Netrin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (6 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
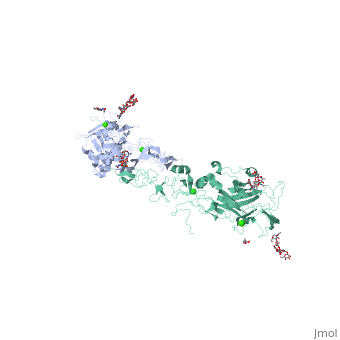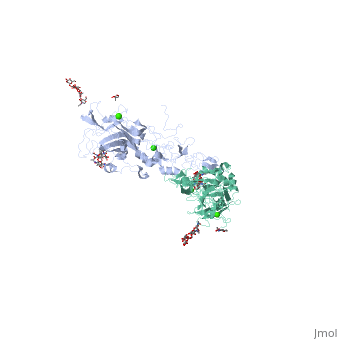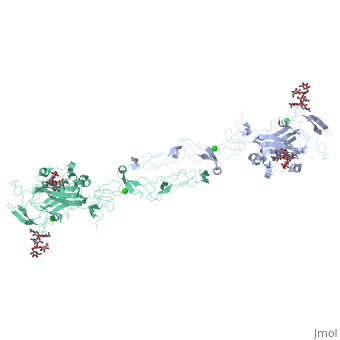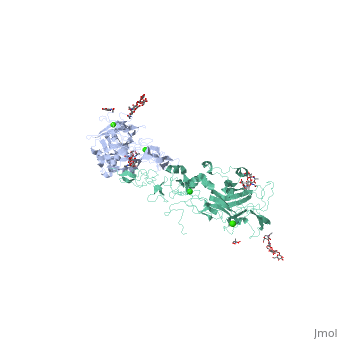
<StructureSection load='4ove' size='350' side='right' caption='Glycosylated mouse netrin-1 complex with Ca+2 and Cl-1 ions (PDB code [[4ove]])' scene='' pspeed='8'> | <StructureSection load='4ove' size='350' side='right' caption='Glycosylated mouse netrin-1 complex with Ca+2 and Cl-1 ions (PDB code [[4ove]])' scene='' pspeed='8'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Netrins''' (Net) direct cell and axon migration during development. Netrins are chemotropic. The growing axon moves either toward or away from netrin concentration. Netrins influence the formation of a variety of tissues. They act as chemoattractants for some cell types and chemorepellent for other types<ref>PMID:18269208</ref>. '''Netrin-1''' is a secreted protein while '''netrin-G2''' is GPI-anchored membrane protein. | + | '''Netrins''' (Net) direct cell and axon migration during development. Netrins are chemotropic. The growing axon moves either toward or away from netrin concentration. Netrins influence the formation of a variety of tissues. They act as chemoattractants for some cell types and chemorepellent for other types<ref>PMID:18269208</ref>. |
| + | *'''Netrin-1''' is a secreted protein while '''netrin-G2''' is GPI-anchored membrane protein. | ||
| + | *'''Netrin-4''' promotes neurite elongation at low concentration and inhibits neurite elongation at high concentration<ref>PMID:19094984</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Netrin-G1''' promotes the growth of dorsal thalamic axons. | ||
| + | *'''Netrin-G2''' plays a role in synaptic and pre-synaptic organisation<ref>PMID:31668703</ref>. | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 13: | ||
The N-terminal of netrin-1 is homologous to the N-terminal type I domain of laminin (LN) followed by 3 cysteine-rich epidermal growth factor repeats. | The N-terminal of netrin-1 is homologous to the N-terminal type I domain of laminin (LN) followed by 3 cysteine-rich epidermal growth factor repeats. | ||
*<scene name='70/705761/Cv/3'>Ca coordination site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | *<scene name='70/705761/Cv/3'>Ca coordination site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| - | *<scene name='70/705761/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='70/705761/Cv/4'>Cl coordination site</scene>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 23: | ||
*Netrin-1 | *Netrin-1 | ||
| + | **[[7ne1]] – hNet1 V-VI domains 39-453 + neogenin - human<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[7ne0]] – hNet1 V-VI domains + neogenin + RGMB<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[7ndg]] – hNet1 V-VI domains + neogenin + RGMB – Cryo EM<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[4urt]] – hNet1 V-VI domains + hNet receptor DCC fourth fibronectin type FN5-FN6 domains <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[6fkq]] – hNet1 V-VI domains + draxin peptide<BR /> | ||
**[[4ove]] – mNet1 – mouse<BR /> | **[[4ove]] – mNet1 – mouse<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[4plm]] – cNet1 LN-LE3 domains – chicken<BR /> | + | **[[4plm]], [[7ler]] – cNet1 LN-LE3 domains 26-457 – chicken<BR /> |
**[[4pln]] – cNet1 LN-LE3 domains + neogenin fibronectin type IV-V domains<br /> | **[[4pln]] – cNet1 LN-LE3 domains + neogenin fibronectin type IV-V domains<br /> | ||
**[[4plo]] – cNet1 LN-LE3 domains + mNet receptor DCC fourth fibronectin type IV-V domains <BR /> | **[[4plo]] – cNet1 LN-LE3 domains + mNet receptor DCC fourth fibronectin type IV-V domains <BR /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[7lrf]] – cNet1 LN-LE3 domains + SOS<br /> |
| - | + | ||
*Netrin-4 | *Netrin-4 | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of netrin
Updated on 16-July-2024
References
- ↑ Moore SW, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kennedy TE. Netrins and their receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;621:17-31. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-76715-4_2. PMID:18269208 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-76715-4_2
- ↑ Nacht M, St Martin TB, Byrne A, Klinger KW, Teicher BA, Madden SL, Jiang Y. Netrin-4 regulates angiogenic responses and tumor cell growth. Exp Cell Res. 2009 Mar 10;315(5):784-94. PMID:19094984 doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.11.018
- ↑ Dias CM, Punetha J, Zheng C, Mazaheri N, Rad A, Efthymiou S, Petersen A, Dehghani M, Pehlivan D, Partlow JN, Posey JE, Salpietro V, Gezdirici A, Malamiri RA, Al Menabawy NM, Selim LA, Vahidi Mehrjardi MY, Banu S, Polla DL, Yang E, Rezazadeh Varaghchi J, Mitani T, van Beusekom E, Najafi M, Sedaghat A, Keller-Ramey J, Durham L, Coban-Akdemir Z, Karaca E, Orlova V, Schaeken LLM, Sherafat A, Jhangiani SN, Stanley V, Shariati G, Galehdari H, Gleeson JG, Walsh CA, Lupski JR, Seiradake E, Houlden H, van Bokhoven H, Maroofian R. Homozygous Missense Variants in NTNG2, Encoding a Presynaptic Netrin-G2 Adhesion Protein, Lead to a Distinct Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Nov 7;105(5):1048-1056. PMID:31668703 doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.09.025
- ↑ Ylivinkka I, Hu Y, Chen P, Rantanen V, Hautaniemi S, Nyman TA, Keski-Oja J, Hyytiainen M. Netrin-1-induced activation of Notch signaling mediates glioblastoma cell invasion. J Cell Sci. 2013 Jun 1;126(Pt 11):2459-69. doi: 10.1242/jcs.120022. Epub 2013 Apr, 2. PMID:23549787 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.120022
- ↑ Layne K, Ferro A, Passacquale G. Netrin-1 as a novel therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease: to activate or inhibit? Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Sep 1;107(4):410-9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv201. Epub 2015 Jul, 24. PMID:26209250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvv201