We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 20003
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==A novel coronavirus was found to be the cause of a respiratory illness first detected in Wuhan, China in 2019.== | ==A novel coronavirus was found to be the cause of a respiratory illness first detected in Wuhan, China in 2019.== | ||
| - | <SX viewer='molstar' load='' size=' | + | <SX viewer='molstar' load='' size='340' side='right' caption='xyz' scene='83/839315/Putty_occlusion/1'> |
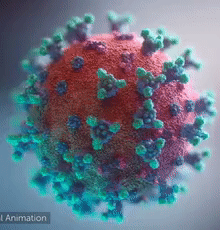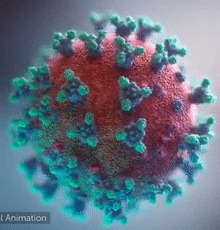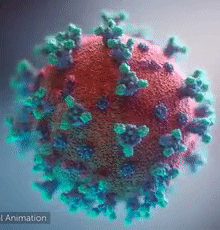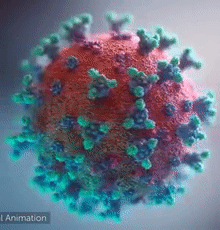
| - | [[Image:Ezgif.com-video-to-gif 240px 65pc speed.gif|left| | + | [[Image:Ezgif.com-video-to-gif 240px 65pc speed.gif|left|240px|thumb|<span style="font-size:125%">COVID-19 virus. The <span style="color:aqua">'''spikes'''</span>, that adorn the <span style="color:red">'''virus surface'''</span>, impart a '''''corona''''' like appearance [http://www.drugtargetreview.com/news/57287/3d-visualisation-of-covid-19-surface-released-for-researchers (Fusion Animation)].</span>]] |
<span style="font-size:110%"> | <span style="font-size:110%"> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | <br>'''LEFT''': Overall view of the virus, showing the spikes in <span style="color:aqua">'''turquoise'''</span>. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <br>''' | + | <br>'''RIGHT''': Cryo-EM structure of a spike, from the McLellan Lab<ref name="McLellan">PMID:32075877</ref> (PDB-ID [[6vsb]]). |
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <br>''' | + | <br>An animation shows how the virus [http://youtu.be/hwVl_-lnoys '''interacts with its host'''], via its spikes, thus permitting the viral genome to enter the human (host) cell and begin infection (by [http://elarasystems.com Elara Systems)].</span> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | < | + | <snapshot name='83/839315/1ea5_tst/1'>green link</snapshot> |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | == Potential treatments for COVID-19 == | |
| - | == Potential treatments | + | * A team of UK & Israeli scientists determined [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/results/results.do?tabtoshow=Current&qrid=C212D599 '''25 crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease in complex with a series of different inhibitors''']. All the experimental details and results are available [http://www.diamond.ac.uk/covid-19/for-scientists/Main-protease-structure-and-XChem.html '''online at the Diamond Light Source''']. |
| + | |||
| + | * An international group of scientists from academia & industry are trying to help combat COVID-19. This effort began when Chinese scientists worked rapidly to determine the structure of the novel SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), which triggered a massive crystal-based fragment screen (see text, in the point just above) at the [http://www.x-chemrx.com XChem facility] at UK’s Diamond Light Source. With the same urgency, they are now trying to progress these data towards what is desperately needed: effective, easy-to-make anti-COVID drugs. They welcome contributions of many forms including scientific expertise, experimental capabilities, and indeed donations to make this possible, go to [http://covid.postera.ai/covid '''PostEra'''] for more information. | ||
| + | |||
* A USA, French UK study '''identified 69 drugs to test against the coronavirus'''<ref> Gordon, et al. A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map Reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-Repurposing: bioRxiv (online) 2020 [http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.002386 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.002386]</ref>. As reported in the [http://www.nytimes.com/2020/03/22/science/coronavirus-drugs-chloroquine.html?action=click&module=Top%20Stories&pgtype=Homepage New York Times] (23-Mar-2020) "The researchers sought drugs that also latch onto the human proteins that the coronavirus seems to need to enter and replicate in human cells." | * A USA, French UK study '''identified 69 drugs to test against the coronavirus'''<ref> Gordon, et al. A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map Reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-Repurposing: bioRxiv (online) 2020 [http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.002386 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.002386]</ref>. As reported in the [http://www.nytimes.com/2020/03/22/science/coronavirus-drugs-chloroquine.html?action=click&module=Top%20Stories&pgtype=Homepage New York Times] (23-Mar-2020) "The researchers sought drugs that also latch onto the human proteins that the coronavirus seems to need to enter and replicate in human cells." | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Analysis by Abby Olena (20-Mar-2020) in ''The Scientist'' on [http://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/remdesivir-works-great-against-coronaviruses-in-the-lab-67298?utm_campaign=TS_OTC_2020&utm_source=hs_email&utm_medium=email&utm_content=85306117&_hsenc=p2ANqtz--t49MmUS_nL_8CL8wosEbymFBDq_4smPhI1pSJmSKWA0bURCpjoMb1eYxIVv30SDzsuiNd9PRGTPC30x-gelTGjK-9r9wPWaMjEZIqjaz5Y0tgW5w&_hsmi=85306117 '''Remdesivir Works Against Coronaviruses in the Lab'''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Analysis by Chris Baraniuk (20-Mar-2020) in ''The Scientist'' on [http://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/is-hype-over-chloroquine-as-a-potential-covid-19-therapy-justified--67301?utm_campaign=TS_OTC_2020&utm_source=hs_email&utm_medium=email&utm_content=85306117&_hsenc=p2ANqtz--t49MmUS_nL_8CL8wosEbymFBDq_4smPhI1pSJmSKWA0bURCpjoMb1eYxIVv30SDzsuiNd9PRGTPC30x-gelTGjK-9r9wPWaMjEZIqjaz5Y0tgW5w&_hsmi=85306117 '''Chloroquine for COVID-19: Cutting Through the Hype'''] | ||
* A French study<ref> Gautret, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open- label non-randomized clinical trial: Intl J Antimcrob Agents (in press) 2020 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949]</ref> showed, despite its small sample size (20 patients treated), that '''hydroxychloroquine treatment is significantly associated with viral load reduction/disappearance in COVID-19 patients''' and its effect is reinforced by azithromycin. | * A French study<ref> Gautret, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open- label non-randomized clinical trial: Intl J Antimcrob Agents (in press) 2020 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949]</ref> showed, despite its small sample size (20 patients treated), that '''hydroxychloroquine treatment is significantly associated with viral load reduction/disappearance in COVID-19 patients''' and its effect is reinforced by azithromycin. | ||
== Movies helping to explain COVID-19 == | == Movies helping to explain COVID-19 == | ||
| - | |||
<html5media height="181" width="322">https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=78jLBNSqc3g</html5media><br> | <html5media height="181" width="322">https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=78jLBNSqc3g</html5media><br> | ||
| - | '''How COVID-19 Impacts your | + | '''Coronavirus animation: How COVID-19 Impacts your body and ways to avoid infection (Mar 20 2020)'''<br> |
by [http://highimpact.com High Impact]<br> | by [http://highimpact.com High Impact]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 40: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<html5media height="181" width="322">https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I0TmBsHaGmI</html5media><br> | <html5media height="181" width="322">https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I0TmBsHaGmI</html5media><br> | ||
| - | '''COVID-19 | + | '''Background about the Coronavirus-COVID-19 and details of its 3D structure'''<br> |
by [http://www.biolution.net biolution GmBH].<br> | by [http://www.biolution.net biolution GmBH].<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<html5media height="181" width="322">https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I-Yd-_XIWJg</html5media><br> | <html5media height="181" width="322">https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I-Yd-_XIWJg</html5media><br> | ||
| - | '''Outbreak of COVID-19 (Feb 11, 2020)'''<br> | + | '''Outbreak of COVID-19 explained through 3D Medical Animation (Feb 11, 2020)'''<br> |
by [http://www.scientificanimations.com Sci Animations].<br> | by [http://www.scientificanimations.com Sci Animations].<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 53: | ||
== Useful sites on COVID-19 == | == Useful sites on COVID-19 == | ||
* [http://deepmind.com/research/open-source/computational-predictions-of-protein-structures-associated-with-COVID-19 Computational predictions of 3D protein structures associated with COVID-19] based on the [http://deepmind.com/blog/article/AlphaFold-Using-AI-for-scientific-discovery AI AlphaFold system]. Coordinates of the 3D structures can be download [http://storage.googleapis.com/deepmind-com-v3-datasets/alphafold-covid19/structures_4_3_2020.zip here as a '''zip''' file]. | * [http://deepmind.com/research/open-source/computational-predictions-of-protein-structures-associated-with-COVID-19 Computational predictions of 3D protein structures associated with COVID-19] based on the [http://deepmind.com/blog/article/AlphaFold-Using-AI-for-scientific-discovery AI AlphaFold system]. Coordinates of the 3D structures can be download [http://storage.googleapis.com/deepmind-com-v3-datasets/alphafold-covid19/structures_4_3_2020.zip here as a '''zip''' file]. | ||
| - | + | ||
* Up to date statistics on [http://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/ Coronavirus cases world-wide at worldometer] | * Up to date statistics on [http://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/ Coronavirus cases world-wide at worldometer] | ||
* A summary of key findings about [http://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/lab/index.html COVID-19] can be found at [http://www.cdc.gov/ CDC]. | * A summary of key findings about [http://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/lab/index.html COVID-19] can be found at [http://www.cdc.gov/ CDC]. | ||
| - | * | + | |
| - | < | + | * '''Coronavirus Evolved Naturally''', and ‘Is '''Not''' a Laboratory Construct,’ in a study in Nature Med by Anderson and colleagues <ref>Andersen, et al. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2: Nature Med (in press) 2020 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0820-9]]</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | * '''Scientists are endeavoring to find antivirals specific to the virus'''. Several drugs such as chloroquine, arbidol, remdesivir, and favipiravir are currently undergoing clinical studies to test their efficacy and safety in the treatment of COVID-19 in China, with some promising results summarized.<ref>PMID:32147628</ref>. | ||
* [http://crowdfightcovid19.org Crowdfight COVID-19] - A scientific crowdsourcing initiative to put all available resources at the service of the fight against COVID-19 | * [http://crowdfightcovid19.org Crowdfight COVID-19] - A scientific crowdsourcing initiative to put all available resources at the service of the fight against COVID-19 | ||
| - | + | * A computer game, developed at the [http://www.ipd.uw.edu Inst for Protein Design] (U Washington), uses crowdsourcing to try to find new lead compound that might become drugs to treat COVID-19. | |
| - | * | + | <html5media height="181" width="322" >https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gGvlNo3nMfw</html5media> |
| - | + | == 3D structural studies on Coronavirus COVID-19== | |
| + | * [http://github.com/thorn-lab/coronavirus_structural_task_force Public resource for the structures from beta-coronavirus with a focus on SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2] | ||
| - | * | + | * A team of UK & Israeli scientists determined [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/results/results.do?tabtoshow=Current&qrid=C212D599 '''25 crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease in complex with a series of different inhibitors''']. All the experimental details and results are available [http://www.diamond.ac.uk/covid-19/for-scientists/Main-protease-structure-and-XChem.html '''online at the Diamond Light Source''']. |
| - | * | + | * A team of Chinese scientists determined, by Cryo-EM, the''' coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with its receptor ACE2 PDB-ID''' [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6LZG 6LZG]. (To be published). |
| - | * | + | * A team of US and Chinese scientists determined the crystal structure of '''2019-nCoV spike receptor-binding domain bound with ACE2''' [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6M0J 6M0J] (To be published). |
| - | * A | + | * A team of US scientists determined, by Cryo-EM, the '''structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (open & closed states)''' <ref>PMID:32155444</ref>, PDB-ID [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6VXX 6VXX] & [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6VYB 6VYB] |
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain in complex with human antibody CR3022 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W41 6W41] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal Structure of the methyltransferase-stimulatory factor complex of NSP16 and NSP10 from SARS CoV-2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W61 6W61] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal Structure of ADP ribose phosphatase of NSP3 from SARS CoV-2 in complex with AMP [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W6Y 6W6Y] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Structure of NSP10 - NSP16 Complex from SARS-CoV-2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W75 6W75] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein N-terminal RNA binding domain [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6M3M 6M3M] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of Nsp9 RNA binding protein of SARS CoV-2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W4B 6W4B] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal Structure of NSP16 - NSP10 Complex from SARS-CoV-2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W4H 6W4H] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV RBD/ACE2-B0AT1 complex<ref>PMID:32132184</ref> [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6M17 6M17]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of RNA binding domain of nucleocapsid phosphoprotein from SARS coronavirus 2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6VYO 6VYO] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of NSP15 Endoribonuclease from SARS CoV-2 in the Complex with a Citrate [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W01 6W01] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of ADP ribose phosphatase of NSP3 from SARS CoV-2 in the complex with ADP ribose [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6W02 6W02] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of 2019-nCoV chimeric receptor-binding domain complexed with its receptor human ACE2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6VW1 6VW1] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of NSP15 Endoribonuclease from SARS CoV-2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6VWW 6VWW] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal Structure of ADP ribose phosphatase of NSP3 from SARS CoV-2 [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6VXS 6VXS] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of the 2019-nCoV HR2 Domain [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6LVN 6LVN] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of post fusion core of 2019-nCoV S2 subunit [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6LXT 6LXT] (To be published). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of '''SARS-CoV-2 main protease''' provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors, from the Hilgenfeld lab<ref>PMID:32198291</ref>, Apo Struture: PDB-ID [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6y2e 6Y2E], and complexes with inhibitors: PDB-ID [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6y2f 6Y2F] and [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/6y2g 6Y2G]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * 3D Structure of '''RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19''', a '''major antiviral drug target''' from the Rao lab in Beijing<ref> Gao, et al. Structure of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from 2019-nCoV, a major antiviral drug target: bioRxiv (online) 2020 [https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.16.993386 https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.16.993386]</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of the '''Mpro from COVID-19''' and '''discovery of inhibitors''' in a study by scientists from Shanghai & Beijing <ref> Jin, et al. Structure of Mpro from COVID-19 virus and discovery of its inhibitors: bioRxiv (online) 2020 [http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.26.964882 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.26.964882]</ref>, PDB-ID [[2h2z]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Crystal structure of '''Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2''' in a study by scientists from USA<ref> Kim, et al. Crystal structure of Nsp15 endoribonuclease NendoU from SARS-CoV-2: bioRxiv (online) 2020 [http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.02.968388 http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.02.968388]</ref>, PDB-ID [[6w01]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * A study by Zhou & colleagues on the structural basis for the '''recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) by full-length human ACE2''' gives insights to the molecular basis for coronavirus recognition and infection<ref>PMID:32132184</ref>. | ||
* '''The CoV spike (S) glycoprotein is a key target for vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and diagnostics'''. A study by McLellan and colleagues in "Science" on the Cryo-EM structure of the COVID-19 spike protein. This structure should greatly aid in the rapid development and evaluation of medical countermeasures to address the ongoing public health crisis<ref name="McLellan" />, PDB-ID [[6vsb]]. | * '''The CoV spike (S) glycoprotein is a key target for vaccines, therapeutic antibodies, and diagnostics'''. A study by McLellan and colleagues in "Science" on the Cryo-EM structure of the COVID-19 spike protein. This structure should greatly aid in the rapid development and evaluation of medical countermeasures to address the ongoing public health crisis<ref name="McLellan" />, PDB-ID [[6vsb]]. | ||
| - | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
</SX> | </SX> | ||
Current revision
A novel coronavirus was found to be the cause of a respiratory illness first detected in Wuhan, China in 2019.
| |||||||||