Platelet-derived growth factors and receptors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m (Platelet-derived moved to PDGF and PDGF-R over redirect: Platelet-derived is just too short a name for this page) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
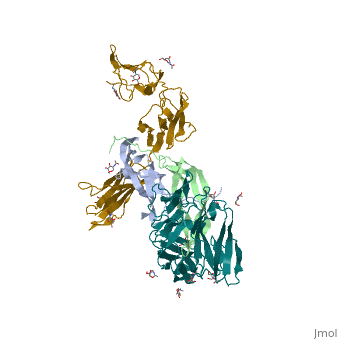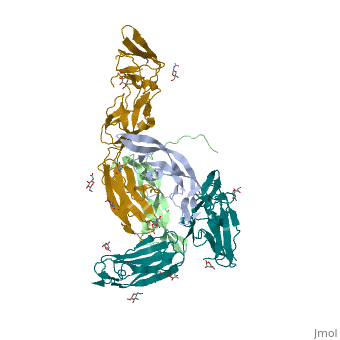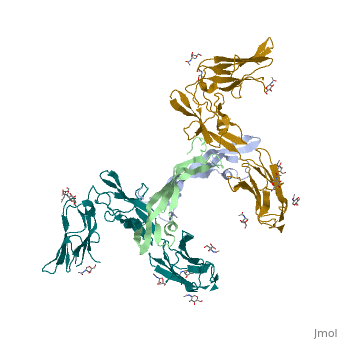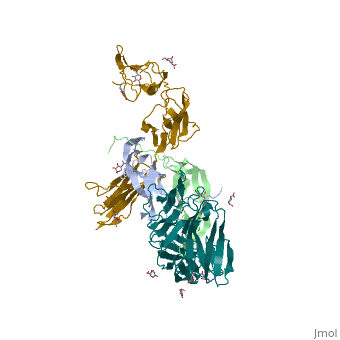
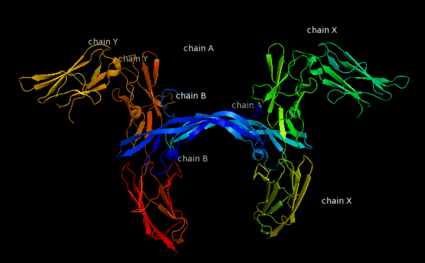
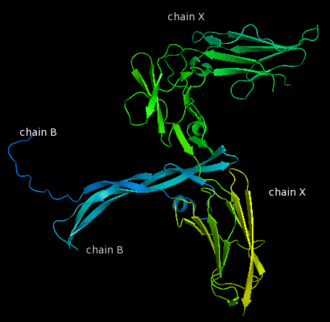
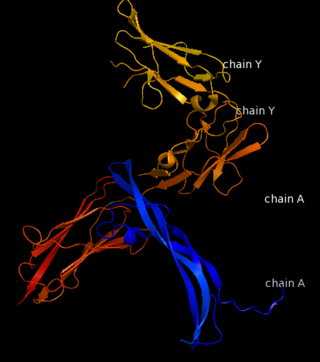
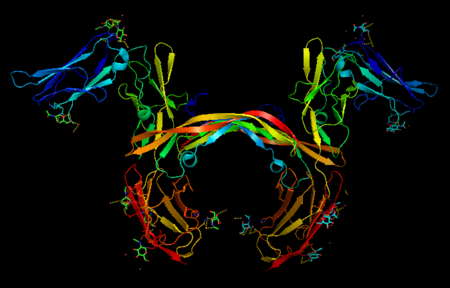
| - | '''Platelet-derived growth factor receptors, PDGF-R''', are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs). PDGF (Chains A and B) is a 172 amino acid sequence consisting of one alpha helix and eight beta-pleated sheets. PDGF function as disulfide-linked dimers. PDGFs have a cysteine-knot-fold growth factor domain of ∼100 amino acids involved in receptor-binding and dimerization. The synthesis and processing of PDGFs is highly regulated. There are two forms of PDGF-R, alpha and beta, which are each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor binds to the receptor, PDGF-R homodimerizes or heterodimerizes<ref>PMID:1315403</ref>. The PDGF-R is a 289 amino acid sequence consisting of two alpha helices and twenty-nine beta-pleated sheets. Together these form the PDGF-R complex<ref>PMID:20534510</ref> . | + | '''Platelet-derived growth factor receptors, PDGF-R''', are cell surface [[Receptor tyrosine kinases|tyrosine kinase receptors]] for members of the '''platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs)'''. PDGF (Chains A and B) is a 172 amino acid sequence consisting of one alpha helix and eight beta-pleated sheets. PDGF function as disulfide-linked dimers. PDGFs have a cysteine-knot-fold growth factor domain of ∼100 amino acids involved in receptor-binding and dimerization. The synthesis and processing of PDGFs is highly regulated. There are two forms of PDGF-R, alpha and beta, which are each encoded by a different gene. Depending on which growth factor binds to the receptor, PDGF-R homodimerizes or heterodimerizes<ref>PMID:1315403</ref>. The PDGF-R is a 289 amino acid sequence consisting of two alpha helices and twenty-nine beta-pleated sheets. Together these form the PDGF-R complex<ref>PMID:20534510</ref> . |
[[Image:Labeled PDGF-R_r.png|left|425px]] | [[Image:Labeled PDGF-R_r.png|left|425px]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Platelet-derived growth factor subunits -A and -B are prototypic growth factors which have critical functions in development: regulating cell propagation, cellular differentiation, cell growth, development and many diseases including cancer<ref name="Williams">PMID:2538922</ref>. PDGFs are the major components signaling mitotic cell division in connective tissues and smooth muscle cells. They also critically regulate embryonic development. PDGFα signaling targets such organs as the lung, intestine, skin, kidneys, skeleton and neuroprotective tissues. PDGFβ signaling targets hematopoiesis and blood vessel formation. While, PDGF signaling is imperative during embryonic development and early childhood, it is detrimental to adults. Some PDGF signaling in adults has lead to cancers, atherosclerosis, pulmonary fibrosis, and restenosis. | Platelet-derived growth factor subunits -A and -B are prototypic growth factors which have critical functions in development: regulating cell propagation, cellular differentiation, cell growth, development and many diseases including cancer<ref name="Williams">PMID:2538922</ref>. PDGFs are the major components signaling mitotic cell division in connective tissues and smooth muscle cells. They also critically regulate embryonic development. PDGFα signaling targets such organs as the lung, intestine, skin, kidneys, skeleton and neuroprotective tissues. PDGFβ signaling targets hematopoiesis and blood vessel formation. While, PDGF signaling is imperative during embryonic development and early childhood, it is detrimental to adults. Some PDGF signaling in adults has lead to cancers, atherosclerosis, pulmonary fibrosis, and restenosis. | ||
| - | |||
== Pharmaceutical Ideas == | == Pharmaceutical Ideas == | ||
Pharmaceutical research has been targeting inhibiting PDGF-PDGFR signaling as a potential for anti-cancer treatments. Strategies of blocking signaling at the cellular level include neutralizing antibiodies for PDGF ligands and receptors, aptamers which are oligonucleic acid or peptide molecules that bind to a specific target molecule, N-terminal processing-deficient PDGFs, and soluble receptors without the kinase domain. | Pharmaceutical research has been targeting inhibiting PDGF-PDGFR signaling as a potential for anti-cancer treatments. Strategies of blocking signaling at the cellular level include neutralizing antibiodies for PDGF ligands and receptors, aptamers which are oligonucleic acid or peptide molecules that bind to a specific target molecule, N-terminal processing-deficient PDGFs, and soluble receptors without the kinase domain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[PDGFR inhibitors]]. | ||
== Quiz == | == Quiz == | ||
| Line 106: | Line 107: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Platelet-derived growth factor | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[3mjk]] – hPDGF subunit A – human<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4qci]] , [[6t9e]]– hPDGF subunit B + antibody <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1pdg]] – hPDGF BB <br /> | ||
| + | **[[4hqu]], [[4hqx]] – hPDGF BB + DNA<br /> | ||
| - | + | *Platelet-derived growth factor receptor | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | **[[5k5x]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain 550-696, 769-973<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6a32]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5grn]] – hPDGF-R-α kinase domain + pyridine derivative <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6jok]], [[6jol]] – hPDGF-R-a residues 550-696, 769-973 + cancer drug<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6joi]], [[6joj]] – hPDGF-R-a residues 550-696, 769-973 (mutant) + cancer drug<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7ram]] – hPDGF-R-a 1-524 + HCMV glycoproteins - CryoEM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7lbf]] – hPDGF-R-a 1-524 + HCMV glycoproteins + antibody - CryoEM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3mjg]] – hPDGF-R-β residues 33-314 + PDGF subunit B<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2l6w]] – hPDGF-R-β residues 526-563 - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of platelet-derived growth factor receptor
Updated on 05-January-2025
References
- ↑ Heldin CH, Ostman A, Eriksson A, Siegbahn A, Claesson-Welsh L, Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: isoform-specific signalling via heterodimeric or homodimeric receptor complexes. Kidney Int. 1992 Mar;41(3):571-4. PMID:1315403
- ↑ Shim AH, Liu H, Focia PJ, Chen X, Lin PC, He X. Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11307-12. Epub 2010 Jun 2. PMID:20534510
- ↑ Heldin CH, Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: three isoforms and two receptor types. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):108-11. PMID:2543106
- ↑ Williams LT. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564-70. PMID:2538922
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Lisa Tice, Michal Harel, Angel Herraez, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky