Sandbox Reserved 1568
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
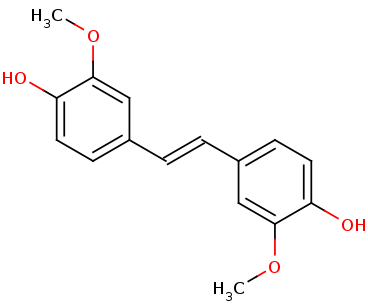
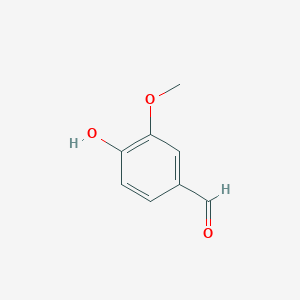
LSDs are in the functional protein family called carotenoid cleavage oxygenases (CCOs). They are characterized by their cleavage of the double bond found in carotenoids. The binding site has ferrous iron supported by histidines and is kept in close proximity to the scissile double bond. There are two suggested mechanisms for LSD cleavage. McAndrew ''et al.'' suggested the hydroxystilbenoid is activated by enzyme-catalyzed deprotonation of the 4-hydroxy group. This causes electron delocalization toward the ferrous iron (-superoxo electrophile). The second proposed mechanism suggested by Sui ''et al.'' says that the pi bond electron density from the scissile double bond is redistributed to the iron-oxy complex to form an iron peroxo-substrate cation intermediate. In either case, deprotonation of the hydoxyl group is critical and assisted by the catalytic triad.<ref>PMID 31292192</ref> | LSDs are in the functional protein family called carotenoid cleavage oxygenases (CCOs). They are characterized by their cleavage of the double bond found in carotenoids. The binding site has ferrous iron supported by histidines and is kept in close proximity to the scissile double bond. There are two suggested mechanisms for LSD cleavage. McAndrew ''et al.'' suggested the hydroxystilbenoid is activated by enzyme-catalyzed deprotonation of the 4-hydroxy group. This causes electron delocalization toward the ferrous iron (-superoxo electrophile). The second proposed mechanism suggested by Sui ''et al.'' says that the pi bond electron density from the scissile double bond is redistributed to the iron-oxy complex to form an iron peroxo-substrate cation intermediate. In either case, deprotonation of the hydoxyl group is critical and assisted by the catalytic triad.<ref>PMID 31292192</ref> | ||
| - | + | The enzyme serves to lower the activation energy and assist in the cleavage and transformation of the lignostilbene to two vanillins. | |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== '''References''' == | == '''References''' == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Aug 26 through Dec 12, 2019 for use in the course CHEM 351 Biochemistry taught by Bonnie_Hall at the Grand View University, Des Moines, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1556 through Sandbox Reserved 1575. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Lignostilbene-α,ß-dioxygenase A structural features and important functional residues
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Kuatsjah E, Verstraete MM, Kobylarz MJ, Liu AKN, Murphy MEP, Eltis LD. Identification of functionally important residues and structural features in a bacterial lignostilbene dioxygenase. J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 10. pii: RA119.009428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428. PMID:31292192 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428
- ↑ Kuatsjah E, Verstraete MM, Kobylarz MJ, Liu AKN, Murphy MEP, Eltis LD. Identification of functionally important residues and structural features in a bacterial lignostilbene dioxygenase. J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 10. pii: RA119.009428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428. PMID:31292192 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428
- ↑ Kuatsjah E, Verstraete MM, Kobylarz MJ, Liu AKN, Murphy MEP, Eltis LD. Identification of functionally important residues and structural features in a bacterial lignostilbene dioxygenase. J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 10. pii: RA119.009428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428. PMID:31292192 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428
- ↑ Kuatsjah E, Verstraete MM, Kobylarz MJ, Liu AKN, Murphy MEP, Eltis LD. Identification of functionally important residues and structural features in a bacterial lignostilbene dioxygenase. J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 10. pii: RA119.009428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428. PMID:31292192 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.009428