This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Siderocalin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
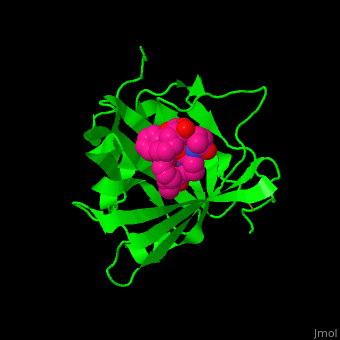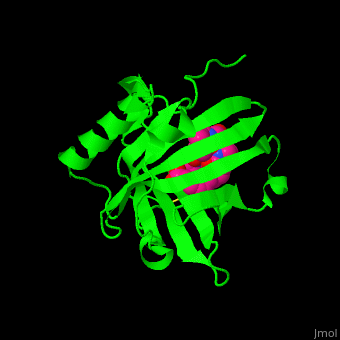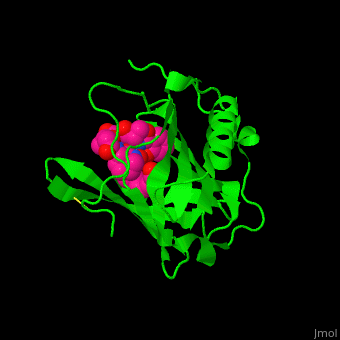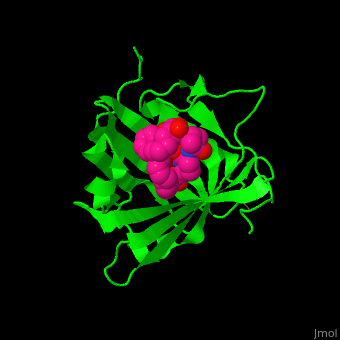
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human siderocalin complex with the siderophore carboxymycobactin (PDB code [[1x89]])' scene='48/488406/Cv/1' > | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human siderocalin complex with the siderophore carboxymycobactin (PDB code [[1x89]])' scene='48/488406/Cv/1' > | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Siderocalin''' (Scn) or '''neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin''' binds ferric siderophores in order to intercept delivery of iron to bacteria which require it thus impeding their virulence<ref>PMID:19053425</ref>. | '''Siderocalin''' (Scn) or '''neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin''' binds ferric siderophores in order to intercept delivery of iron to bacteria which require it thus impeding their virulence<ref>PMID:19053425</ref>. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
Scn-NGAL interacts with the <scene name='48/488406/Cv/4'>siderophore carboxymycobactin where the latter is centered in the protein calyx</scene> making <scene name='48/488406/Cv/5'>multiple interactions including cation-π bonds involving several lysines and arginine</scene><ref>PMID:15642259</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='48/488406/Cv/6'>Fe coordination site</scene>. | Scn-NGAL interacts with the <scene name='48/488406/Cv/4'>siderophore carboxymycobactin where the latter is centered in the protein calyx</scene> making <scene name='48/488406/Cv/5'>multiple interactions including cation-π bonds involving several lysines and arginine</scene><ref>PMID:15642259</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. <scene name='48/488406/Cv/6'>Fe coordination site</scene>. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of siderocalin== | ==3D structures of siderocalin== | ||
| + | [[Siderocalin 3D structures]] | ||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | *Siderocalin or lipocalin-2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5jr8]], [[3bx8]], [[5khp]], [[5kid]], [[5kic]], [[5mhh]], [[6gqz]], [[1qqs]] – hScn NGAL - human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1l6m]], [[3dtq]], [[4iaw]], [[4iax]], [[6qmu]] – hScn NGAL (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3s26]] – mScn NGAL - mouse<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2k23]] – Scn NGAL – rat - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2kt4]] – qScn Q83 – quail<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Siderocalin complex | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[4mvi]], [[4mvk]], [[4mvl]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + β-amyloid protein 40 peptide<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3bx7]] – hScn NGAL + CTLA-4<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3tzs]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + phenylurea<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4zfx]], [[4zhc]], [[4zhd]], [[4zhf]], [[4zhg]], [[4zhh]], [[4qae]], [[4k19]], [[4aiw]], [[4aix]], [[6o5d]], [[3u0d]], [[3k3l]], [[3dsz]], [[1x89]], [[1x8u]], [[1x71]] – hScn NGAL + siderophore<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3tf6]], [[3t1d]], [[3i0a]], [[3hwd]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + siderophore<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3pec]], [[3ped]] – hScn NGAL + siderophore + Fe<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3hwe]], [[3hwf]], [[3hwg]], [[3cmp]], [[3by0]], [[3cbc]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + siderophore + Fe<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3fw4]], [[3fw5]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + catechol + Fe<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4gh7]], [[5n48]], [[5n47]] – hScn NGAL + fibronectin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5nkn]] – hScn NGAL + conchicine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6gr0]] – hScn NGAL + petrobactin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3u9p]] – mScn NGAL + Fab <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2lbv]] – qScn Q83 + enterobactin – NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3sao]] – cScn + myristoyl lysophosphatidic acid - chicken<br /> | ||
| - | > | ||
| - | |||
| - | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Hoette TM, Abergel RJ, Xu J, Strong RK, Raymond KN. The role of electrostatics in siderophore recognition by the immunoprotein Siderocalin. J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Dec 24;130(51):17584-92. doi: 10.1021/ja8074665. PMID:19053425 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja8074665
- ↑ Paragas N, Qiu A, Hollmen M, Nickolas TL, Devarajan P, Barasch J. NGAL-Siderocalin in kidney disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1823(9):1451-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.014., Epub 2012 Jun 19. PMID:22728330 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.014
- ↑ Holmes MA, Paulsene W, Jide X, Ratledge C, Strong RK. Siderocalin (Lcn 2) also binds carboxymycobactins, potentially defending against mycobacterial infections through iron sequestration. Structure. 2005 Jan;13(1):29-41. PMID:15642259 doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.10.009