Proteopedia:Featured SEL/2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(featured GFP) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<table> | <table> | ||
| - | <tr><td> | + | <tr><td> |
| - | <tr><td><div class="scrolling">''' | + | <imagemap> |
| - | '' | + | Image:GFP-4.gif|center |
| - | + | default [[Green Fluorescent Protein]] | |
| + | </imagemap> | ||
| + | </td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><td><div class="scrolling">'''Green Fluorescent Protein'''<br> | ||
| + | ''by Eran Hodis''<br> | ||
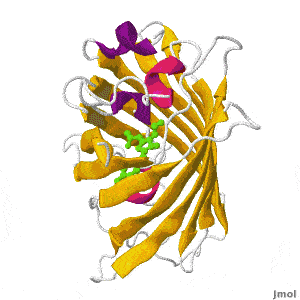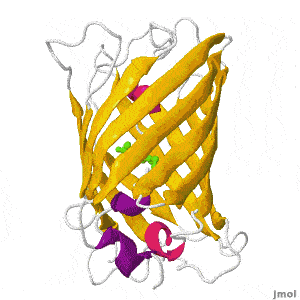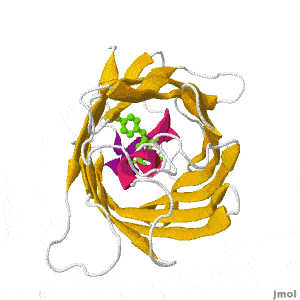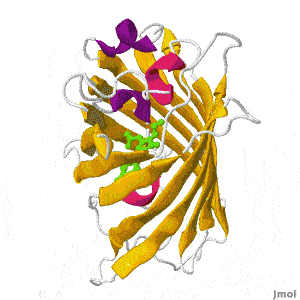
| + | Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a bioluminescent polypeptide isolated from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victoria''. GFP converts the blue chemiluminescence of aequorin into green fluorescent light. In the laboratory, GFP can be incorporated into a variety of biological systems in order to function as a marker protein. Since its discovery in 1962, GFP has become a significant contributor to the research of monitoring gene expression, localization, mobility, traffic, or interactions between various membrane and cytoplasmic proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | >>> [[Green Fluorescent Protein|Visit this page]] >>> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Featured in Selected Pages]] | ||
Current revision
Green Fluorescent Protein
by Eran Hodis >>> Visit this page >>> |