12-oxophytodienoate reductase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
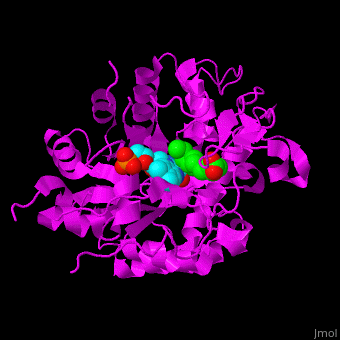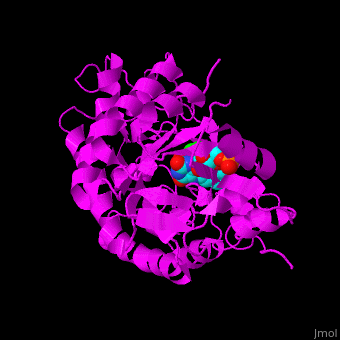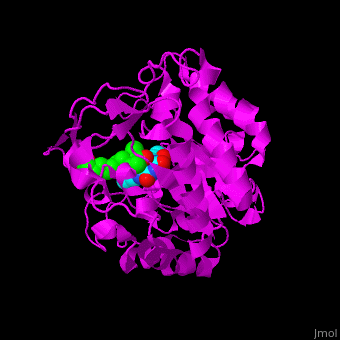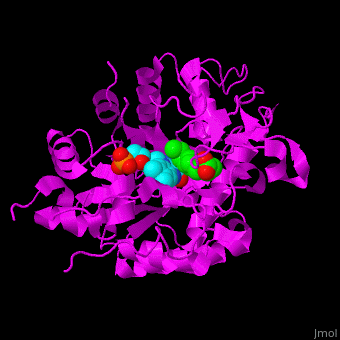
<StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' caption='Tomato OPR1 complex with FMN (cyan) and 12-oxophytodienoate (green), (PDB code [[1icq]])' scene='71/710043/Cv/18'> | <StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' caption='Tomato OPR1 complex with FMN (cyan) and 12-oxophytodienoate (green), (PDB code [[1icq]])' scene='71/710043/Cv/18'> | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
| + | '''12-Oxophytodienoate reductase''' (OPR) is an enzyme that plays a key role in the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid (JA), a plant hormone involved in various physiological processes, including defense responses, growth regulation, and development. OPR catalyzes the reduction of 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (OPDA) to produce the biologically active JA. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 5: | Line 8: | ||
'''12-oxophytodienoate reductase''' (OPR) catalyzes the conversion of <scene name='71/710043/Cv/11'>12-oxophytodienoate</scene> <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">(green)</span> to 3-oxo-pentenyl-cyclopentane octanoate. The expression of OPR is induced by stimuli like touch, wind, wounding, UV light and detergent. OPR uses the cofactor <scene name='71/710043/Cv/12'>flavin mononucleotide (FMN)</scene> <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">(cyan)</span> which is reduced by NADPH. | '''12-oxophytodienoate reductase''' (OPR) catalyzes the conversion of <scene name='71/710043/Cv/11'>12-oxophytodienoate</scene> <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">(green)</span> to 3-oxo-pentenyl-cyclopentane octanoate. The expression of OPR is induced by stimuli like touch, wind, wounding, UV light and detergent. OPR uses the cofactor <scene name='71/710043/Cv/12'>flavin mononucleotide (FMN)</scene> <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">(cyan)</span> which is reduced by NADPH. | ||
*<scene name='71/710043/Cv/16'>12-oxophytodienoate binding site</scene>. | *<scene name='71/710043/Cv/16'>12-oxophytodienoate binding site</scene>. | ||
| - | *<scene name='71/710043/Cv/17'>FMN binding site</scene>. Water molecules are | + | *<scene name='71/710043/Cv/17'>FMN binding site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
*<scene name='71/710043/Cv/15'>Click here to see whole active site</scene>. | *<scene name='71/710043/Cv/15'>Click here to see whole active site</scene>. | ||
OPR exhibits self inhibition by dimerization.<ref>PMID:11377202</ref> Three isozymes of OPR are known – OPR1, OPR2, OPR3.<br /> | OPR exhibits self inhibition by dimerization.<ref>PMID:11377202</ref> Three isozymes of OPR are known – OPR1, OPR2, OPR3.<br /> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 19: | ||
== 3D Structures of 12-oxophytodienoate reductase == | == 3D Structures of 12-oxophytodienoate reductase == | ||
| - | + | [[12-oxophytodienoate reductase 3D structures]] | |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Breithaupt C, Strassner J, Breitinger U, Huber R, Macheroux P, Schaller A, Clausen T. X-ray structure of 12-oxophytodienoate reductase 1 provides structural insight into substrate binding and specificity within the family of OYE. Structure. 2001 May 9;9(5):419-29. PMID:11377202