Erythropoietin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | '''Erythropoietin''' (EPO) is a hormone produced in the kidneys that stimulates the formation of red blood cells. EPO is a glycoprotein that is stimulated when the levels of O2 are abnormally low. This event signals more red blood cells to made from the erythrocytes. Abnormal levels of erythropoietin can be associated with bone marrow disorders, kidney disease, or a synthesized recombinant form that has been injected into the blood stream. Synthesized recombinant EPO has made many headlines in the past few years, due to its use to by Tour de France athletes. They used EPO to illegally dope their blood and increase the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by the body at the time of administration thus increasing endurance. They used EPO because there was no test at the time that could differentiate between naturally produced EPO and the form that was injected. | + | '''Erythropoietin''' (EPO) is a [[Hormones|hormone]] produced in the kidneys that stimulates the formation of red blood cells. EPO is a glycoprotein that is stimulated when the levels of O2 are abnormally low. This event signals more red blood cells to made from the erythrocytes. Abnormal levels of erythropoietin can be associated with bone marrow disorders, kidney disease, or a synthesized recombinant form that has been injected into the blood stream. Synthesized recombinant EPO has made many headlines in the past few years, due to its use to by Tour de France athletes. They used EPO to illegally dope their blood and increase the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by the body at the time of administration thus increasing endurance. They used EPO because there was no test at the time that could differentiate between naturally produced EPO and the form that was injected. |
==History== | ==History== | ||
Current revision
Erythropoietin Structure, Function, and History
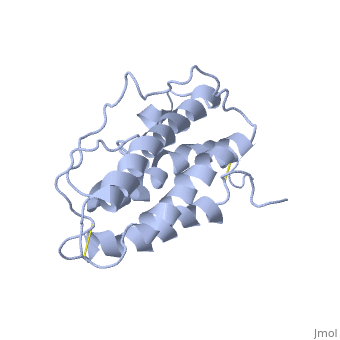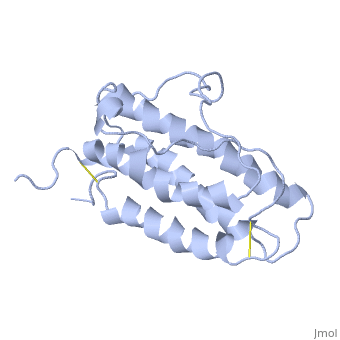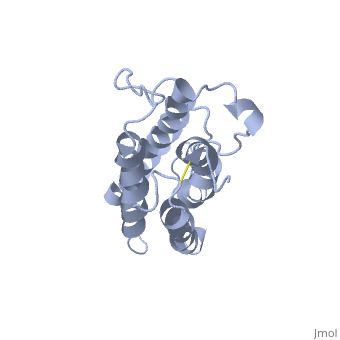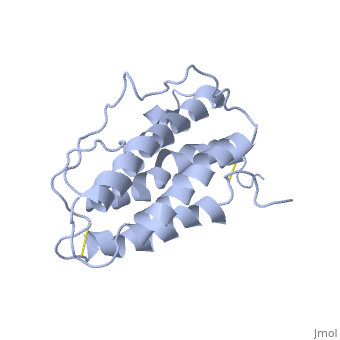
| |||||||||||
3D structures of erythropoietin
Updated on 11-December-2019
1cn4 – hEP (mutant) + EP receptor – human
1buy – hEP (mutant) - NMR
1eer – hEP (mutant) + EP receptor (mutant)
References
- ↑ Kawakita M, Ogawa M, Goldwasser E, Miyake T. Characterization of human megakaryocyte colony-stimulating factor in the urinary extracts from patients with aplastic anemia and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):556-60. PMID:6600633
- ↑ Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin after a century of research: younger than ever. Eur J Haematol. 2007 Mar;78(3):183-205. Epub 2007 Jan 23. PMID:17253966 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2007.00818.x
- ↑ Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin after a century of research: younger than ever. Eur J Haematol. 2007 Mar;78(3):183-205. Epub 2007 Jan 23. PMID:17253966 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2007.00818.x
- ↑ Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin: structure, control of production, and function. Physiol Rev. 1992 Apr;72(2):449-89. PMID:1557429
- ↑ Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin after a century of research: younger than ever. Eur J Haematol. 2007 Mar;78(3):183-205. Epub 2007 Jan 23. PMID:17253966 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2007.00818.x
- ↑ Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164.
- ↑ Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164.
- ↑ Erslev, A. J., and J. Caro. "Physiologic and molecular biology of erythropoietin." Medical oncology and tumor pharmacotherapy 3.3-4 (1986): 159-164.
- ↑ Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin after a century of research: younger than ever. Eur J Haematol. 2007 Mar;78(3):183-205. Epub 2007 Jan 23. PMID:17253966 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2007.00818.x
- ↑ Constantinescu, Stefan N., Saghi Ghaffar, Harvey F. Lodish. The Erythropoietin Receptor: Structure, Activation and Intracellular Signal Transduction. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, Volume10, Issue 1, 1January 1999, Pages 18-23.
- ↑ Constantinescu, Stefan N., Saghi Ghaffar, Harvey F. Lodish. The Erythropoietin Receptor: Structure, Activation and Intracellular Signal Transduction. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, Volume10, Issue 1, 1January 1999, Pages 18-23.
- ↑ Constantinescu, Stefan N., Saghi Ghaffar, Harvey F. Lodish. The Erythropoietin Receptor: Structure, Activation and Intracellular Signal Transduction. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, Volume10, Issue 1, 1January 1999, Pages 18-23.
- ↑ Syed RS, Reid SW, Li C, Cheetham JC, Aoki KH, Liu B, Zhan H, Osslund TD, Chirino AJ, Zhang J, Finer-Moore J, Elliott S, Sitney K, Katz BA, Matthews DJ, Wendoloski JJ, Egrie J, Stroud RM. Efficiency of signalling through cytokine receptors depends critically on receptor orientation. Nature. 1998 Oct 1;395(6701):511-6. PMID:9774108 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/26773
- ↑ Constantinescu, Stefan N., Saghi Ghaffar, Harvey F. Lodish. The Erythropoietin Receptor: Structure, Activation and Intracellular Signal Transduction. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, Volume10, Issue 1, 1January 1999, Pages 18-23.