We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
LDL receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (6 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein) receptor''' (LDLR) mediates the endocytosis of cholesterol-rich LDL. LDLR recognizes the apoprotein B100 which is embedded in the outer layer of the LDL particle. LDLR sits on the cell surface and binds LDL particles which circulate in the blood stream. LDLR transports the LDL particle into the cell where the cholesterol is used. Upon release of the LDL particle, the LDLR is recycled back into the cell membrane surface<ref>PMID:19299327</ref>. | '''LDL (Low Density Lipoprotein) receptor''' (LDLR) mediates the endocytosis of cholesterol-rich LDL. LDLR recognizes the apoprotein B100 which is embedded in the outer layer of the LDL particle. LDLR sits on the cell surface and binds LDL particles which circulate in the blood stream. LDLR transports the LDL particle into the cell where the cholesterol is used. Upon release of the LDL particle, the LDLR is recycled back into the cell membrane surface<ref>PMID:19299327</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
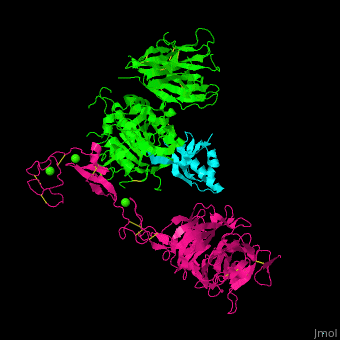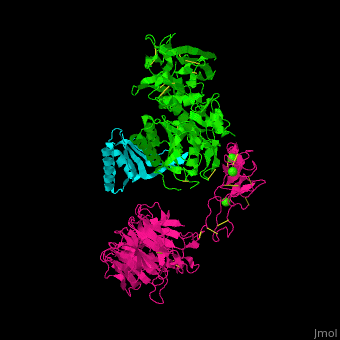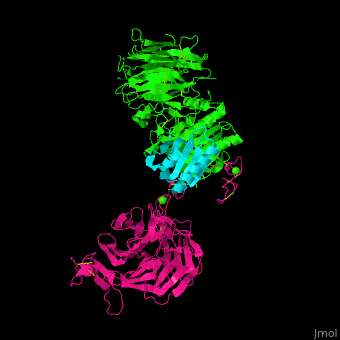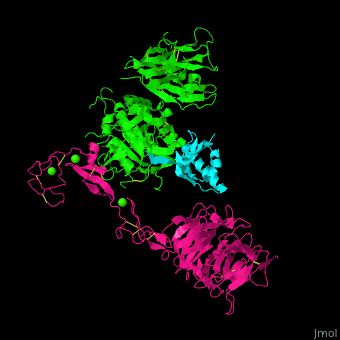
<scene name='54/545853/Cv/7'>Ligand-binding domain (LBD) and epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain (EGFP) of LDLR</scene>. | <scene name='54/545853/Cv/7'>Ligand-binding domain (LBD) and epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain (EGFP) of LDLR</scene>. | ||
| - | LDLR consists of a ligand-binding domain (LBD residues 1-292), epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain (EGFP residues 293-699), oligosaccharide-rich domain (residues 700-758), membrane-spanning domain (residues 759-781) and cytoplasmic domain (residues 782-832). | + | LDLR consists of a ligand-binding domain (LBD residues 1-292), epidermal growth factor precursor homology domain (EGFP residues 293-699), oligosaccharide-rich domain (residues 700-758), membrane-spanning domain (residues 759-781) and cytoplasmic domain (residues 782-832). LDLR LBD contains 7 ca. 40 amino acid long repeats (LB1 residues 20-67; LB2 residues 55-104; LB3 residues 105-143; LB4 residues 144-196; LB5 residues 196-232; LB6 residues 234-272) containing 6 cysteine residues, making a calcium binding octahedral structure. LDLR EGFP contains 2 EGF repeats followed by 6 <scene name='54/545853/Cv/8'>YWTD repeats</scene> and another EGF repeat. LDLR LBD residues 133-273 are named C-type lectin-like domain. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | *hLDLR ligand-binding domain | + | *hLDLR ligand-binding domain;Repeats - LB1 20-67; LB2 55-104; LB4 144-195; LB5 196-232; LB6 234-272; LB7 274-313 |
**[[1ldl]] – hLDLR LB1 - human - NMR<br /> | **[[1ldl]] – hLDLR LB1 - human - NMR<br /> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
**[[2lgp]] – hLDLR LB4,LB5 - NMR<br /> | **[[2lgp]] – hLDLR LB4,LB5 - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[1xfe]] – hLDLR LB7,EGF - NMR<br /> | **[[1xfe]] – hLDLR LB7,EGF - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1yxj]], [[1yxk]] – hLDLR LBD LB4,LB5, LB6<br /> | + | **[[1yxj]], [[1yxk]], [[6tl7]], [[6tla]] – hLDLR LBD LB4,LB5,LB6<br /> |
| + | **[[6tl9]] – hLDLR LBD LB4,LB5,LB6 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
*hLDLR ligand-binding domain complex with protein | *hLDLR ligand-binding domain complex with protein | ||
| Line 38: | Line 41: | ||
**[[5oy9]] – hLDLR LBD LB3 + glycoprotein G<br /> | **[[5oy9]] – hLDLR LBD LB3 + glycoprotein G<br /> | ||
| - | *hLDLR EGFP | + | *hLDLR EGFP domain 263-699 |
**[[1ijq]] – hLDLR YWTD-EGF<br /> | **[[1ijq]] – hLDLR YWTD-EGF<br /> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 54: | ||
**[[2w2n]], [[3gcw]] – hLDLR EGF1, EGF2 (mutant) + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9<br /> | **[[2w2n]], [[3gcw]] – hLDLR EGF1, EGF2 (mutant) + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9<br /> | ||
| - | *hLDLR cytoplasmic domain | + | *hLDLR cytoplasmic domain C terminal 817-832 |
**[[3so6]] – hLDLR C terminal + LDLR adaptor protein<br /> | **[[3so6]] – hLDLR C terminal + LDLR adaptor protein<br /> | ||
| - | *hLDLR lectin-like domain | + | *hLDLR lectin-like domain 136-273 |
| + | **[[1ypo]], [[1ypq]], [[1ypu]], [[7w5d]], [[7xmp]] – hLDLR<br /> | ||
**[[3vlg]] – hLDLR (mutant)<br /> | **[[3vlg]] – hLDLR (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *hLDLR Cys-rich domain 70-190 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[6byv]] – hLDLR - NMR<br /> | ||
*hLDLR multiple domains | *hLDLR multiple domains | ||
| Line 64: | Line 72: | ||
**[[3m0c]] – hLDLR LBD,EGFP, oligosaccharide-rich, membrane-spanning domains + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9<br /> | **[[3m0c]] – hLDLR LBD,EGFP, oligosaccharide-rich, membrane-spanning domains + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9<br /> | ||
**[[3p5b]], [[3p5c]] – hLDLR EGFP, oligosaccharide-rich, domains + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9<br /> | **[[3p5b]], [[3p5c]] – hLDLR EGFP, oligosaccharide-rich, domains + proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9<br /> | ||
| + | **[[9bdt]], [[9coo]] – hLDLR + apolipoprotein B + legobody + nanobody + MBP – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[9bd8]], [[9bde]] – hLDLR + apolipoprotein B – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | |||
}} | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of LDL receptor
Updated on 26-October-2025
References
- ↑ Goldstein JL, Brown MS. The LDL receptor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Apr;29(4):431-8. doi:, 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.179564. PMID:19299327 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.179564
- ↑ Mak YT, Pang CP, Tomlinson B, Zhang J, Chan YS, Mak TW, Masarei JR. Mutations in the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene in Chinese familial hypercholesterolemia patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998 Oct;18(10):1600-5. PMID:9763532