General Description
4EQV is 428 kDa invertase(SInv) isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. SInv catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose into fructose and glucose, thus making it an essential enzyme to plants and other organisms, such as honey bees[1]. Invertase also lends itself to industry and is extensively used in fermentation, where yeast are employed to process sugar into ethanol.
Yeast invertase was first isolated in 1860 by Berthelot, but had been alluded to by Dubrunfaut in 1847.[2] Invertase was posited to be an intracellular enzyme, yet de la Fuente and Sols were able to show that invertase can be excreted by the cell, thus classifying it as extracellular[3]. The intracellular form of the enzyme is non-glycosylated, while the extracellular form is extensively glycosylated[1]. The same gene codes for glycosylated and non-glycosylated forms of the enzyme they differ when being transcribed into mRNA, and the extracellular bound SInv is tagged with a signal peptide.[4]
Structure
Though it is an octamer, SInv can be best described as a tetramer of dimers[1]. The illustrates this high degree of symmetry. It should also be pointed out that the A/B and C/D dimers have been dubbed "closed" while the E/F and G/H dimers have been dubbed "open"[1]. This idea of "open" and closed" dimers is explained in more detail in the section titled Open & Closed Assembly.
Catalytic β-propeller Domain
The of 4EQV, shown in crimson, is the catalytic domain of the monomer. The domain is composed mostly of antiparallel β-strands which form five blades, each containing four antiparallel β-strands. The of the β-propeller domain is formed at the axis of the five blades. This catalytic pocket contains nucleophilic residue Asp22 at its base and is lined with multiple hydrophobic residues, namely Trp48, Phe82, Trp291, Phe296, and Phe388. The of the A/B and C/D chains are rather specific for sucrose. This specificity is due to Gln201, which binds to sucrose and Asp228 conveys an affinity for glucose moiety[5].
The catalytic process is two-step. First, there is the nucleophilic attack of the anomeric carbon of the fructose moiety by Asp22, to form a covalent enzyme-substrate complex[5]. Glucose, the leaving group, is simultaneously protonated by Glu203, which then deprontonates the "acceptor" molecule to activate it as a nucleophile, which then releases fructose[5]. The figure below illustrates this process using a cartoon.
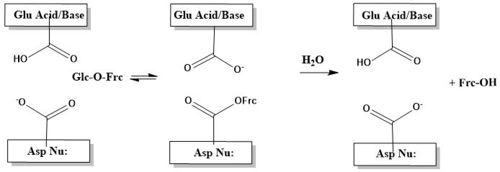
β-sandwich Domain
The of invertase, shown in crimson, spans residues 342-512. The β-sandwich is formed from two antiparallel β-sheets, of which each antiparallel sheet is composed of six β-strands. Strands are labeled 1-12.
The β-sandwich domain's function was elusive for some time, now, it has been found to be involved in catalytic pocket stabilization and dimerization[1]. A formed by chain A, chain B, and chain F showing how the β-sandwich domain functions in 4EQV. In the trimer scene, the β-Pocket illustrates how loops, showing in crimson, from the β-sandwich are involved in stabilizing the catlytic pocket, shown in teal. Additionally, the β-sandwich domain is intimately involved in the dimerization, and ultimately tetramerization, via numerous between residues 343-363.
Open & Closed Assembly
The β-sandwich domain section touches on the topic of dimerization and tetramerization, and that will be explored here further. SInv is an octamer, though is better described as a tetramer of dimers. The dimers can be further categorized into open(chains E, F, G, H) and closed assemblies(chains A, B, C, D). The difference in assembly type - open versus closed - has implications involving substrate scope. The closed assembly is borne out of many polar interactions and large surface area of interactions between the β-sandwich domain of one chain and catalytic pocket(β-propeller domain) of the corresponding chain[6]. Compared with the open assembly, the closed assembly has an interaction surface twice as large as the open assembly[5]. This strong interaction between monomers makes the catalytic pocket highly specific for sucrose[5]. The images below illustrate difference between the monomers that make up 4EQV. The upper left image shows the alignment of chains B and F, upper right shows the alignment of chains A and E. The differences highlighted here are responsible for the open vs. closed assemblies. The lower left image shows the alignment of chains E and F, lower right shows the alignment of chains A and B.



Though it may seem like a deficiency that only four of the eight catalytic sites are highly specific for sucrose or oligosaccharide with more than 4 units, this is actually allows 4EQV to much more versatile. The open assemblies(chains E, F, G, H), are capable of accommodating larger substrates such as ketoses or extended fructans. This can explain yeast's ability to to utilize the varied sugars found in its environment, and contributing to the the metabolic success of yeast[1].
Evolutionary Conservation & Related Proteins
4EQV is an essential protein for microorganisms and plants. Its primary role is to catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose and other small oligosaccharides into fructose and glucose. Most of the conserved residues are located in the β-propeller domain. The interior of the five blades of the β-propeller are highly conserved, with blade one the most conserved and blade four the least conserved[1]. The catalytic pocket of the enzyme is located within the five blades, so it reasonable that this section would be highly conserved. The β-sandwich domain shows relatively little conservation and this could have implications for the evolution of open and closed assemblies.
has been colored coded according to the scale below to show conserved and non-conserved residues for a monomer that forms a closed assembly.

Available Structures
- 1uyp – TmINV – Thermotoga maritima
- 4eqv – INV 2 – yeast
- 3kf5 – SoINV – Schwanniomyces occidentalis
- 1w2t – TmINV (mutant) + trisaccharide
- 3kf3 – SoINV + fructose
- 3uj3 – muINV – enterobacteria phage mu
- 4m6f – muINV + DNA
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Sainz-Polo MA, Ramirez-Escudero M, Lafraya A, Gonzalez B, Marin-Navarro J, Polaina J, Sanz-Aparicio J. The three-dimensional structure of Saccharomyces invertase: role of a non-catalytic domain in oligomerization and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 21. PMID:23430743 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.446435
- ↑ Sainz-Polo MA, Ramirez-Escudero M, Lafraya A, Gonzalez B, Marin-Navarro J, Polaina J, Sanz-Aparicio J. The three-dimensional structure of Saccharomyces invertase: role of a non-catalytic domain in oligomerization and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 21. PMID:23430743 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.446435
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3002(62)90526-7
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425540
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Lafraya A, Sanz-Aparicio J, Polaina J, Marin-Navarro J. Fructo-oligosaccharide synthesis by mutant versions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Sep;77(17):6148-57. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05032-11. Epub , 2011 Jul 15. PMID:21764973 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AEM.05032-11
- ↑ Krissinel E, Henrick K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J Mol Biol. 2007 Sep 21;372(3):774-97. Epub 2007 May 13. PMID:17681537 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.022






