Vitamin D receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
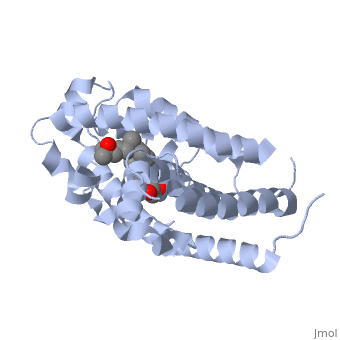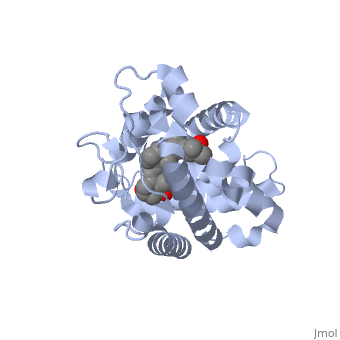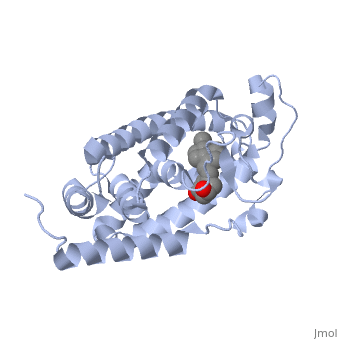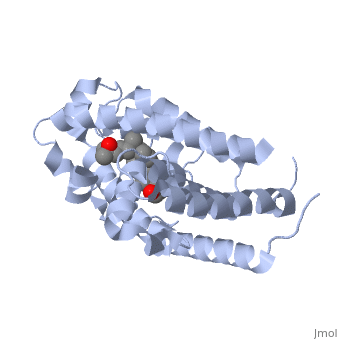
<StructureSection load='1db1' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human vitamin D receptor ligand-binding domain complex with vitamin D (PDB entry [[1db1]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1db1' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of human vitamin D receptor ligand-binding domain complex with vitamin D (PDB entry [[1db1]])' scene=''> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| - | '''Vitamin D receptor''' (<scene name='56/562378/Vit_d_receptor_3m7r/3'>VDR</scene>) is a transcription factor. Upon binding to vitamin D, VDR forms a heterodimer with retinoid | + | '''Vitamin D receptor''' (<scene name='56/562378/Vit_d_receptor_3m7r/3'>VDR</scene>; also called calcitriol receptor) is a transcription factor. Upon binding to vitamin D, VDR forms a heterodimer with [[retinoid X receptor]] and binds to hormone response receptors on DNA causing gene expression. The <scene name='56/562378/Vit_d_receptor_ligand/1'>vitamin D hormone</scene> (in green) binds to receptors in its target cells, controlling the synthesis of many different proteins involved in calcium transport and utilization. <scene name='51/517370/Cv/2'>Vitamin D hormone binding site</scene>. <scene name='51/517370/Cv/3'>Vitamin D hormone is located in deep pocket</scene>. VDR contains two domains: a <scene name='56/562378/Lbd/1'>ligand binding domain (LBD)</scene> (see [[Nuclear receptors]]). that binds to the hormone (grey) and <scene name='56/562378/Dbd/2'>DNA-binding domain (DBD)</scene> that binds to DNA. (Green and blue are two same VDR structures). It pairs up with a similar protein, 9-cis retinoic acid receptor (RXR), and together they bind to the DNA, activating synthesis in some cases and repressing it in others<ref>PMID:11425573</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Secosteroids]], [[Intracellular receptors]], and [[Calcipotriol]]. | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 31: | Line 33: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
[[1db1]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1DB1 OCA]. On right hand side is Structure of human vitamin D receptor ligand-binding domain complex with vitamin D (PDB entry [[1db1]]). | [[1db1]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1DB1 OCA]. On right hand side is Structure of human vitamin D receptor ligand-binding domain complex with vitamin D (PDB entry [[1db1]]). | ||
| + | ==3D structures of vitamin D receptor== | ||
| + | [[Vitamin D receptor 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | ==3D structures of vitamin D receptor== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Vitamin D receptor ligand-binding domain | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3m7r]] - hVDR LBD (mutant) – human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1db1]] – hVDR LBD + vitamin D <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3ogt]], [[2ham]], [[2har]], [[2has]], [[2hb7]], [[2hb8]], [[3p8x]], [[3az1]], [[3az2]], [[3az3]], [[3tkc]], [[1s0z]], [[1s19]], [[3a78]], [[4g2i]] - hVDR LBD + vitamin D analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3auq]], [[3aur]], [[3kpz]], [[3x36]], [[3x31]], [[4ynk]], [[3a2i]], [[3a2j]], [[3b0t]], [[3ax8]], [[3vhw]] - hVDR LBD (mutant) + vitamin D analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3a3z]], [[3a40]] - hVDR LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ie8]], [[1ie9]], [[3cs4]], [[3cs6]], [[1txi]] – hVDR LBD + superagonist <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3w5q]], [[3w5r]], [[3w5t]] - hVDR LBD + lithocholic acid derivative <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5gt4]] - hVDR LBD + secocholesta derivative <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5v39]] - hVDR LBD + VDRM <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5xuq]], [[5ysy]], [[5yt2]] - hVDR LBD + antagonist <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Vitamin D receptor LBD binary complex with peptide | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1rjk]], [[1rk3]], [[1rkg]], [[1rkh]], [[2o4j]], [[2o4r]] – rVDR LBD (mutant) + peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor peptide – rat<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2zfx]], [[3a2h]], [[2zxm]], [[2zxn]] - rVDR LBD + coactivator peptide DRIP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3aun]], [[2zmh]], [[2zmi]], [[2zmj]], [[3afr]], [[3vjs]], [[3vjt]], [[5zwe]], [[5zwf]], [[5zwh]] - rVDR LBD (mutant) + coactivator peptide DRIP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5gic]], [[5gid]], [[5gie]] - rVDR LBD + steroid receptor coactivator 1 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5h1e]] - rVDR LBD + NCOA-2 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2hbh]], [[2hcd]] - zVDR LBD + steroid receptor coactivator 1 peptide – zebrafish<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5nky]], [[5nma]], [[5nmb]], [[5ow9]], [[5owd]] - zVDR LBD + NCOA-1 peptide derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ruj]], [[4rup]] - zVDR LBD (mutant) + NCOA-1 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5lga]] - zVDR LBD + NCOA-2 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4roj]] - zVDR LBD (mutant) + NCOA-2 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Vitamin D receptor LBD ternary complex with peptide | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2zl9]], [[2zla]], [[2zlc]] - rVDR LBD + coactivator peptide DRIP + vitamin D analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3vrt]], [[3vru]], [[3vrv]], [[3vrw]] - rVDR LBD (mutant) + coactivator peptide DRIP + vitamin D analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5zwi]] - rVDR LBD + coactivator peptide DRIP + ligand<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3w0g]], [[3w0h]], [[3w0i]], [[3w0j]] - rVDR LBD + mediator of RNA polymerase II peptide + nonsecosteroidal ligand<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3w5p]] - rVDR LBD + mediator of RNA polymerase II peptide + lithocholic acid derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3wt5]], [[3wt6]], [[3wt7]], [[3wtq]], [[5b41]], [[5b5b]], [[5xzf]], [[5xzh]] - rVDR LBD + mediator of RNA polymerase II peptide + vitamin D analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5awj]], [[5awk]] - rVDR LBD + mediator of RNA polymerase II peptide + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5xpl]], [[5xpm]], [[5xpn]], [[5xpo]], [[5xpp]] - rVDR LBD + NCOA-2 peptide + vitamin D analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2hc4]], [[5e7v]], [[6f0b]] - zVDR LBD + steroid receptor coactivator 1 peptide + vitamin D derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6fo7]], [[6fo8]], [[6fo9]], [[6fod]] - zVDR LBD + NCOA-1 peptide + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ow7]] - zVDR LBD + NCOA-1 peptide + vitamin D analog<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Vitamin D receptor DNA-binding domain | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1kb2]] – hVDR DBD + osteopontin response element DNA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1kb4]] – hVDR DBD + DR3 response element DNA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ynw]] – hVDR DBD (mutant) + DR3 response element DNA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1kb6]] – hVDR DBD + osteocalcin response element DNA<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Choi M, Yamamoto K, Masuno H, Nakashima K, Taga T, Yamada S. Ligand recognition by the vitamin D receptor. Bioorg Med Chem. 2001 Jul;9(7):1721-30. PMID:11425573
- ↑ Hughes MR, Malloy PJ, Kieback DG, Kesterson RA, Pike JW, Feldman D, O'Malley BW. Point mutations in the human vitamin D receptor gene associated with hypocalcemic rickets. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1702-5. PMID:2849209
- ↑ Yagi H, Ozono K, Miyake H, Nagashima K, Kuroume T, Pike JW. A new point mutation in the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor in a kindred with hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Feb;76(2):509-12. PMID:8381803
- ↑ Saijo T, Ito M, Takeda E, Huq AH, Naito E, Yokota I, Sone T, Pike JW, Kuroda Y. A unique mutation in the vitamin D receptor gene in three Japanese patients with vitamin D-dependent rickets type II: utility of single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis for heterozygous carrier detection. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Sep;49(3):668-73. PMID:1652893
- ↑ Sone T, Marx SJ, Liberman UA, Pike JW. A unique point mutation in the human vitamin D receptor chromosomal gene confers hereditary resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):623-31. PMID:2177843
- ↑ Malloy PJ, Weisman Y, Feldman D. Hereditary 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets resulting from a mutation in the vitamin D receptor deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Feb;78(2):313-6. PMID:8106618
- ↑ Kristjansson K, Rut AR, Hewison M, O'Riordan JL, Hughes MR. Two mutations in the hormone binding domain of the vitamin D receptor cause tissue resistance to 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):12-6. PMID:8392085 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI116539
- ↑ Rut AR, Hewison M, Kristjansson K, Luisi B, Hughes MR, O'Riordan JL. Two mutations causing vitamin D resistant rickets: modelling on the basis of steroid hormone receptor DNA-binding domain crystal structures. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1994 Nov;41(5):581-90. PMID:7828346
- ↑ Lin NU, Malloy PJ, Sakati N, al-Ashwal A, Feldman D. A novel mutation in the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor causes hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Jul;81(7):2564-9. PMID:8675579
- ↑ Whitfield GK, Selznick SH, Haussler CA, Hsieh JC, Galligan MA, Jurutka PW, Thompson PD, Lee SM, Zerwekh JE, Haussler MR. Vitamin D receptors from patients with resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: point mutations confer reduced transactivation in response to ligand and impaired interaction with the retinoid X receptor heterodimeric partner. Mol Endocrinol. 1996 Dec;10(12):1617-31. PMID:8961271
- ↑ Malloy PJ, Eccleshall TR, Gross C, Van Maldergem L, Bouillon R, Feldman D. Hereditary vitamin D resistant rickets caused by a novel mutation in the vitamin D receptor that results in decreased affinity for hormone and cellular hyporesponsiveness. J Clin Invest. 1997 Jan 15;99(2):297-304. PMID:9005998 doi:10.1172/JCI119158
- ↑ Fujiki R, Kim MS, Sasaki Y, Yoshimura K, Kitagawa H, Kato S. Ligand-induced transrepression by VDR through association of WSTF with acetylated histones. EMBO J. 2005 Nov 16;24(22):3881-94. Epub 2005 Oct 27. PMID:16252006 doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600853
- ↑ Rochel N, Wurtz JM, Mitschler A, Klaholz B, Moras D. The crystal structure of the nuclear receptor for vitamin D bound to its natural ligand. Mol Cell. 2000 Jan;5(1):173-9. PMID:10678179
- ↑ Eelen G, Verlinden L, Rochel N, Claessens F, De Clercq P, Vandewalle M, Tocchini-Valentini G, Moras D, Bouillon R, Verstuyf A. Superagonistic action of 14-epi-analogs of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D explained by vitamin D receptor-coactivator interaction. Mol Pharmacol. 2005 May;67(5):1566-73. Epub 2005 Feb 22. PMID:15728261 doi:10.1124/mol.104.008730
- ↑ Hourai S, Fujishima T, Kittaka A, Suhara Y, Takayama H, Rochel N, Moras D. Probing a water channel near the A-ring of receptor-bound 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 with selected 2 alpha-substituted analogues. J Med Chem. 2006 Aug 24;49(17):5199-205. PMID:16913708 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm0604070
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky, Isita Amin