Penicillin-binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='47/478544/Cv/1' caption='E. coli PBP 4 complex with the antibiotic ampicillin and glycerol [[2ex6]]'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='47/478544/Cv/1' caption='E. coli PBP 4 complex with the antibiotic ampicillin and glycerol [[2ex6]]'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| + | '''Penicillin-binding protein''' (PBPs) are a group of proteins that are characterized by their affinity for and binding of penicillin. They are a normal constituent of many bacteria; the name just reflects the way by which the protein was discovered. All β-lactam antibiotics (except for tabtoxinine-β-lactam, which inhibits glutamine synthetase) bind to PBPs, which are essential for bacterial cell wall synthesis. PBPs are members of a subgroup of enzymes called transpeptidases. Specifically, PBPs are DD-transpeptidases. See also [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Penicillin-binding_proteins Penicillin-binding proteins]. | ||
| - | '''Penicillin-binding protein''' or '''peptidoglycan d,d-transpeptidase''' (PBP) is a bacterial protein which binds antibiotics. There are several PBPs in each organism. PBPs are involved in the synthesis of bacterial cell wall<ref>PMID:1103132</ref>. The PBP are classified to high-molecular weight and low-molecular weight groups. | + | '''Penicillin-binding protein''' or '''peptidoglycan d,d-transpeptidase''' or '''D-alanyl-D-alanine carboxypeptidase''' (PBP) is a bacterial protein which binds antibiotics. There are several PBPs in each organism. PBPs are involved in the synthesis of bacterial cell wall<ref>PMID:1103132</ref>. The PBP are classified to high-molecular weight and low-molecular weight groups. '''PBP 3''' is also named '''FtsI'''. |
| + | |||
| + | See also: | ||
| + | *[[DD-transpeptidase (Hebrew)]]. | ||
| + | *[[Sandbox 126|Penicillin-binding proteins and antibiotics]] | ||
| + | For ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' PBP complex with penicillin see [[Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Transpeptidase Domain]]. | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
PBP inhibition by antibiotics leads to irregularities in the cell wall and eventual bacterial death<ref>PMID:11369864</ref>. | PBP inhibition by antibiotics leads to irregularities in the cell wall and eventual bacterial death<ref>PMID:11369864</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[How B-lactam drugs work]]. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
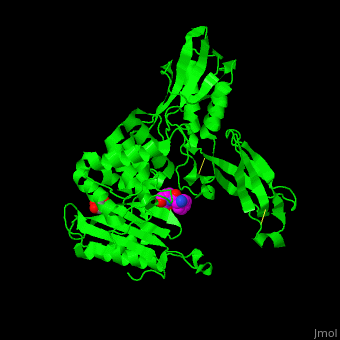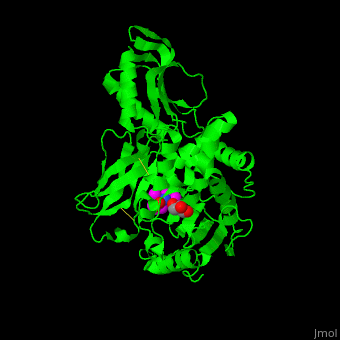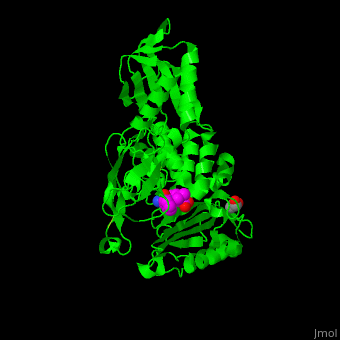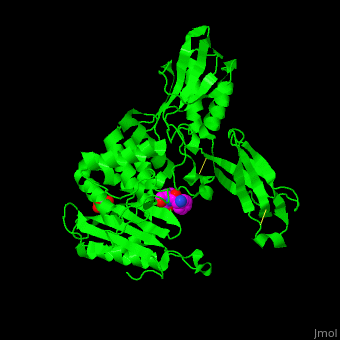
''E. coli'' PBP structure shows a distinct <scene name='47/478544/Cv/5'>3 domain structures</scene>. The <scene name='47/478544/Cv/6'>active site</scene> contains the <scene name='47/478544/Cv/7'>covalently bond between Ser62 and antibiotic ampicillin</scene><ref>PMID:16411754</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ''E. coli'' PBP structure shows a distinct <scene name='47/478544/Cv/5'>3 domain structures</scene>. The <scene name='47/478544/Cv/6'>active site</scene> contains the <scene name='47/478544/Cv/7'>covalently bond between Ser62 and antibiotic ampicillin</scene><ref>PMID:16411754</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| - | + | ||
==3D structures of penicillin-binding protein== | ==3D structures of penicillin-binding protein== | ||
| + | [[Penicillin-binding protein 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Spratt BG. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999-3003. PMID:1103132
- ↑ Beadle BM, Nicholas RA, Shoichet BK. Interaction energies between beta-lactam antibiotics and E. coli penicillin-binding protein 5 by reversible thermal denaturation. Protein Sci. 2001 Jun;10(6):1254-9. PMID:11369864 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1110/ps.52001
- ↑ Kishida H, Unzai S, Roper DI, Lloyd A, Park SY, Tame JR. Crystal structure of penicillin binding protein 4 (dacB) from Escherichia coli, both in the native form and covalently linked to various antibiotics. Biochemistry. 2006 Jan 24;45(3):783-92. PMID:16411754 doi:10.1021/bi051533t