We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
TGF-beta receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
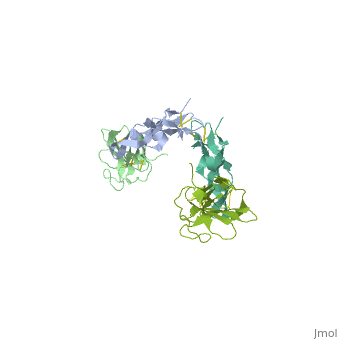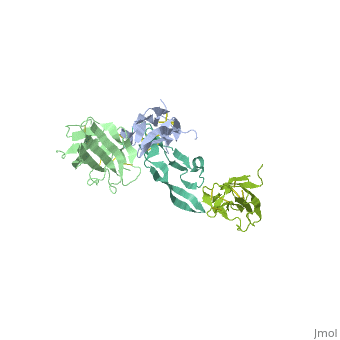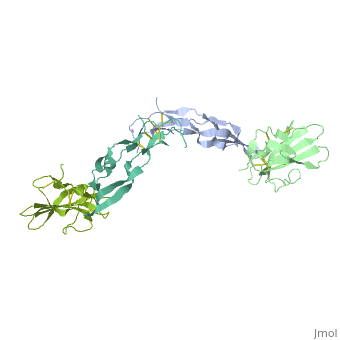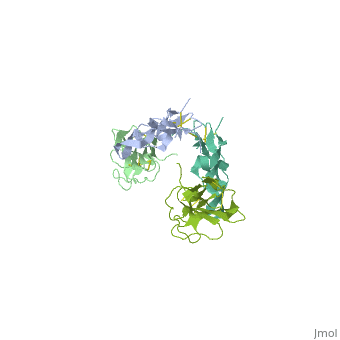
| - | <StructureSection load='1ktz' size='340' side='right' caption='Human | + | <StructureSection load='1ktz' size='340' side='right' caption='Human hTGFR-II extracellular domain (green) complex with TGF-β3 (grey) (PDB code [[1ktz]])' scene=''> |
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''TGF-β receptors''' (Transforming Growth Factor) ( | + | '''TGF-β receptors''' (Transforming Growth Factor) (TGFR) are [[serine/threonine kinase]] receptors. They are involved in paracrine signaling and are found in many types of tissue. TGF-β ligands include bone morphogenetic proteins, growth and initiation factors, anti-Mullerian hormone, activin, nodal TGF-β<ref>PMID:9525694</ref>. There are 3 types of TGFR: <br /> |
| - | *''' | + | *'''TGFR I''' forms heteromeric complex with TGFR II when it is bound to TGF-β. The complex transduces the TGF-β signal from the cell surface to the cytoplasm by phosphorylating proteins which regulate the transcription of genes related to cell proliferation. TGFR I has high affinity for TGF-β1 and low affinity for TGF-β2. <br /> |
| - | *''' | + | *'''TGFR II''' is a tumor suppressor transmembrane protein. TGFR II has high affinity for TGF-β1 and low affinity for TGF-β2. <br /> |
| - | *''' | + | *'''TGFR III''' is a cell-surface chondroitin sulfate / heparin sulfate proteoglycan. It acts as a reservoir of ligand for TGFRs. TGFR III has high affinity for TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β1.2. |
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Receptor]], [[TGF beta signaling pathway]], and [[Growth factors]]. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | Over-expression of TGF causes kidney disease, diabetes and renal disease. Mutations in | + | Over-expression of TGF causes kidney disease, diabetes and renal disease. Mutations in TGFR II cause various types of tumors<ref>PMID:23884466</ref>. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | + | TGFR structure contains a 100-140 residues ligand-binding N-terminal extracellular domain; a transmembrane domain; a 350-400 amino acid cytoplasmic kinase domain; and a C-terminal zona pellucida (ZP) domain of ca 260 residues which has a role in protein polymerization. | |
| + | |||
| + | == 3D Structures of TGF-beta receptor== | ||
| + | [[TGF-beta receptor 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | == 3D Structures of TGF-β receptor== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | |||
| - | * TGF-β receptor I; kinase domain 200-503 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1ias]], [[5e8s]] – hTGFBR-I kinase domain – human <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5e8t]], [[5e8u]] – hTGFBR-I kinase domain (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5e8w]], [[5e8x]] – hTGFBR-I kinase domain (mutant) + staurosporine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5e8z]] – hTGFBR-I kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2l5s]] – hTGFBR-I extracellular domain - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1b6c]] – hTGFBR-I kinase domain + FKBP12 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1py5]], [[3faa]], [[3gxl]], [[3hmm]], [[2wot]], [[2wou]], [[3kcf]], [[2x7o]], [[3tzm]], [[4x0m]], [[4x2j]], [[4x2k]], [[4x2n]] – hTGFBR-I kinase domain + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1vjy]] – hTGFBR-I residues 1-303 + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5usq]] – hTGFBR-I residues 123-421 + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1rw8]] – hTGFBR-I truncated kinase domain + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | * TGF-β receptor II | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1m9z]] – hTGFBR-II extracellular domain <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1plo]], [[4p7u]] – hTGFBR-II extracellular domain (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5e8v]] – hTGFBR-II kinase domain (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5e8y]] – hTGFBR-II kinase domain (mutant) + staurosporine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5e92]] – hTGFBR-II kinase domain (mutant) + AMPPNP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ks6]] – cTGFBR-II extracellular domain - chicken<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ktz]] – hTGFBR-II extracellular domain + TGF-β3 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ty4]] – hTGFBR-II extracellular domain + mmTGF-β2 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5tx4]] – mTGFBR-II extracellular domain (mutant) + hTGF-β2 - mouse<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | * TGF-β receptor III | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3qw9]] – TGFBR-III ZP-C domain - rat<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ajv]] – mTGFBR-III ZP-C domain <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | * TGF-β receptor I+II | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2pjy]] – hTGFBR-I extracellular domain (mutant) + hTGFBR-II extracellular domain (mutant) + TGF-β3 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3kfd]] – hTGFBR-I extracellular domain + hTGFBR-II extracellular domain + TGF-β1 <br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wrana JL. TGF-beta receptors and signalling mechanisms. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1998;24(2-3):120-30. PMID:9525694
- ↑ Frischmeyer-Guerrerio PA, Guerrerio AL, Oswald G, Chichester K, Myers L, Halushka MK, Oliva-Hemker M, Wood RA, Dietz HC. TGFbeta receptor mutations impose a strong predisposition for human allergic disease. Sci Transl Med. 2013 Jul 24;5(195):195ra94. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006448. PMID:23884466 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3006448