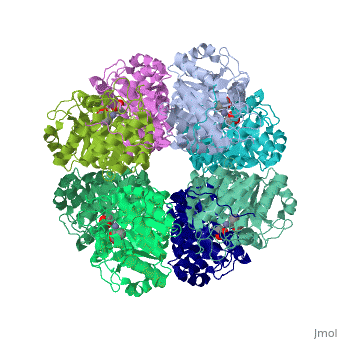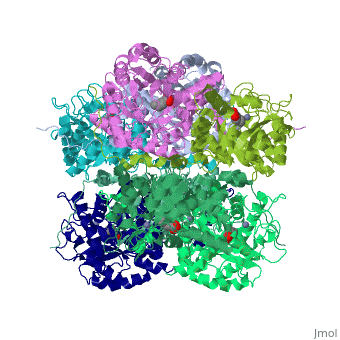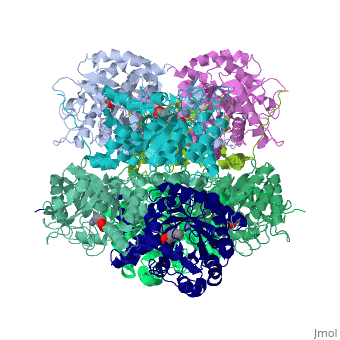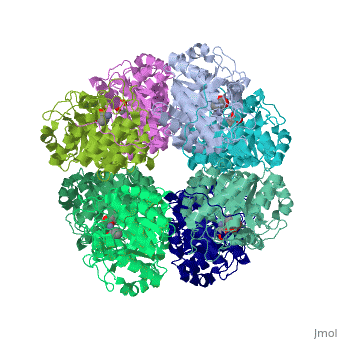|
|
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
| | <StructureSection load='1h7n' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1h7n]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.60Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='1h7n' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1h7n]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.60Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1h7n]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atcc_18824 Atcc 18824]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1H7N OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1H7N FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1h7n]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saccharomyces_cerevisiae Saccharomyces cerevisiae]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1H7N OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1H7N FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SHF:LAEVULINIC+ACID'>SHF</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 1.6Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1aw5|1aw5]], [[1qml|1qml]], [[1qnv|1qnv]], [[1ylv|1ylv]]</td></tr> | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SHF:LAEVULINIC+ACID'>SHF</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Porphobilinogen_synthase Porphobilinogen synthase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=4.2.1.24 4.2.1.24] </span></td></tr>
| + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1h7n FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1h7n OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1h7n PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1h7n RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1h7n PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1h7n ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1h7n FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1h7n OCA], [http://pdbe.org/1h7n PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1h7n RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1h7n PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1h7n ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HEM2_YEAST HEM2_YEAST]] Catalyzes an early step in the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Binds two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate per subunit, each at a distinct site, and catalyzes their condensation to form porphobilinogen. | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HEM2_YEAST HEM2_YEAST] Catalyzes an early step in the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Binds two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate per subunit, each at a distinct site, and catalyzes their condensation to form porphobilinogen. |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 37: |
Line 36: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Atcc 18824]] | |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Porphobilinogen synthase]] | + | [[Category: Saccharomyces cerevisiae]] |
| - | [[Category: Brindley, A A]] | + | [[Category: Brindley AA]] |
| - | [[Category: Cooper, J B]] | + | [[Category: Cooper JB]] |
| - | [[Category: Erskine, P T]] | + | [[Category: Erskine PT]] |
| - | [[Category: Newbold, R]] | + | [[Category: Newbold R]] |
| - | [[Category: Shoolingin-Jordan, P M]] | + | [[Category: Shoolingin-Jordan PM]] |
| - | [[Category: Warren, M J]] | + | [[Category: Warren MJ]] |
| - | [[Category: Wood, S P]] | + | [[Category: Wood SP]] |
| - | [[Category: Aldolase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Dehydratase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Lyase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Tetrapyrrole synthesis]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Tim barrel]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
HEM2_YEAST Catalyzes an early step in the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Binds two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate per subunit, each at a distinct site, and catalyzes their condensation to form porphobilinogen.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The structures of 5-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) complexed with substrate (5-aminolaevulinic acid) and three inhibitors: laevulinic acid, succinylacetone and 4-keto-5-aminolaevulinic acid, have been solved at high resolution. The ligands all bind by forming a covalent link with Lys263 at the active site. The structures define the interactions made by one of the two substrate moieties that bind to the enzyme during catalysis. All of the inhibitors induce a significant ordering of the flap covering the active site. Succinylacetone appears to be unique by inducing a number of conformational changes in loops covering the active site, which may be important for understanding the co-operative properties of ALAD enzymes. Succinylacetone is produced in large amounts by patients suffering from the hereditary disease type I tyrosinaemia and its potent inhibition of ALAD also has implications for the pathology of this disease. The most intriguing result is that obtained with 4-keto-5-amino-hexanoic acid, which seems to form a stable carbinolamine intermediate with Lys263. It appears that we have defined the structure of an intermediate of Schiff base formation that the substrate forms upon binding to the P-site of the enzyme.
The x-ray structure of yeast 5-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase complexed with substrate and three inhibitors.,Erskine PT, Newbold R, Brindley AA, Wood SP, Shoolingin-Jordan PM, Warren MJ, Cooper JB J Mol Biol. 2001 Sep 7;312(1):133-41. PMID:11545591[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Erskine PT, Newbold R, Brindley AA, Wood SP, Shoolingin-Jordan PM, Warren MJ, Cooper JB. The x-ray structure of yeast 5-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase complexed with substrate and three inhibitors. J Mol Biol. 2001 Sep 7;312(1):133-41. PMID:11545591 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4947
|