This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Glycogen synthase kinase 3
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
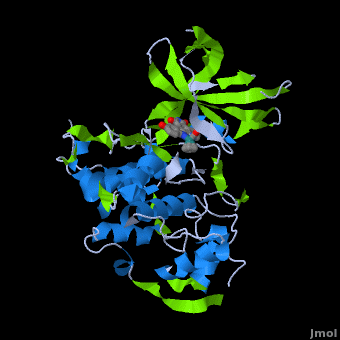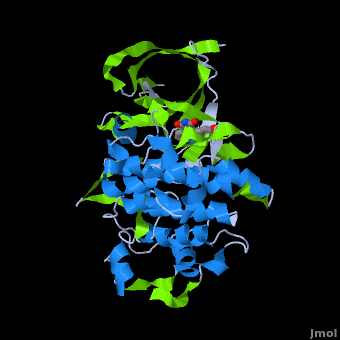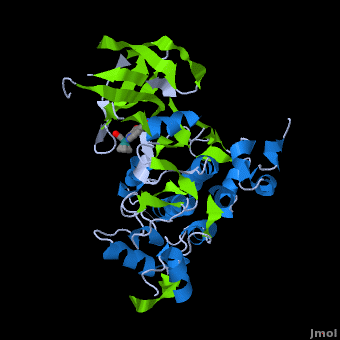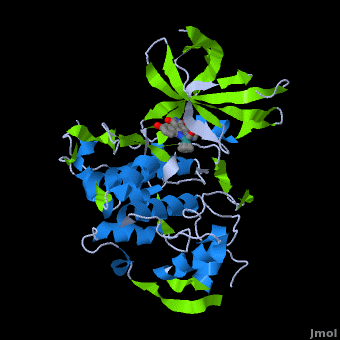
A crystal structure of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex_no_bonds/1'>organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex </scene>bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Atp_binding_site2/2'>ATP binding site</scene> via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex/3'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic_stic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic/5'>sandwiched between the faces of the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene> and to interact tightly with <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Glycine_rich_loop2/4'>the flexible glycine-rich loop</scene>. Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities. | A crystal structure of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex_no_bonds/1'>organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex </scene>bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Atp_binding_site2/2'>ATP binding site</scene> via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex/3'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic_stic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic/5'>sandwiched between the faces of the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene> and to interact tightly with <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Glycine_rich_loop2/4'>the flexible glycine-rich loop</scene>. Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities. | ||
| - | + | ==3D structures of glycogen synthase kinase 3== | |
[[Glycogen synthase kinase 3 3D structures]] | [[Glycogen synthase kinase 3 3D structures]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | ===3D structures of glycogen synthase kinase 3=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | |||
| - | *GSK-3 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1i09]], [[1h8f]] – hGSK-3 β – human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4e7w]] – GSK-3 (mutant) – smut fungus<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *GSK-3 binary complex | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1gng]] - hGSK-3 β + Frattide peptide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1q4l]], [[1uv5]], [[1q5k]], [[1r0e]], [[2o5k]], [[2ow3]], [[3du8]], [[3f7z]], [[3f88]], [[3i4b]], [[3gb2]], [[3l1s]], [[3q3b]], [[3zrk]], [[3zrl]], [[3zrm]], [[3sd0]], [[4dit]], [[4afj]], [[4acc]], [[4acd]], [[4acg]], [[4ach]], [[3say]], [[4iq6]], [[4j1r]], [[4j71]], [[5k5n]], [[5hlp]], [[5hln]], [[5f94]], [[5f95]], [[5kpk]], [[5kpl]], [[5kpm]], [[6gjo]], [[6gn1]], [[6h0u]] - hGSK-3 β + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5t31]] - hGSK-3 β (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1pyx]], [[1j1b]] - hGSK-3 β + AMPPNP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1j1c]] - hGSK-3 β + ADP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1q3d]], [[1q3w]], [[1q41]] - hGSK-3 β + ATP-mimetic inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ptc]], [[4pte]], [[4ptg]] - hGSK-3 β + acylaminopyridine inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3m1s]], [[3pup]] - hGSK-3 β + Ru complex<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4nm0]], [[4nm3]], [[4nu1]], [[1o9u]], [[4b7t]] - hGSK-3 β + Axin peptide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6ae3]] - GSK-3 β + morin - mouse<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *GSK-3 ternary complex | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2jld]] - hGSK-3 β + Ru complex + peptide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3zdi]], [[6b8j]] - hGSK-3 β + Axin peptide + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5oy4]] - hGSK-3 β + FRAT-1 peptide + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4nm5]], [[4nm7]] - hGSK-3 β + Axin peptide + WNT receptor LRP6 peptide<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Forde JE, Dale TC. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Aug;64(15):1930-44. PMID:17530463 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7045-7
- ↑ Jope RS, Roh MS. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3) in psychiatric diseases and therapeutic interventions. Curr Drug Targets. 2006 Nov;7(11):1421-34. PMID:17100582
- ↑ Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Di Costanzo L, Meggers E. Structure of anticancer ruthenium half-sandwich complex bound to glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2010 Sep 7. PMID:20821241 doi:10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x