Lawler S, Curmi P, Sobel A. The stathmin phosphoprotein family: intracellular localization and effects on the microtubule network. J Cell Sci. 1998 Nov;111 ( Pt 22):3333-46. PMID:9788875
- ↑ Liu A, Stadelmann C, Moscarello M, Bruck W, Sobel A, Mastronardi FG, Casaccia-Bonnefil P. Expression of stathmin, a developmentally controlled cytoskeleton-regulating molecule, in demyelinating disorders. J Neurosci. 2005 Jan 19;25(3):737-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4174-04.2005. PMID:15659612 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4174-04.2005
|