Acyl carrier protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
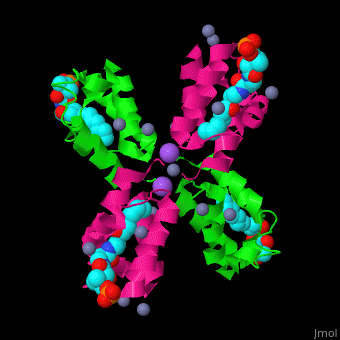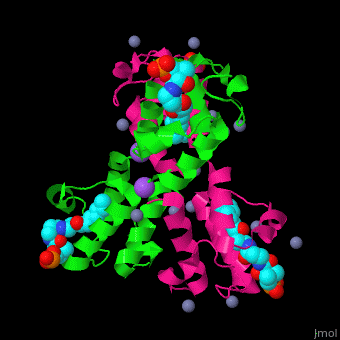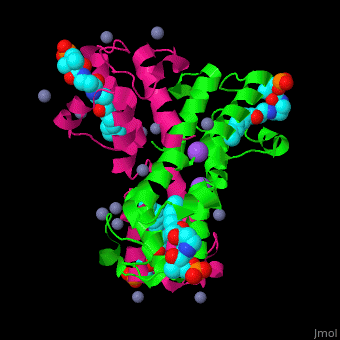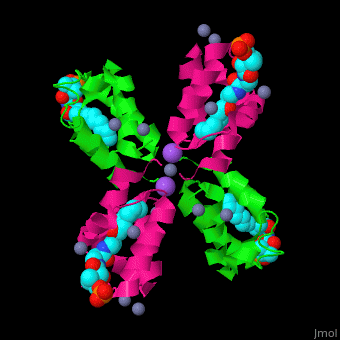
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of E. coli acyl carrier protein complex with thioester, Zn+2 (grey) and Na+ (purple) ions (PDB code [[2fad]]).' scene='59/592131/Cv/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of E. coli acyl carrier protein complex with thioester, Zn+2 (grey) and Na+ (purple) ions (PDB code [[2fad]]).' scene='59/592131/Cv/1'> | ||
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Acyl carrier protein''' (ACP) is a component of the fatty acid biosynthesis cycle. ACP catalyzes the addition of a thioester to a phosphopantetheine moiety. The phosphopantetheine moiety is added post-translationally to ACP serine residue by ACP synthetase (ACPS). The phosphopantetheine contains a free SH group which binds acyl groups in the fatty acid biosynthesis as thioesters. The acyl groups from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA are transferred to ACP. There are 2 types of ACP. '''ACP I''' is a multifunctional polypeptide found in yeast and mammals while '''ACP II''' is a monomeric protein found in bacteria and plants.<ref>PMID:18059524</ref> | '''Acyl carrier protein''' (ACP) is a component of the fatty acid biosynthesis cycle. ACP catalyzes the addition of a thioester to a phosphopantetheine moiety. The phosphopantetheine moiety is added post-translationally to ACP serine residue by ACP synthetase (ACPS). The phosphopantetheine contains a free SH group which binds acyl groups in the fatty acid biosynthesis as thioesters. The acyl groups from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA are transferred to ACP. There are 2 types of ACP. '''ACP I''' is a multifunctional polypeptide found in yeast and mammals while '''ACP II''' is a monomeric protein found in bacteria and plants.<ref>PMID:18059524</ref> | ||
| - | See also [[Molecular Playground/ACP apo]] | + | See also: |
| + | *[[Molecular Playground/ACP apo]] | ||
| + | *[[Acyl carrier protein synthase]] | ||
| + | *[[Lipid metabolism]] | ||
| + | *[[Fatty acid synthesis]] | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Byers DM, Gong H. Acyl carrier protein: structure-function relationships in a conserved multifunctional protein family. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;85(6):649-62. PMID:18059524 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/o07-109
- ↑ Roujeinikova A, Simon WJ, Gilroy J, Rice DW, Rafferty JB, Slabas AR. Structural studies of fatty acyl-(acyl carrier protein) thioesters reveal a hydrophobic binding cavity that can expand to fit longer substrates. J Mol Biol. 2007 Jan 5;365(1):135-45. Epub 2006 Sep 23. PMID:17059829 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.049