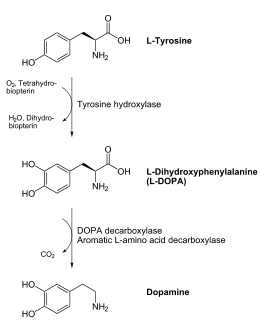
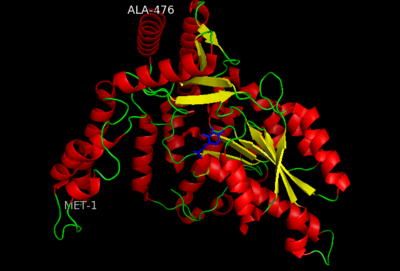
DOPA decarboxylase (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) (EC 4.1.1.28) is an approximately 104 kDa protein that belongs to the aspartate aminotransferase family (fold type 1) of PLP-dependent (vitamin B6-dependent) enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes.[1] The homodimeric form of the enzyme purified from sus scrofa is shown in complex with the inhibitor carbidopa to the right.
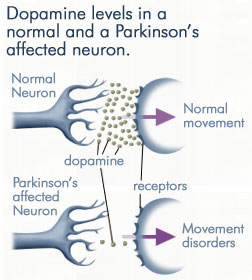
DDC catalyzes the conversion of aromatic amino acids into their corresponding amines. DOPA decarboxylase is responsible for the synthesis of dopamine and serotonin from L-DOPA and L-5-hydroxytryptophan, respectively. It is highly stereospecific, yet relatively nonspecific in terms of substrate, making it a somewhat uninteresting enzyme to study. Although it is not typically a rate-determining step of dopamine synthesis, the decarboxylation of L-DOPA to dopamine by DDC is the controlling step for individuals with Parkinson's disease[2] , the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, occuring in 1% of the population over the age of 65. The loss of dopaminergic neurons is the main cause of cognitive impairment and tremors observed in patients with the disease. The hallmark of the disease is the formation of alpha-synuclein containing Lewy bodies.
Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition. Since dopamine cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, it cannot be used to directly treat Parkinson's disease. Thus, exogenously administered L-DOPA is the primary treatment for patients suffering from this neurodegenerative disease. Unfortunately, DOPA decarboxylase rapidly converts L-DOPA to dopamine in the blood stream, with only a small percentage reaching the brain. By inhibiting the enzyme, greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA can reach the brain, where it can then be converted to dopamine. [3]. Unfortunately, with continued L-Dopa treatment, up to 80% of patients experience 'wearing-off' symptoms, dyskinesias and other motor complications (referred to as the "on-off phenomenon". [4]. Clearly, a better understanding of the catalytic mechanism and enzymatic activity of DDC in both healthy and PD individuals is critical to drug design and treatment of the disease.
PLP-Dependent Enzymes
Overview
Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP) is the biologically active phosphorylated derivative of vitamin B6. PLP-dependent enzymes are functionally diverse, with 150+ distinct activities, including transiminations, decarboxylations, racemizations, and deaminations. With few exceptions, all PLP-dependent enzymes participate in amino acid metabolism. The versatility of PLP-dependent enzymes is, in large part, due to two basic chemical properties of the coenzyme. First, it can form a covalent bond with the substrate via its aldehyde group. Second, it can act as an electrophilic catalyst, serving as an electron sink which stabilizes the obligatory carbanionic intermediates formed during the reaction.
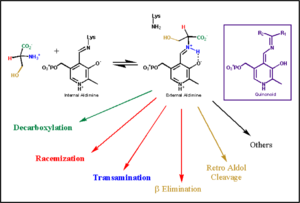
transimination reaction common to all PLP-dependent enzymes. In the resting state, PLP forms a covalent bond with the amino group of the active site Lysine (internal aldimine). Upon introduction of the substrate into the active site, a new Schiff base is generated (external aldimine). This transimination step is common to all PLP-dependent enzymes.
Although these enzymes have wide range of function, they can be classified into only five structural families: the
aspartate amino transferase', the tryptophan synthase β, the alanine racemase, the D-amino acid, and the glycogen phosphorylase. [5] [1] 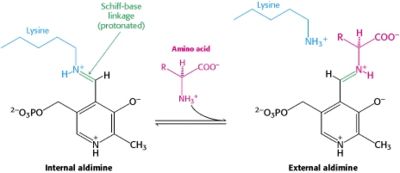
The PLP is bound covalently to lysine residues in a Schiff base linkage (aldimine). In this form, it reacts with many free amino acids to replace the Schiff base to the lysine of the enzyme with a Schiff base to the amino acid substrate.
The Aspartate Aminotransferase Family
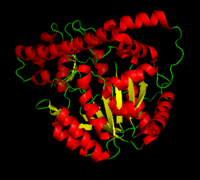
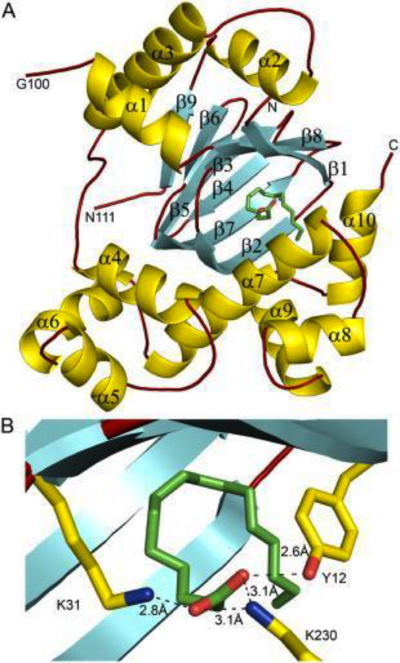
Aspartate Aminotransferase This family of PLP-dependent enzymes is also referred to as fold-type I, with aspartate aminotransferase serving as the prototype. It is the most common structure of the five classes of PLP-dependent enzymes. This fold it is found in a variety of aminotransferases and decarboxylases, amongst them DOPA decarboxylase. PLP-dependent enzymes belonging to this family are catalytically active as homodimers and share a common, well-characterized structure, despite low-sequence identity. Each subunit has a large domain and a small domain. The central feature of the large domain is a seven-stranded β sheet. The small domain has either a three or four-stranded β sheet that is surrounded by α helices on one side. The cofactor PLP is covalently attached to a lysine residue in the large domain and is anchored in a way that allows the aromatic ring of PLP to pack against neighboring β strands. The active site is located in a cleft between the two domains at the interface between the two subunits. Thus, enzymes of fold-type I have residues from both domains and both subunits involved in PLP-binding.
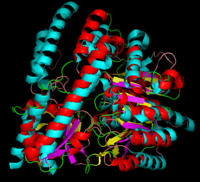
DOPA decarboxylase superimposed on aspartate aminotransferase
DOPA Decarboxylase
Primary Structure
The amino acid sequence of a proteins polypeptide chain is referred to as its primary structure. Each polypeptide chain of DOPA decarboxylase is composed of 486 amino acids that ultimately encode the three-dimensional structure of the protein. In 1991, the complete amino acid sequence was determined by peptide analysis, significantly increasing the structural and functional understanding of the enzyme [6].
Secondary Structure
The formation of secondary structural elements (like α helices and β sheets) arise in response to the hydrophobic effect and the need to neutralize main-chain polar groups by hydrogen bonding. Each polypeptide chain of DOPA decarboxylase is composed of a seven-stranded mixed , a four-stranded anti-parallel , several , and other, lesser known, secondary structural elements (like loops and the extended strand). Another common secondary structure is the β-turn, or reverse turn. Depicted below is an example of a Type 1 β-turn of DOPA decarboxylase. This β-turn is comprised of residues Leu-440, Arg-441, Gly-442, and Gln-443. The distance between Cαi and Cαi+3 is 5.1Å, within the acceptable limit of 7Å. As in most β-turns, there is a hydrogen bond between the C=O of Leu-440 and the NH of Gln-443. The phi and psi angles of residues i+1 (Arg-441) and i+2 (Gly-442) are indicated in the diagram.
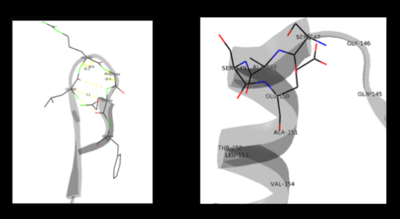
The α helix is characterized by main chain hydrogen bonds between the C=O of residue n and the NH of residue n+4. All residues in the helix participate in this type of hydrogen bonding except the first NH groups and the last C=O groups at the ends of the helix. Helix-capping motifs are specific hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions found at the ends of helices. Seven distinct capping motifs have been identified; three at the N-terminus and four at the C-terminus [7] . Shown above is the capping-box motif found at the end of the helix composed of residues 147-171. This form of special capping satisfies two of the four non hydrogen-bonded helix N-terminal amides. The side-chain capping apparent here is typical at the N-terminus.
Tertiary Structure
This level of protein structure refers to the overall three-dimensional shape the polypeptide chain creates. Domains are the fundamental units that generate the tertiary structure, and DOPA decarboxylase is composed of three distinct domains.
The contains the PLP-binding site, and consists of a seven-stranded mixed β sheet that is surrounded by eight α helices, resulting in a typical α/β fold, the most regular and common of the protein structures (recall that α helices and β strands typically alternate in this fold, generating an outer layer of α helices and an inner layer of β sheets). This particular fold falls into the class of open twisted parallel or mixed β sheet with α helices on both sides of the sheet. The small is comprised of a four-stranded anti-parallel β sheet that has three α helices packed against the face opposite to the large domain. Although the aforementioned domains exist in all members of this family of PLP-dependent enzymes, including bacterial ornithine decarboxylase (OrnDC) and dialkylglycine decarboxylase (DGD), the is unique to DOPA decarboxylase, and is a representative case of domain swapping. This domain is composed of two parallel helices linked by an extended strand, which essentially lies like a flap over the second subunit. As well, residues from the N-terminal domain and the small domain form a short
Quaternary Structure
The level of protein structure exists solely in multisubunit complexes. DOPA decarboxylase is a homodimeric enzyme with the active site located near the monomer-monomer interface, thus highlighting the importance of this level of protein structure to the enzymes function. Furthermore, since the N-terminal domain of one monomer packs on top of the other monomer, resulting in an extended dimer interface, this level of tertiary structure is most likely stable only in the dimeric form of the enzyme.
Function
The Active Site
The active site of DOPA decarboxylase is located in a cleft at the between the two subunits of the dimer, like all PLP-dependent enzymes of the aspartate aminotransferase family. Since it is at the interface, residues from both domains and both subunits are involved in cofactor binding, although the active site is composed of residues mainly from one monomer. The is composed of several key residues, including Lys-303, Asp-271, His-192, Thr-82, Ile-101, and Phe-103. serves to bind PLP via a Schiff base linkage in the absence on substrate.
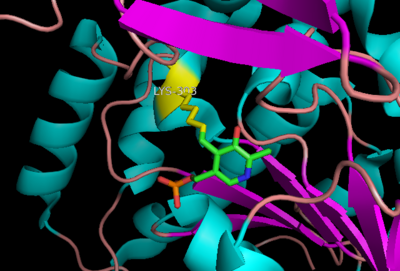
Schiff base linkage of PLP to Lys303 in the active site
As well, a salt bridge exists between the carboxyl group of and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP to further stabilize intermediate. Essentially, a salt bridge combines hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions (two common types non-covalent interactions). This interaction serves to provide an electron sink that can stabilize the carbanionic intermediates [8] . PLP is further anchored to the protein by an extended hydrogen bond network, as shown below.
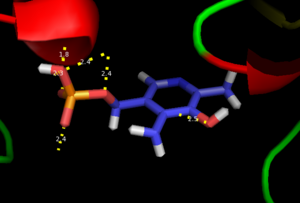
H-bonding network of PLP in the active site
The only two active site residues from the adjacent monomer, Ile-101 and Phe-103, are part of the substrate binding pocket.
Inhibitor Binding
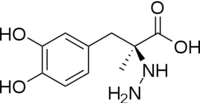
The inhibitor binds to the enzyme by forming a hydrazone linkage with PLP through its hydrazine moiety. The catechol ring of carbiDOPA is deeply buried in the active site cleft and is stabilized by with Ile-101 and Phe-103. The 4' hydroxyl group of the catechol ring participates in hydrogen bonding with , further stabilizing the inhibitor in the active site cleft. PLP is further involved in substrate binding by forming a hydrogen bond to the 3' of the catechol ring. , a highly conserved residue of PLP-dependent decarboxylases [9] hydrogen bonds to the carboxylate group of carbiDOPA.
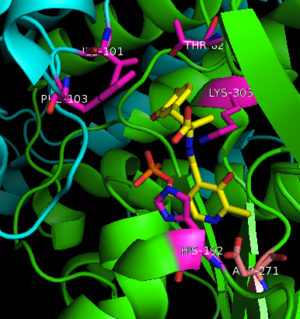
Key interactions between the active site residues, PLP, and carbiDOPA Other inhibitors include Benserazide (Serazide), α-Difluoromethyl-DOPA, and α-methyldopa. However, Benserazide is unapproved for use in the U.S. and is replaced by carbiDOPA instead. Both inhibitors act by preventing peripheral metabolism of L-DOPA, and cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.
Flexible Loop
In all three crystal structures of DOPA decarboxylase solved to date, residues 328-339 are invisible in the electron density map. This is because these amino acids form a short mobile loop that is believed to be important to the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme [9]. Although the highly conserved Tyr332 residue was found to be essential for catalytic activity, its role was unknown prior to solving the crystal structure. During catalysis, this loop is proposed to lose its flexibility and extend toward the active site, both occluding the active site from solvent during catalysis and possibly even taking part in the catalytic mechanism. Based on the catalytic role of Tyr in other PLP-dependent enzymes, Tyr332 could act as a proton donor for the quinonoid Cα. For example, the mobile loop is found in other PLP-depended enzymes, such as glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase.
Mechanism
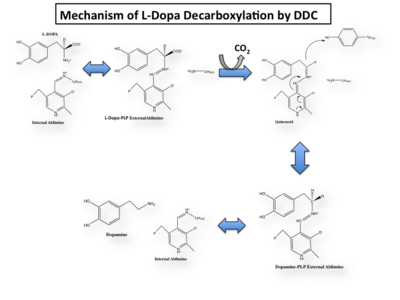
The mechanism of DDC catalyzed decarboxylation of L-Dopa to Dopamine has been well-studied due to the enzymes role in PD. Shown below is the mechanism of decarboxylation, as determined by several experimental approaches, including site-directed mutagenesis, UV-Vis Spectroscopy, X-Ray Crystallography, Multiple Sequence Alignment, and Stopped-Flow Spectroscopy.
Once again, the transimination step (conversion of internal to external aldimine) is common to all PLP-dependent enzymes. The unique absorption wavelengths of the PLP intermediates has allowed for their straightforward detection (for example, an internal Schiff base in the enolimine form absorbs at 310-330 nm, whereas the quinonoid intermediate absorbs at ~500 nm). The orientation of the quinonoid intermediate allows for stereospecific decarboxylation of the substrate at the alpha carbon, as predicted by Dunathan's stereoelectronic hypothesis [10], in which he proposed that the substrate binds PLP such that the external aldimine intermediate is oriented perpendicular to the coenzyme pi bonding system. In doing so, the sigma-pi orbital overlap in the transition state is maximized, thus maximizing the rate of the reaction.
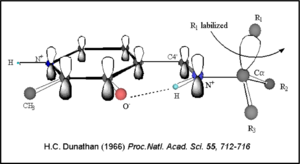
Dunathan's Stereoeletronic Hypothesis, 1966 This way, the developing p orbital is aligned for maximal overlap with the extended p system, lowering the energy of the transition state and increasing the rate of the reaction. As well, by controlling substrate orientation, the enzyme can distinguish between deprotonation and decarboxylation.
Mechanism Breakdown
Step 1: Formation of an Internal Aldimine
The first step of the reaction involves the binding of PLP to the enzyme via a Schiff base linkage between the aldehyde group of PLP and the ε—amino group of Lys303. An extensive hydrogen bond network further anchors PLP to the enzyme.
Step 2: Formation of an External Aldimine
The second step of the reaction involves the binding of PLP with the substrate via a Schiff base linkage. The imine formed in the first step of the reaction is more succeptible than a free aldehyde to nucleophilic attack by the amino group of the substrate. Thus, not only does the internal aldimine between PLP and the Lys303 bind cofactor, it also serves to facilitate chemistry occurring in this second step.
Step 3: Formation of a Quinonoid Intermediate
The formation of the quinonoid intermediate is common to all PLP-dependent enzymes, yet the orientation of the intermediate, as determined by key residues of the enzyme active site, determines the subsequent reaction (for example whether it will be a decarboxylation or transamination). A salt bridge that exists between Asp271 and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP further enhances the ability of PLP to act as an electron sink and promote catalysis. As well, During the formation of the quinonoid intermediate, carbon dioxide is released.
Step 4: Formation of an External Aldimine
The formation of the external aldimine between the product and PLP is the fourth step of the reaction. Here, Tyr332, with the assistance of His192, likely donates a proton to the quinonoid Cα intermediate.
Step 5: Formation of an Internal Aldimine and Product Release
Formation of an internal aldimine between PLP and Lys303 regenerates the enzyme. It has been shown that Lys303 plays a role in product release by presumably displacing the amino group of the product by nucleophilic attack of the imine bond of the external aldimine.
DDC and Parkinson's Disease
Treatment
Parkinson's disease can be characterized by
tremor,
bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability.
With it's possible relation to degenerative dopamine-producing cells in the brain, administration of L-DOPA can increase the amount of synthesized dopamine in the nerve cell; whereas, direct treatment with dopamine is not sufficient as dopamine itself cannot pass the blood-brain barrier[11]. Even still, only a small percentage of the dose actually reaches the nervous system, with the remaining majority being rapidly decarboxylated to dopamine in the blood stream. This dopamine-rich blood causes side effects of nausea, daytime sleepiness, orthostatic hypotension, involuntary movements, decreased appetite, insomnia, and cramping. Addition of a DDC inhibitor would block peripheral conversion to dopamine and allow a greater percentage of L-DOPA to reach the brain, causing an increase in brain dopamine levels, and reducing the side effects of dopamine-rich blood.
Classification
DOPA decarboxylase is classified in the following manner using SCOP:
- Class: alpha and beta proteins (α/β)
- Fold: PLP-dependent transferase-like
- Superfamily: PLP-dependent transferases
- Family: Pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylase
- Domain: DOPA decarboxylase
DOPA decarboxylase is classified in the following manner using CATH:
- Class: alpha beta
- Architecture: 3-layer sandwich
- Topology: Aspartate aminotransferase
- Class: alpha beta
- Architecture: alpha-beta complex
- Topology: Aspartate aminotransferase
- Class: mainly alpha
- Architecture: up-down bundle
- Topology: dopa decarboxylase
3D structures of DOPA decarboxylase
Updated on 27-April-2025
3rbf, 3rbl – hDDC – human
3rch, 8or9, 8ora – hDDC + PLP
3k40 – DDC – Drosophila melanogaster
1js3 – pDDC + inhibitor – pig
1js6 - pDDC
6eew – MpDDC + Trp – Madagascar periwinkle
6eem – MpDDC + Tyr
6liu – poDDC - poppy
6liv – poDDC + PLP derivative
8x0p – poDDC + PLP + carbidopa
8x0o – poDDC + Tyr + PLP derivative
7xin – DDC + PLP - Pseudomonas
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
- ↑ Miles EW. The tryptophan synthase alpha 2 beta 2 complex. Cleavage of a flexible loop in the alpha subunit alters allosteric properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10715-8. PMID:1904055
- ↑ Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963
- ↑ Miles EW. The tryptophan synthase alpha 2 beta 2 complex. Cleavage of a flexible loop in the alpha subunit alters allosteric properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10715-8. PMID:1904055
- ↑ Percudani R, Peracchi A. A genomic overview of pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent enzymes. EMBO Rep. 2003 Sep;4(9):850-4. PMID:12949584 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.embor914
- ↑ Maras B, Dominici P, Barra D, Bossa F, Voltattorni CB. Pig kidney 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (dopa) decarboxylase. Primary structure and relationships to other amino acid decarboxylases. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 15;201(2):385-91. PMID:1935935
- ↑ Aurora R, Rose GD. Helix capping. Protein Sci. 1998 Jan;7(1):21-38. PMID:9514257 doi:10.1002/pro.5560070103
- ↑ Jansonius JN. Structure, evolution and action of vitamin B6-dependent enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Dec;8(6):759-69. PMID:9914259
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Ishii S, Mizuguchi H, Nishino J, Hayashi H, Kagamiyama H. Functionally important residues of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase probed by sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 1996 Aug;120(2):369-76. PMID:8889823
- ↑ Hiscott JB, Defendi V. Simian virus 40 gene A regulation of cellular DNA synthesis. I. In permissive cells. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):590-9. PMID:224217
- ↑ Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963