Kelch-like protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
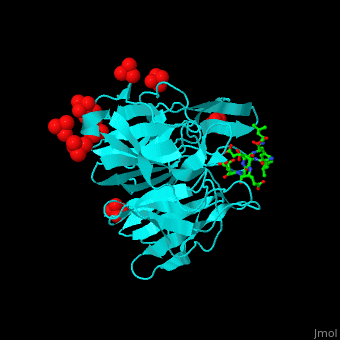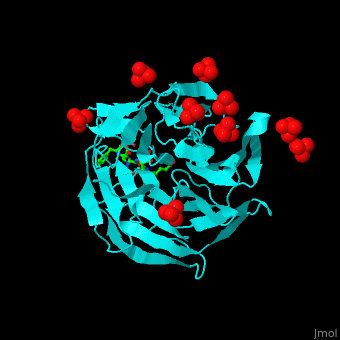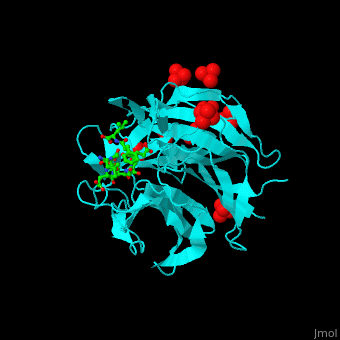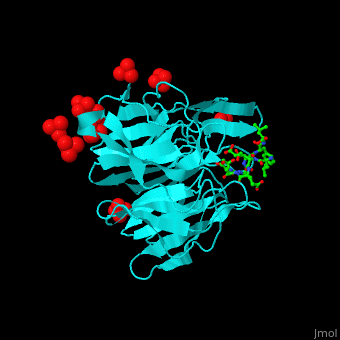
'''Kelch-like proteins''' (KLHL) contain multiple Kelch motifs. This motif is about 50 residues long and forms a four-stranded β-sheet blade. <scene name='70/706701/Cv/6'>Six to eight such blades form a circular β-propeller domain</scene>. β-propellers are involved in protein-protein interactions. The N-terminal of KLHL contains other protein domains like BTB (Broad-Tramtrack-Bric-a-brac) which is also involved in protein-protein interactions<ref>PMID:23676014</ref>.<br /> | '''Kelch-like proteins''' (KLHL) contain multiple Kelch motifs. This motif is about 50 residues long and forms a four-stranded β-sheet blade. <scene name='70/706701/Cv/6'>Six to eight such blades form a circular β-propeller domain</scene>. β-propellers are involved in protein-protein interactions. The N-terminal of KLHL contains other protein domains like BTB (Broad-Tramtrack-Bric-a-brac) which is also involved in protein-protein interactions<ref>PMID:23676014</ref>.<br /> | ||
| - | *'''KLHL1''' may play a role in organizing the actin cytoskeleton in brain cells.<br /> | ||
*'''KLHL2''' '''KLHL11''' is a component of the cullin-RING based E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase system.<br /> | *'''KLHL2''' '''KLHL11''' is a component of the cullin-RING based E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase system.<br /> | ||
*'''KLHL3''' and '''KLHL7''' '''KLHL10''' are substrate-specific adapters of the cullin-RING based E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase system.<br /> | *'''KLHL3''' and '''KLHL7''' '''KLHL10''' are substrate-specific adapters of the cullin-RING based E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase system.<br /> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | |||
| - | == 3D Structures of Kelch-like protein == | ||
| - | |||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2xn4]] – hKLHL2 Kelch domain - human <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 3 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[4chb]], [[4ch9]], [[5nkp]] – hKLHL3 Kelch domain + serine/threonine protein kinas WNK4 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4hxi]] – hKLHL3 BTB-BACK domain (mutant) + cullin-3 N terminal <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 4 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2eqx]] – hKLHL4 BACK domain - NMR <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 5 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[4asc]] – hKLHL5 Kelch domain <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 7 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3ii7]] – hKLHL7 Kelch domain <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 10 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2woz]] – KLHL10 Kelch domain - rat <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 11 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3i3n]] – hKLHL11 BTB-BACK domain <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ap2]], [[4apf]] – hKLHL11 BTB-BACK domain + cullin-3 N terminal <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 12 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2vpj]] – hKLHL12 Kelch domain <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 16 (gigaxonin) | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3hve]] – hKLHL16 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2ppi]] – hKLHL16 BTB domain <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 17 (actinfilin) | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[6hrl]] – hKLHL17 <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 19 (kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; Keap1)); domains: BTB 48-140; kelch 320-812 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1u6d]], [[1zgk]], [[4ifj]], [[6rog]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3zgd]], [[5wfl]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4cxi]], [[4cxj]] – hKeap1 BTB domain (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1x2j]] – mKeap1 Kelch domain <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Keap1 complex with peptide | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[4ifl]], [[2flu]], [[3zgc]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain + NRF2 Neh2 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5wfv]], [[5wg1]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain (mutant) + NRF2 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6fmp]], [[6fmq]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain + peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5f72]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain + antibody <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5x54]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain + tetrapeptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5nlb]] – hKLHL1 BTB+ 3-BOX domains + CUL-3 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4xmb]] – hKLHL1 Kelch domain + NRF2 activator <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5cgj]] – mKLHL1 Kelch domain + NRF2 activator - mouse <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1x2r]] – mKeap1 Kelch domain + NRF2 Neh2 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2z32]] – mKeap1 Kelch domain + prothymosin a peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3ade]], [[3wdz]] – mKeap1 Kelch domain + sequestosome-1 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2dyh]] – mKeap1 Kelch domain + NRF2 residues 22-36 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3wn7]] – mKeap1 Kelch domain + NRF2 residues 17-51 <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Keap1 complex with small molecule | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3vng]], [[3vnh]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain + oxadiazole derivative <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4ifn]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain + quinoline derivative <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4l7b]], [[4l7c]], [[4l7d]] [[4n1b]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain (mutant) + quinoline derivative <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4in4]], [[4zy3]], [[5fnq]], [[5fnr]], [[5fns]], [[5fnt]], [[5fnu]], [[5fzj]], [[5fzn]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4iqk]], [[4n1b]], [[5wiy]], [[5whl]], [[5who]] – hKeap1 Kelch domain (mutant) + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4cxt]] – hKeap1 BTB domain (mutant) + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5dad]], [[5daf]] – hKeap1 BTB domain + activator <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5git]] – hKeap1 BTB domain + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6qmc]], [[6qmd]], [[6qme]], [[6qmj]], [[6qmk]] – mKeap1 Kelch domain + inhibitor <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Kelch-like protein 20 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5yq4]] – hKLHL20 kelch domain <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6gy5]] – hKLHL20 kelch domain + DAPK1 peptide <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Dhanoa BS, Cogliati T, Satish AG, Bruford EA, Friedman JS. Update on the Kelch-like (KLHL) gene family. Hum Genomics. 2013 May 15;7:13. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-7-13. PMID:23676014 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1479-7364-7-13
- ↑ Padmanabhan B, Tong KI, Ohta T, Nakamura Y, Scharlock M, Ohtsuji M, Kang MI, Kobayashi A, Yokoyama S, Yamamoto M. Structural basis for defects of Keap1 activity provoked by its point mutations in lung cancer. Mol Cell. 2006 Mar 3;21(5):689-700. PMID:16507366 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.013