|
|
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | | | |
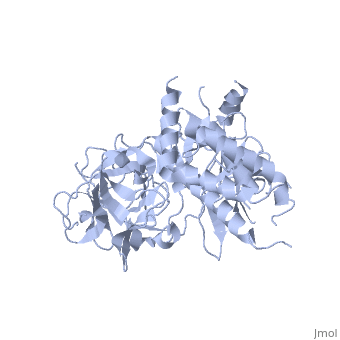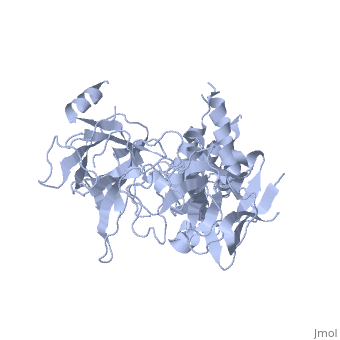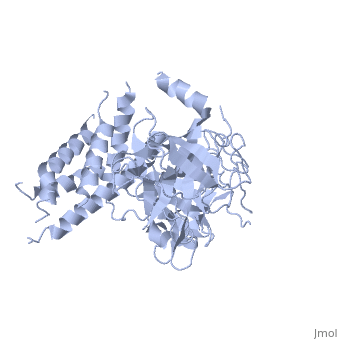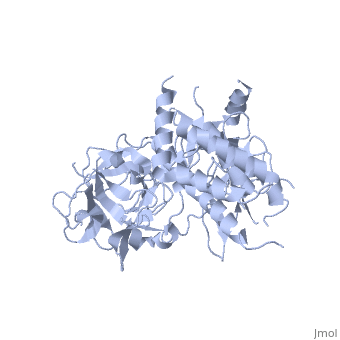
| | ==Crystal Structure of the N-terminal three domains of the skeletal muscle Ryanodine Receptor (RyR1)== | | ==Crystal Structure of the N-terminal three domains of the skeletal muscle Ryanodine Receptor (RyR1)== |
| - | <StructureSection load='2xoa' size='340' side='right' caption='[[2xoa]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.50Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='2xoa' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2xoa]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.50Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2xoa]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_rabbit European rabbit]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2XOA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2XOA FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2xoa]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oryctolagus_cuniculus Oryctolagus cuniculus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2XOA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2XOA FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[2bcx|2bcx]]</td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.5Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2xoa FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2xoa OCA], [http://pdbe.org/2xoa PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2xoa RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2xoa PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2xoa ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2xoa FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2xoa OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2xoa PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2xoa RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2xoa PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2xoa ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/RYR1_RABIT RYR1_RABIT]] Calcium channel that mediates the release of Ca(2+) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm and thereby plays a key role in triggering muscle contraction following depolarization of T-tubules. Repeated very high-level exercise increases the open probability of the channel and leads to Ca(2+) leaking into the cytoplasm. Can also mediate the release of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores in neurons, and may thereby promote prolonged Ca(2+) signaling in the brain. Required for normal embryonic development of muscle fibers and skeletal muscle. Required for normal heart morphogenesis, skin development and ossification during embryogenesis (By similarity).<ref>PMID:10388749</ref> <ref>PMID:22036948</ref> | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/RYR1_RABIT RYR1_RABIT] Calcium channel that mediates the release of Ca(2+) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm and thereby plays a key role in triggering muscle contraction following depolarization of T-tubules. Repeated very high-level exercise increases the open probability of the channel and leads to Ca(2+) leaking into the cytoplasm. Can also mediate the release of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores in neurons, and may thereby promote prolonged Ca(2+) signaling in the brain. Required for normal embryonic development of muscle fibers and skeletal muscle. Required for normal heart morphogenesis, skin development and ossification during embryogenesis (By similarity).<ref>PMID:10388749</ref> <ref>PMID:22036948</ref> |
| | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == |
| Line 21: |
Line 21: |
| | ==See Also== | | ==See Also== |
| | *[[Ryanodine receptor|Ryanodine receptor]] | | *[[Ryanodine receptor|Ryanodine receptor]] |
| | + | *[[Ryanodine receptor 3D structures|Ryanodine receptor 3D structures]] |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: European rabbit]] | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Kimlicka, L]] | + | [[Category: Oryctolagus cuniculus]] |
| - | [[Category: Lobo, P A]] | + | [[Category: Kimlicka L]] |
| - | [[Category: Petegem, F Van]] | + | [[Category: Lobo PA]] |
| - | [[Category: Tung, C]] | + | [[Category: Tung C]] |
| - | [[Category: Calcium channel]] | + | [[Category: Van Petegem F]] |
| - | [[Category: Cardiac arrhythmia]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Ion channel]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Malignant hyperthermia]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Membrane protein]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Metal transport]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
RYR1_RABIT Calcium channel that mediates the release of Ca(2+) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm and thereby plays a key role in triggering muscle contraction following depolarization of T-tubules. Repeated very high-level exercise increases the open probability of the channel and leads to Ca(2+) leaking into the cytoplasm. Can also mediate the release of Ca(2+) from intracellular stores in neurons, and may thereby promote prolonged Ca(2+) signaling in the brain. Required for normal embryonic development of muscle fibers and skeletal muscle. Required for normal heart morphogenesis, skin development and ossification during embryogenesis (By similarity).[1] [2]
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Many physiological events require transient increases in cytosolic Ca(2+) concentrations. Ryanodine receptors (RyRs) are ion channels that govern the release of Ca(2+) from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Mutations in RyRs can lead to severe genetic conditions that affect both cardiac and skeletal muscle, but locating the mutated residues in the full-length channel structure has been difficult. Here we show the 2.5 A resolution crystal structure of a region spanning three domains of RyR type 1 (RyR1), encompassing amino acid residues 1-559. The domains interact with each other through a predominantly hydrophilic interface. Docking in RyR1 electron microscopy maps unambiguously places the domains in the cytoplasmic portion of the channel, forming a 240-kDa cytoplasmic vestibule around the four-fold symmetry axis. We pinpoint the exact locations of more than 50 disease-associated mutations in full-length RyR1 and RyR2. The mutations can be classified into three groups: those that destabilize the interfaces between the three amino-terminal domains, disturb the folding of individual domains or affect one of six interfaces with other parts of the receptor. We propose a model whereby the opening of a RyR coincides with allosterically coupled motions within the N-terminal domains. This process can be affected by mutations that target various interfaces within and across subunits. The crystal structure provides a framework to understand the many disease-associated mutations in RyRs that have been studied using functional methods, and will be useful for developing new strategies to modulate RyR function in disease states.
The amino-terminal disease hotspot of ryanodine receptors forms a cytoplasmic vestibule.,Tung CC, Lobo PA, Kimlicka L, Van Petegem F Nature. 2010 Nov 3. PMID:21048710[3]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Dulhunty AF, Laver DR, Gallant EM, Casarotto MG, Pace SM, Curtis S. Activation and inhibition of skeletal RyR channels by a part of the skeletal DHPR II-III loop: effects of DHPR Ser687 and FKBP12. Biophys J. 1999 Jul;77(1):189-203. PMID:10388749 doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(99)76881-5
- ↑ Kakizawa S, Yamazawa T, Chen Y, Ito A, Murayama T, Oyamada H, Kurebayashi N, Sato O, Watanabe M, Mori N, Oguchi K, Sakurai T, Takeshima H, Saito N, Iino M. Nitric oxide-induced calcium release via ryanodine receptors regulates neuronal function. EMBO J. 2011 Oct 28;31(2):417-28. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.386. PMID:22036948 doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.386
- ↑ Tung CC, Lobo PA, Kimlicka L, Van Petegem F. The amino-terminal disease hotspot of ryanodine receptors forms a cytoplasmic vestibule. Nature. 2010 Nov 3. PMID:21048710 doi:10.1038/nature09471
|