We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Cassandra Marsh/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Cassandra Marsh(Difference between revisions)
| (18 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8), ''H. sapians''= | =Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8), ''H. sapians''= | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='2v5w' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='2v5w' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='HDAC 8 (PDB:2v5w)' scene=''> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
===Histones=== | ===Histones=== | ||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone Histones] are a family of basic, positively charged proteins that associate with DNA inside the nucleus to help condense the DNA into [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromatin chromatin] <ref name="Histones"> Histones | Learn Science at Scitable https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/histone-histones-57</ref>. The nuclear DNA is wrapped around the histone in order to fit in the nucleus. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleosome Nucleosomes] are chromatin beads made up of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins, or a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_octamer histone octamer] <ref name="Histones" />. Four different examples of modifying histones including [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_acetylation_and_deacetylation Histone acetylation, Histone deacetylation], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_methylation Histone methylation] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demethylase Histone demethylation] <ref name="Histones" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)=== | ||
| + | ε-Amino-lysine acetylation is a type of histone modification that controls the stability of proteins and biological function in eukaryotic cells <ref name="Vanninni">doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7401047</ref>. Histone Deacetylation is the reversal process for this acetylation modification. There are different classes of HDACs based on phylogenetic analysis: | ||
| + | |||
| + | •Class I - HDACs 1-3 and 8, which are homologous to yeast Rpd3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | •Class II - HDACs 4-7, 9 and 10, which are homologous to yeast Hda1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | •Class III - Sirtuin deacetylases | ||
| + | |||
| + | •Class IV - HDAC 11 <ref name="Vanninni" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | HDACs 1-11 are metalloenzymes and require a zinc ion for deacetylation <ref name="Vanninni" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====HDAC8==== | ||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HDAC8 Histone Deacetylase 8] is | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Structure== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===General Structure Information=== | ||
| - | === | + | ===Inhibitor=== |
| - | == | + | ===Potassium Binding Site=== |
| - | == | + | ==Deacetylation== |
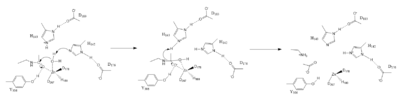
| - | == | + | ===Zn<sup>2+</sup> Metal Ion Mechanism=== |
| + | [[Image:Hdac mech.PNG|400 px|left|thumb|Figure 1. Mechanism of HDAC8]] | ||
| - | == | + | ===Active Site=== |
| + | ==Disease== | ||
| + | [https://friedreichsataxianews.com/friedreichs-ataxia-experimental-treatments/histone-deacetylase-inhibitors/ HDACis] | ||
| - | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8), H. sapians
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Histones | Learn Science at Scitable https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/histone-histones-57
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7401047
Student Contributors
- Cassandra Marsh
- Courtney Brown
- Carolyn Hurdle