Phospholipase A2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (6 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
*'''Pro-phosphlipase (PPLA2)''' is a pancreatic PLA2 whose 7-mer N-terminal peptide is cleaved off to produce the active PLA2.<br /> | *'''Pro-phosphlipase (PPLA2)''' is a pancreatic PLA2 whose 7-mer N-terminal peptide is cleaved off to produce the active PLA2.<br /> | ||
*For details on Lys49 snake-venom PLA2 see [[Anum-II]].<br /> | *For details on Lys49 snake-venom PLA2 see [[Anum-II]].<br /> | ||
| - | *For PLA2 inhibitor see [[Atropine]]<br /> | ||
*See also [[Phospholipase (Hebrew)]]. | *See also [[Phospholipase (Hebrew)]]. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
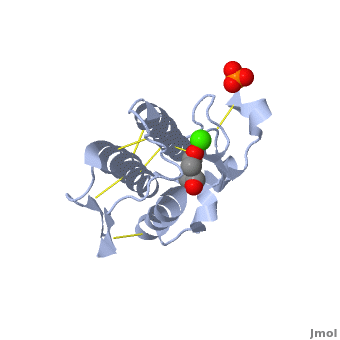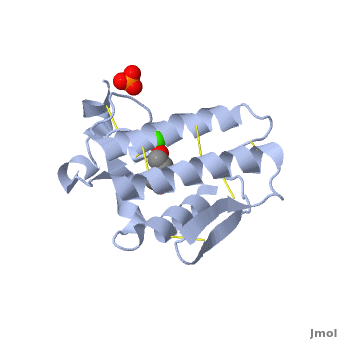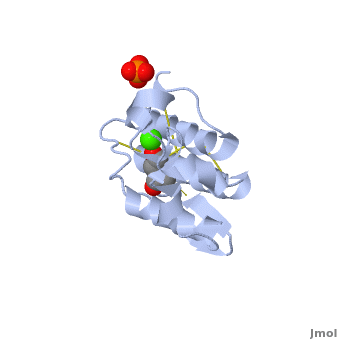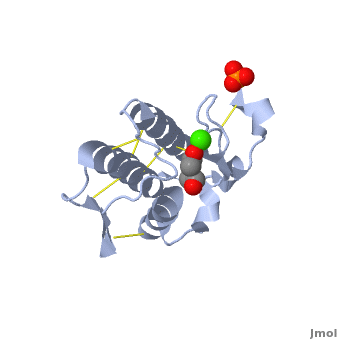
shows three mail helices in phospholipase A2. | shows three mail helices in phospholipase A2. | ||
The <scene name='Diclofenac_binding_to_Phospholipase_A2/Active_site/2'>active site residues</scene> are His 48, Asp 49, Tyr 52 and Glu 99 in the structure. | The <scene name='Diclofenac_binding_to_Phospholipase_A2/Active_site/2'>active site residues</scene> are His 48, Asp 49, Tyr 52 and Glu 99 in the structure. | ||
| - | Diclofenac makes several <scene name='Diclofenac_binding_to_Phospholipase_A2/Hydro/1'>Hydrophobic interactions</scene> with the substrate binding site of enzyme. ligand binding is shown in <scene name='Diclofenac_binding_to_Phospholipase_A2/Space_filling/1'>space filling</scene> model of the complex. | + | Diclofenac makes several <scene name='Diclofenac_binding_to_Phospholipase_A2/Hydro/1'>Hydrophobic interactions</scene> with the substrate binding site of enzyme. ligand binding is shown in <scene name='Diclofenac_binding_to_Phospholipase_A2/Space_filling/1'>space filling</scene> model of the complex. See also [[Diclofenac]]. |
== Crystal structure of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A<sub>2</sub> in complex with 2-methoxycyclohexa-2-5-diene-1,4-dione == | == Crystal structure of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A<sub>2</sub> in complex with 2-methoxycyclohexa-2-5-diene-1,4-dione == | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
<scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/4'>Curcumin</scene> possesses anti-inflammatory activity. The binding of curcumin with PLA<sub>2</sub> was studied using X-ray crystallography. Since the electron density found in the active site did not match with curcumin, <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/5'>2-methoxycyclohexa-2-5-diene-1,4-dione (MCW)</scene> (the photo-degraded product of curcumin) <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/6'>was fitted</scene> in the unexplained electron density. To understand the <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/9'>binding mode of actual curcumin</scene>, molecular docking studies was carried out. <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/10'>Both crystallographic and docked structures were superimposed</scene> with respect to the ligand position and identified that <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/13'>curcumin is binding in the hydrophobic cavity</scene> of PLA<sub>2</sub> with a binding energy -16.81 Kcal/mol. The binding mode is in such a manner that it can prevent the entry of substrate to the hydrophobic active site. These studies indicate that curcumin can be act as an inhibitor to PLA<sub>2</sub>. | <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/4'>Curcumin</scene> possesses anti-inflammatory activity. The binding of curcumin with PLA<sub>2</sub> was studied using X-ray crystallography. Since the electron density found in the active site did not match with curcumin, <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/5'>2-methoxycyclohexa-2-5-diene-1,4-dione (MCW)</scene> (the photo-degraded product of curcumin) <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/6'>was fitted</scene> in the unexplained electron density. To understand the <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/9'>binding mode of actual curcumin</scene>, molecular docking studies was carried out. <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/10'>Both crystallographic and docked structures were superimposed</scene> with respect to the ligand position and identified that <scene name='Journal:FLS:1/Cv/13'>curcumin is binding in the hydrophobic cavity</scene> of PLA<sub>2</sub> with a binding energy -16.81 Kcal/mol. The binding mode is in such a manner that it can prevent the entry of substrate to the hydrophobic active site. These studies indicate that curcumin can be act as an inhibitor to PLA<sub>2</sub>. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | == | + | == '''Interaction of Atropine with Phospholipase A2''' == |
| - | + | <scene name='42/420811/Cv/1'>Atropine in complex with phospholipase A2</scene> ([[1th6]]). | |
| - | + | ||
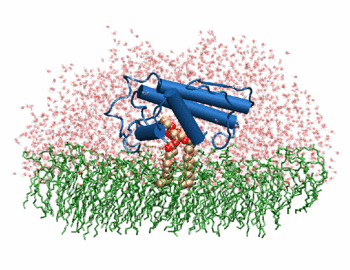
| - | + | [[Image:Phospholipase A2.gif|thumb|left|350px|Phospholipase 2A in complex with cell membrane]] | |
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | In addition to its ability to form complexes with acetylcholine receptors, atropine can also complex with phospholipase A2. Phospholipase A2 is a category of heat-stable enzymes which are involved in cell signaling processes, such as the inflammatory response. <ref>Kumar, Jainendra; Bala, Priti; Vihwal, Preeti. ''Analysis of Interaction of atropine with phospholipase A2 (1th6.pdb)''. Department of Botany and Biotechnlogy, College of Commerce, Patna, India.</ref>. Phospholipase 2A is an upstream regulator of inflammatory processes, and more specifically, it recognizes the sn-2 acyl bond of phospholipids and catalytically hydrolyzes the bond, releasing lysophospholipids <ref> Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2 </ref>. | ||
| - | + | This protein is found in mammals, reptile venom, and bacteria. In humans, the overproduction of phospholipase A2 leads to neurologic disorders such as schizophrenia and possibly autism <ref> Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2 </ref>. An inhibitor of Phospholipase A2, such as Atropine, could be used to treat disorders associated with neural trauma, since Phospholipase A2 increases inflammation which could be potentially complicate neural trauma cases <ref> Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2 </ref>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | The image to the above shows the membrane-bound phospholipase A2 in blue <ref> pla2. http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/smd_imd/pla2/pla2.gif </ref>. | |
| - | + | === '''Atropine in the Active Site of Phospholipase A2''' === | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Atropine is an inhibitor of phospholipase 2A, and can be seen in complex with this enzyme on the left. The <scene name='Sandbox_53/Atropine_structure/1'>structure of atropine</scene> can be seen more clearly in gray using the ball-and stick representation of the drug and protein. It can also be seen in green in this <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_composition/1'>space-filling model</scene>, where protein appears in brown, ligands appear in green, and solvents appear in blue. Finally, the | |
| + | <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_rainbow/1'>N to C terminal</scene> portions of the protein can be highlighted from blue to red in a rainbow, and the active site with atropine can be seen in the middle of the protein. | ||
| - | + | Atropine interacts with phospholipase 2A at residues asp29 and tyr49 on the protein. The | |
| - | + | <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_residues/1'>residues</scene> of atropine interacting with phospholipase 2A can be seen on the right. The amino acid residues in the active site are labeled. As seen in the acetylcholine receptor, the <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase_hyrophobic/1'>hydrophobic</scene> regions of the phospholipase 2A enzyme are found in the active site, which is where the atropine binds and inhibits the enzyme. The hydrophobic regions, represented in gray, can be seen surrounding atropine, which is positioned in the active site and capped by red oxygen atoms. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Removing the labels, atropine can be seen making contact with the atoms emphasized by the space filling model, interacting with the <scene name='Sandbox_53/Phospholipase2a_interactions/1'>active site</scene> of phospholipase 2A through white as-tricks. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | == 3D Structures of Phospholipase A2 == | |
| + | [[Phospholipase A2 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[1hn4]] – pPPLA2+MJ33<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4bp2]] – bPPLA2 | ||
| - | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Dennis EA. Diversity of group types, regulation, and function of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13057-60. PMID:8175726
- ↑ Leitinger N, Watson AD, Hama SY, Ivandic B, Qiao JH, Huber J, Faull KF, Grass DS, Navab M, Fogelman AM, de Beer FC, Lusis AJ, Berliner JA. Role of group II secretory phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis: 2. Potential involvement of biologically active oxidized phospholipids. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999 May;19(5):1291-8. PMID:10323782
- ↑ Lapointe S, Brkovic A, Cloutier I, Tanguay JF, Arm JP, Sirois MG. Group V secreted phospholipase A2 contributes to LPS-induced leukocyte recruitment. J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;224(1):127-34. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22106. PMID:20232296 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22106
- ↑ Hallstrand TS, Lai Y, Hooper KA, Oslund RC, Altemeier WA, Matute-Bello G, Gelb MH. Endogenous secreted phospholipase A2 group X regulates cysteinyl leukotrienes synthesis by human eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Jan;137(1):268-77.e8. doi:, 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.05.026. Epub 2015 Jun 30. PMID:26139511 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.05.026
- ↑ Platt RW, Brookhart MA, Cole SR, Westreich D, Schisterman EF. Reply to taguri and matsuyama. Stat Med. 2013 Sep 10;32(20):3592-3. doi: 10.1002/sim.5805. PMID:23943550 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.5805
- ↑ Duncan RE, Sarkadi-Nagy E, Jaworski K, Ahmadian M, Sul HS. Identification and functional characterization of adipose-specific phospholipase A2 (AdPLA). J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 12;283(37):25428-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804146200. Epub 2008, Jul 9. PMID:18614531 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804146200
- ↑ Tjoelker LW, Wilder C, Eberhardt C, Stafforini DM, Dietsch G, Schimpf B, Hooper S, Le Trong H, Cousens LS, Zimmerman GA, Yamada Y, McIntyre TM, Prescott SM, Gray PW. Anti-inflammatory properties of a platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Nature. 1995 Apr 6;374(6522):549-53. PMID:7700381 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/374549a0
- ↑ Quach ND, Arnold RD, Cummings BS. Secretory phospholipase A2 enzymes as pharmacological targets for treatment of disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Aug 15;90(4):338-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.05.022. Epub, 2014 Jun 4. PMID:24907600 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2014.05.022
- ↑ Tellis CC, Tselepis AD. The role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis may depend on its lipoprotein carrier in plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 May;1791(5):327-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.02.015. PMID:19272461 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.02.015
- ↑ Singh N, Jabeen T, Sharma S, Somvanshi RK, Dey S, Srinivasan A, Singh TP. Specific binding of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to phospholipase A2: structure of the complex formed between phospholipase A2 and diclofenac at 2.7 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006 Apr;62(Pt 4):410-6. Epub 2006, Mar 18. PMID:16552142 doi:10.1107/S0907444906003660
- ↑ Crystal structure of porcine pancreatic phospholipase a2 in complex with 2-methoxycyclohexa-2-5-diene-1,4-dione. Dileep KV, Tintu I, Mandal PK, Karthe P, Haridas M, Sadasivan C. Frontiers In Life Sci. (2012) doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/21553769.2012.689262
- ↑ Kumar, Jainendra; Bala, Priti; Vihwal, Preeti. Analysis of Interaction of atropine with phospholipase A2 (1th6.pdb). Department of Botany and Biotechnlogy, College of Commerce, Patna, India.
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ Phospholipase A2. http://www.worldlingo.com/ma/enwiki/en/Phospholipase_A2
- ↑ pla2.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky