Arginine kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Arginine kinase''' (AK) is a phosphagen kinase which catalyzes the conversion of L-arginine and ATP to N-phospho-L-arginine and ADP. AK is part of arginine and proline metabolism. The phosphagen kinase reaction of AK is central to cellular energy homeostasis, i.e. maintenance of ATP level in invertebrates. <ref>PMID:25849389</ref> Another phosphagen kinase found mostly in vertebrates is [[Creatine Kinase]] whose substrate is creatine. | + | '''Arginine kinase''' or '''Protein-arginine kinase''' (AK) is a phosphagen kinase which catalyzes the conversion of L-arginine and ATP to N-phospho-L-arginine and ADP. AK is part of arginine and proline metabolism. The phosphagen kinase reaction of AK is central to cellular energy homeostasis, i.e. maintenance of ATP level in invertebrates. <ref>PMID:25849389</ref> Another phosphagen kinase found mostly in vertebrates is [[Creatine Kinase]] whose substrate is creatine. |
For more details see [[Arginine Kinase AK]]. | For more details see [[Arginine Kinase AK]]. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
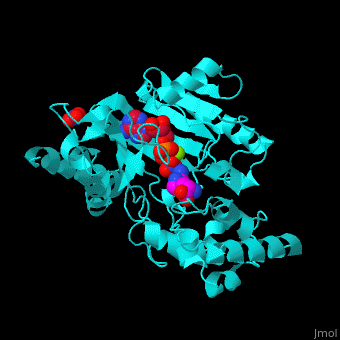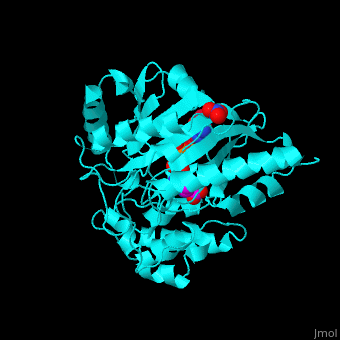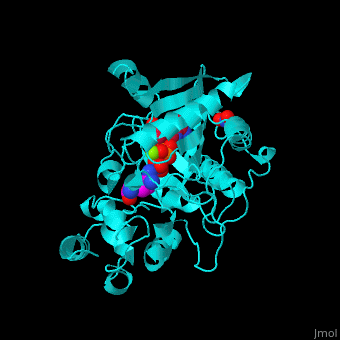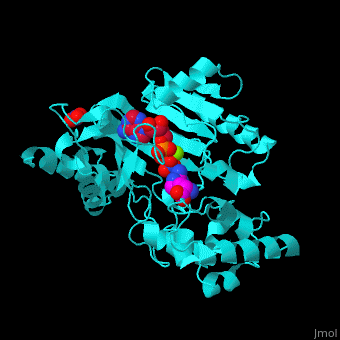
The <scene name='71/715906/Cv/3'>active site</scene> of AK is located between its N-terminal helical region and the larger C-terminal region. <ref>PMID:9671698</ref> Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='71/715906/Cv/4'>Mg+2 coordination site</scene>. | The <scene name='71/715906/Cv/3'>active site</scene> of AK is located between its N-terminal helical region and the larger C-terminal region. <ref>PMID:9671698</ref> Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='71/715906/Cv/4'>Mg+2 coordination site</scene>. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of arginine kinase== | ==3D structures of arginine kinase== | ||
| + | [[Arginine kinase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[5j99]], [[5j9a]] – cAK + ADP + Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1bg0]] – cAK + ADP + D-Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1rl9]] – cAK + ADP <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1m15]], [[1p50]], [[1sd0]] – cAK (mutant) + ADP + Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1p52]], [[4gvz]] – cAK (mutant) + ADP + D-Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4gvy]] – cAK (mutant) + ADP + citrulline <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4gw0]], [[4gw2]] – cAK (mutant) + ADP + ornithine <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3ju6]] – scAK + AMPPNP + Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4bg4]] – sAK + ADP + Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4bhl]] – sAK + Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4rf7]] – saAK + Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5u92]] – PpAK + Arg <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4rf8]] – saAK + ADP <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4rf9]] – saAK + ATP-gS + Arg<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wang Z, Qiao Z, Ye S, Zhang R. Structure of a double-domain phosphagen kinase reveals an asymmetric arrangement of the tandem domains. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015 Apr;71(Pt 4):779-89. doi:, 10.1107/S1399004715001169. Epub 2015 Mar 26. PMID:25849389 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S1399004715001169
- ↑ Zhou G, Somasundaram T, Blanc E, Parthasarathy G, Ellington WR, Chapman MS. Transition state structure of arginine kinase: implications for catalysis of bimolecular reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jul 21;95(15):8449-54. PMID:9671698