Rhodopsin
Rhodopsin is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Rhodopsin is the
common GPCR structure used to understand functionality of G-protein coupled receptors.
Rhodopsin is commonly found in the photoreceptors in the retina, specifically in the rod
photoreceptors and become activated by photons of light. Rhodopsin contains a chromophore
(compound that absorbs light), specifically 11-cis-retinal, which when active recruites G proteins
to transmit a signaling cascade in neural impulses to the gray matter of the occipital lobe. Once
the receptor has been activated, a new rhodopsin needs to be regenerated. Rhodopsin is
located in the rod outer segment (ROS) which consists of stacked disks enclosed by a
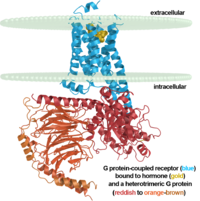
membrane. The entire family of GPCR’s have the common structure of seven alpha-helices
across membranes. Rhodopsin’s structure changes upon photoactivation. The sixth helix bends
away from the seventh creating a pocket that allows for binding of a G protein. A salt bridge
covers this pocket until the helices shift away from one another. Once the G protein has bound
then the signal can be transmitted to the occipital lobe. Over 120 point mutations to rhodopsin
have been identified which can lead to night blindness and more several visual problems[1].
Function
Rhodopsin performs two functions. One function is to bind retinal. Rhodopsin is a protein that is essential for vision, especially in dim light. The photoreceptors in the retina that contain rhodopsin are rods. Rhodopsin is attached to 11-cis retinal which becomes excited by a photon of light and isomerizes to become all-trans conformation[2]. This excitation activates rhodopsin and leads to depolarizing of neurons. The depolarizing of neurons is how the image is transmitted to the brain[3]. Another function of rhodopsin is to function as a G protein-coupled receptor. When rhodopsin is activated by light the protein couples with the G protein transducin which is the first step in the signal cascade[2]. Rhodopsin must undergo several conformational changes before being able to bind transducin[4]. Rhodopsin is initially converted to metarhodopsin II which is the active form of rhodopsin. Once the protein is active then metarhodopsin binds the G-protein tranducin and the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The G protein subunits dissociate and causes a decrease in cytosolic cGMP. The decrease in cGMP also causes the closing of calcium channels. When calcium concentrations drop the photoreceptors become hyperpolarized and this ensures the action potential is sent onward toward the brain[5]. Photoreceptors are unable to be immediately restimulated, rhodopsin kinase phosphorylates the protein on serine and threonine residues which leads to the binding of arrestin. Arrestin prevents rhodopsin from interacting with tranducin again, thus preventing restimulation of the protein. Arrestin is released from the protein via phospotase A which dephosphorylates rhodopsin[5].
Disease
Mutations to rhodopsin can lead to stationary night blindness or retinitis pigmentosa.
Autosomal Dominant Congenial Stationary Night Blindness
Stationary night blindness is an autosomal dominant disease that causes a loss of vision in dim light. The mutation to rhodopsin causes the protein to be constantly activated. Since the protein is continuously activated without any photon of light, the brain continues to receive stimulation from the photoreceptors. The brain begins to ignore the visual stimulation from the rods, therefore leading to night blindness[3].
Retinitis Pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa is also an autosomal dominant disorder, but can also be recessive in rare circumstances. There are two main classes of mutations that cause retinitis pigmentosa, class I and class II[2]. A mutation that affect rhodopsin that cause retinitis pigmentosa result in a misfolding or transportation of the protein. Class I mutations are commonly associated with a defect in the C-terminus of the protein which results in defective trafficking of the protein[2]. Class II mutations are commonly associated with the N-terminus of the protein and results in misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum[2]. Another mutation to rhodopsin can affect the activation of the protein in response to light. These mutations can lead to apoptosis of rods in the retina. Without rods to perceive dim light, night blindness results[3].
Relevance
Up until 2007, rhodopsin was the only GPCR that had a high-resolution crystal structure and was the basis for other GPCR structures[3]. Most G-protein coupled receptors are a target for pharmaceutical companies as the receptors are involved in a variety of physiological and pathophysiological processes[4]. Most GPCRs bind ligands with an open domain. Rhodopsin and other vision proteins are unique as the proteins acquire ligands via transient pores in that open between the transmembrane helices of the GPCR. The use of transient pores allows thermal stability of the rhodopsin protein[2].
Structural highlights
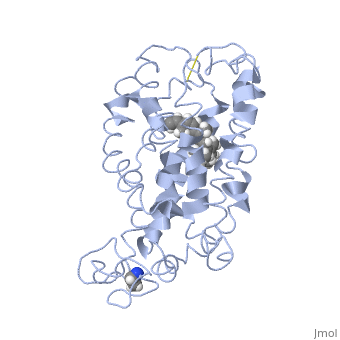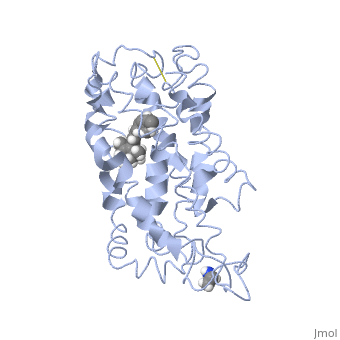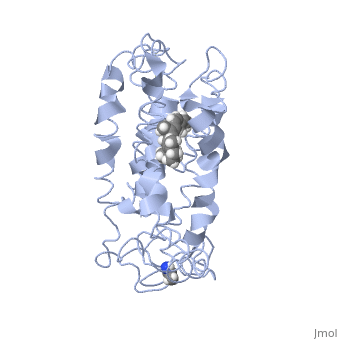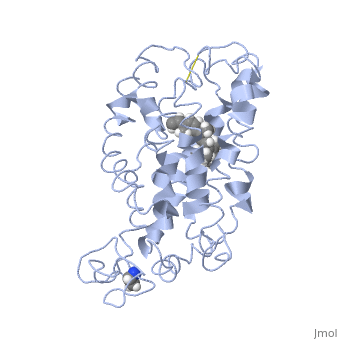
Fully functional rhodopsin has the typical GPCR structure of a seven transmembrane helical bundle with the N-terminus on the interior of the rods and the C-terminus in the cytoplasm. The N-terminus is located near the extracellular loops and ends of the transmembrane protein. There are hydrogen bonding between the transmembrane sections and the extracellular loops that are involved in the activation of rhodopsin when a photon is received. The N-terminus is thought to play a role in orientation of the extracellular loops[2]. Transmembrane domain 1 and 2 play a role in stabilizing the protein and giving the protein functionality[4]. Rhodopsin has two components: opsin (a membrane-bound polypeptide) and 11-cis-retinal (a chromophore that is bound to opsin via a protonated Schiff-base)[5].
11-cis retinal, a molecule that is derived from vitamin A, is necessary for rhodopsin function. The ligand performs an inverse agonist suppressing activity on the photon receptor and is associated with the protein via protonated Schiff-bases linked to a lysine reside on the seventh domain[4]. A negative agonist means the ligand, when present in the binding pocket of the protein, inhibits the receptor activity[5]. The isomerization of cis to trans causes the protein complex to relax which allows for binding of transducin and the signal cascade to progress[4].
This is rhodopsin with 11-cis retinal bound. After 11-cis retinal becomes activated and becomes all-trans, rhodopsin undergoes the conformational change to become metarhodopsin I and then metarhodopsin II which is the fully active form of rhodopsin. Metarhodopsin II then associates with the G protein transducin and the signal cascade can continue.
See also: