|
|
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
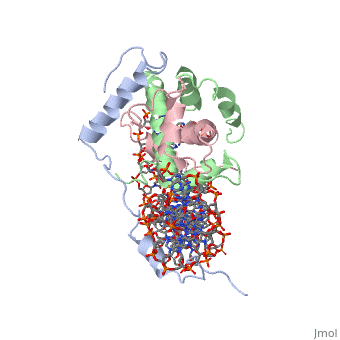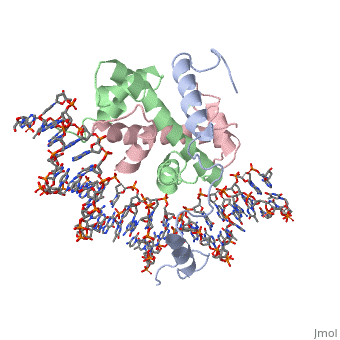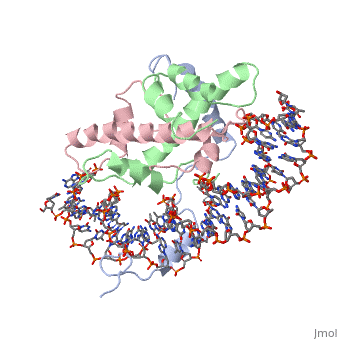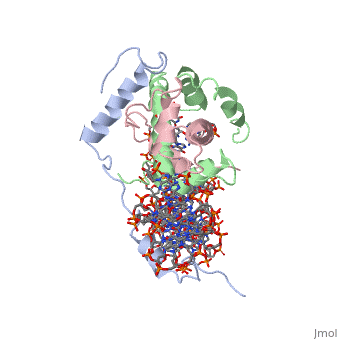
| | <StructureSection load='4awl' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4awl]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.08Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='4awl' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4awl]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.08Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4awl]] is a 5 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4AWL OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4AWL FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4awl]] is a 5 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4AWL OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4AWL FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1n1j|1n1j]]</td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 3.08Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4awl FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4awl OCA], [http://pdbe.org/4awl PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4awl RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4awl PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4awl ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4awl FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4awl OCA], [https://pdbe.org/4awl PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4awl RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4awl PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4awl ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NFYA_HUMAN NFYA_HUMAN]] Component of the sequence-specific heterotrimeric transcription factor (NF-Y) which specifically recognizes a 5'-CCAAT-3' box motif found in the promoters of its target genes. NF-Y can function as both an activator and a repressor, depending on its interacting cofactors. NF-YA positively regulates the transcription of the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1.<ref>PMID:12741956</ref> [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NFYC_HUMAN NFYC_HUMAN]] Stimulates the transcription of various genes by recognizing and binding to a CCAAT motif in promoters, for example in type 1 collagen, albumin and beta-actin genes. [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NFYB_HUMAN NFYB_HUMAN]] Stimulates the transcription of various genes by recognizing and binding to a CCAAT motif in promoters, for example in type 1 collagen, albumin and beta-actin genes. | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/NFYA_HUMAN NFYA_HUMAN] Component of the sequence-specific heterotrimeric transcription factor (NF-Y) which specifically recognizes a 5'-CCAAT-3' box motif found in the promoters of its target genes. NF-Y can function as both an activator and a repressor, depending on its interacting cofactors. NF-YA positively regulates the transcription of the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1.<ref>PMID:12741956</ref> |
| | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == |
| Line 20: |
Line 20: |
| | | | |
| | ==See Also== | | ==See Also== |
| - | *[[NF-Y Transcription Factor|NF-Y Transcription Factor]] | |
| | *[[Nuclear transcription factor Y|Nuclear transcription factor Y]] | | *[[Nuclear transcription factor Y|Nuclear transcription factor Y]] |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| Line 26: |
Line 25: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| - | [[Category: Bolognesi, M]] | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Donati, G]] | + | [[Category: Bolognesi M]] |
| - | [[Category: Forni, C]] | + | [[Category: Donati G]] |
| - | [[Category: Fossati, A]] | + | [[Category: Forni C]] |
| - | [[Category: Gatta, R]] | + | [[Category: Fossati A]] |
| - | [[Category: Gnesutta, N]] | + | [[Category: Gatta R]] |
| - | [[Category: Mantovani, R]] | + | [[Category: Gnesutta N]] |
| - | [[Category: Moras, D]] | + | [[Category: Mantovani R]] |
| - | [[Category: Nardini, M]] | + | [[Category: Moras D]] |
| - | [[Category: Romier, C]] | + | [[Category: Nardini M]] |
| - | [[Category: Vonrhein, C]] | + | [[Category: Romier C]] |
| - | [[Category: Dna-binding]]
| + | [[Category: Vonrhein C]] |
| - | [[Category: Nf-y]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transcription-dna complex]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
NFYA_HUMAN Component of the sequence-specific heterotrimeric transcription factor (NF-Y) which specifically recognizes a 5'-CCAAT-3' box motif found in the promoters of its target genes. NF-Y can function as both an activator and a repressor, depending on its interacting cofactors. NF-YA positively regulates the transcription of the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1.[1]
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The sequence-specific transcription factor NF-Y binds the CCAAT box, one of the sequence elements most frequently found in eukaryotic promoters. NF-Y is composed of the NF-YA and NF-YB/NF-YC subunits, the latter two hosting histone-fold domains (HFDs). The crystal structure of NF-Y bound to a 25 bp CCAAT oligonucleotide shows that the HFD dimer binds to the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone, mimicking the nucleosome H2A/H2B-DNA assembly. NF-YA both binds to NF-YB/NF-YC and inserts an alpha helix deeply into the DNA minor groove, providing sequence-specific contacts to the CCAAT box. Structural considerations and mutational data indicate that NF-YB ubiquitination at Lys138 precedes and is equivalent to H2B Lys120 monoubiquitination, important in transcriptional activation. Thus, NF-Y is a sequence-specific transcription factor with nucleosome-like properties of nonspecific DNA binding and helps establish permissive chromatin modifications at CCAAT promoters. Our findings suggest that other HFD-containing proteins may function in similar ways.
Sequence-Specific Transcription Factor NF-Y Displays Histone-like DNA Binding and H2B-like Ubiquitination.,Nardini M, Gnesutta N, Donati G, Gatta R, Forni C, Fossati A, Vonrhein C, Moras D, Romier C, Bolognesi M, Mantovani R Cell. 2013 Jan 17;152(1-2):132-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.047. PMID:23332751[2]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Kawata H, Yamada K, Shou Z, Mizutani T, Yazawa T, Yoshino M, Sekiguchi T, Kajitani T, Miyamoto K. Zinc-fingers and homeoboxes (ZHX) 2, a novel member of the ZHX family, functions as a transcriptional repressor. Biochem J. 2003 Aug 1;373(Pt 3):747-57. PMID:12741956 doi:10.1042/BJ20030171
- ↑ Nardini M, Gnesutta N, Donati G, Gatta R, Forni C, Fossati A, Vonrhein C, Moras D, Romier C, Bolognesi M, Mantovani R. Sequence-Specific Transcription Factor NF-Y Displays Histone-like DNA Binding and H2B-like Ubiquitination. Cell. 2013 Jan 17;152(1-2):132-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.047. PMID:23332751 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.047
|