This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (11 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase''' (ACDH) catalyzes the introduction of a double bond between C2 and C3 of the thio-ester CoA substrate. This is the first reaction in fatty acid metabolism which produces acetyl-CoA. FAD is the cofactor of ACDH activity. ACDH is classified according to the length of its substrates as short- (SCAD), medium- (MCAD), very- and very long-chain (VLCAD) ACDH. MCAD can bind a broad range of chain length acyl-CoA substrates.<ref>PMID:7601336</ref> | + | '''Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase''' (ACDH) catalyzes the introduction of a double bond between C2 and C3 of the thio-ester CoA substrate. This is the first reaction in fatty acid metabolism which produces acetyl-CoA. FAD is the cofactor of ACDH activity. ACDH is classified according to the length of its substrates as short- (SCAD), medium- (MCAD), very- and very long-chain (VLCAD) ACDH. MCAD can bind a broad range of chain length acyl-CoA substrates.<ref>PMID:7601336</ref> See also [[Beta oxidation]] and [[Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase]]. |
| + | *'''Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase''' is required for the metabolism of Lys, Trp and hydroxyLys. | ||
| + | *'''Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase''' catalyzes the conversion of isovaleryl-CoA to 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA<ref>PMID:9665741</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase''' oxidates straight chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA<ref>PMID:16176262</ref>. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | Impairment of the activity of ACDH causes a variety of diseases associated with lack of fatty acid metabolism. MCAD mutations are associated with Sudden Infant Death. | + | Impairment of the activity of ACDH causes a variety of diseases associated with lack of fatty acid metabolism. MCAD mutations are associated with Sudden Infant Death and with Medium-chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (MCADD)<ref>PMID:32809672</ref>. For details see [[Investigating the Mechanisms of Active Site Mutations to the 1T9G WT MCAD Protein to Better Understand Medium Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (MCADD)]]. SCAD deficiency is a recessive disorder of fatty acid β-oxidation. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
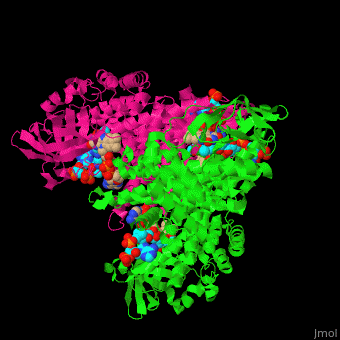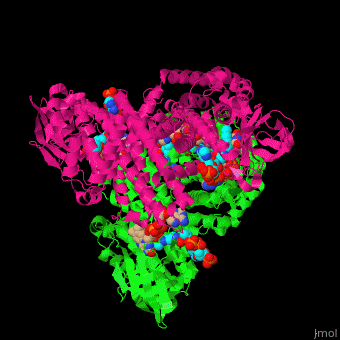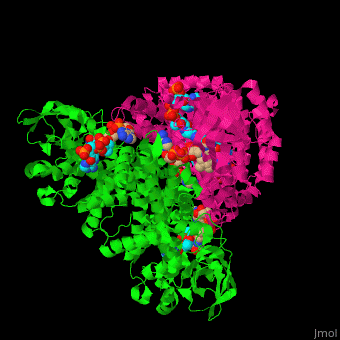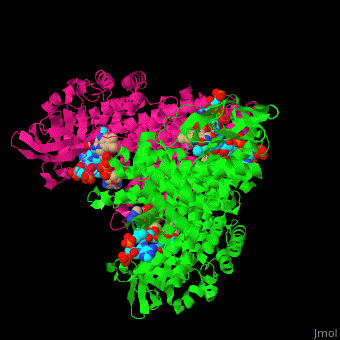
SCAD is a homodimer with a single FAD binding site. <scene name='49/491924/Cv/12'>MCAD is a homotetramer</scene> with 4 FAD binding sites in the subunits interface and 4 binding sites for acyl-CoA substrate within each monomer. | SCAD is a homodimer with a single FAD binding site. <scene name='49/491924/Cv/12'>MCAD is a homotetramer</scene> with 4 FAD binding sites in the subunits interface and 4 binding sites for acyl-CoA substrate within each monomer. | ||
*One of the <scene name='49/491924/Cv/9'>FAD binding sites</scene> in homotetramer of rat ACDH. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | *One of the <scene name='49/491924/Cv/9'>FAD binding sites</scene> in homotetramer of rat ACDH. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| - | *One of the <scene name='49/491924/Cv/11'>CoA binding sites</scene> in homotetramer of rat ACDH.<ref>PMID:11812788</ref> | + | *One of the <scene name='49/491924/Cv/11'>CoA binding sites</scene> in homotetramer of rat ACDH.<ref>PMID:11812788</ref> |
==3D structures of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase== | ==3D structures of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase== | ||
[[Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase 3D structures]] | [[Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | ==3D structures of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Short chain ACDH | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1jqi]] - SCAD + acetoacetyl-CoA + FAD – rat<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2dvl]], [[2z1q]] - TtSCAD + FAD – ''Thermus thermophilus''<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2jif]], [[2vig]] - hSCAD + CoA persulfide + FAD – human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ol2]] – ACDH + FAD + CoA persulfide + electron transfer flavoprotein – ''Clostridium difficile''<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Medium chain ACDH | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1ws9]], [[2cx9]] - TtMCAD <BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3mdd]] – pMCAD + FAD – pig<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1egd]], [[1ege]], [[4p13]] - hMCAD (mutant) + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1ukw]], [[2d29]] - TtMCAD + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1egc]] - hMCAD (mutant) + octanoyl-CoA + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3mde]] - pMCAD + octanoyl-CoA + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1udy]] - pMCAD + thiaoctanoyl-CoA + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1t9g]] - hMCAD + electron transfer flavoprotein + AMP + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2a1t]] - hMCAD + electron transfer flavoprotein (mutant) + AMP + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Very long chain ACDH | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2uxw]] - hVLCAD + tetradecanoyl CoA + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3b96]] - hVLCAD + trans-δ2-palmitenoyl CoA + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Unspecified length ACDH | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2oku]] – ACDH C terminal – ''Porphyromonas gingivalis''<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2pg0]] - ACDH + FAD – ''Geobacillus kaustophilus''<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2wbi]] – hACDH 11 + FAD<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3nf4]], [[3pfd]] – ACHD + FAD – ''Mycobacterium thermoresistibile''<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[3oib]], [[4iv6]] - ACHD + FAD – ''Mycobacterium smegmatis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4x28]] - ACHD + FAD – ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4m9a]] – ACDH + FAD – ''Burkholderia thailandensis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3owa]] - ACDH + FAD – ''Bacillus anthracis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4rm7]] – ShACDH – ''Slackia heliotrinireducens''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4w9u]] – ACDH – ''Brucella abortus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ez3]] – ACDH + FAD – ''Brucella melitensis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4y9l]] – CeACDH + FAD – ''Caenorhabditis elegans''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4y9j]] – CeACDH + FAD + CoA-11<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5af7]] – AmACDH + FAD – ''Advenella mimigardefordensis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ahs]] – AmACDH + FAD + succinyl-CoA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5lnx]] – ACDH + FAD – ''Bacillus subtilis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6es9]] – ACDH + FAD + CoA – ''Paracoccus denitrificans''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4y9l]] – CeACDH + FAD – ''Caenorhabditis elegans''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4y9j]] – CeACDH + FAD + undecanoyl-CoA <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[4u83]] – ShBCDH <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1buc]] – BCDH + acetoacetyl-CoA + FAD – ''Megasphaera elsdenii''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1rx0]] – hiso-BCDH + methacrylyl-CoA + FAD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6cy8]], [[6cxt]] – BCDH + alpha/beta hydrolase fold protein + FAD – ''Marinomonas mediterranea''<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Thorpe C, Kim JJ. Structure and mechanism of action of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):718-25. PMID:7601336
- ↑ Mohsen AW, Anderson BD, Volchenboum SL, Battaile KP, Tiffany K, Roberts D, Kim JJ, Vockley J. Characterization of molecular defects in isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase in patients with isovaleric acidemia. Biochemistry. 1998 Jul 14;37(28):10325-35. PMID:9665741 doi:10.1021/bi973096r
- ↑ Yang SY, He XY, Schulz H. 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase and short chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase in human health and disease. FEBS J. 2005 Oct;272(19):4874-83. PMID:16176262 doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04911.x
- ↑ Ibrahim SA, Temtem T. Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency. PMID:32809672
- ↑ Battaile KP, Molin-Case J, Paschke R, Wang M, Bennett D, Vockley J, Kim JJ. Crystal structure of rat short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase complexed with acetoacetyl-CoA: comparison with other acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 5;277(14):12200-7. Epub 2002 Jan 25. PMID:11812788 doi:10.1074/jbc.M111296200