RA Mediated T-reg Differentiation
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
T-regulatory cells (T-regs) are a small subset of CD4+ T-cells that exhibit strong down regulation of immune system activity in their local environment. They are distinguished from other CD4+ T-cells by the expression of FOXP3, a gene regulator. <ref> PMID: 19410687 </ref> The exact mechanisms used by T-regs to down regulate the immune system has not yet been clearly elucidated. These cells have been shown to differentiate from CD4+ T-helper cells upon activation and exposure to the following cytokines: tumor growth factor β (TGF-β), Interleukin-2 (IL-2) and retinoic acid (RA). <ref> PMID: 21839265 </ref> Both TGF-β and IL-2 are used in other immune system differentiation, however, RA has been shown to bias T-cells to the T-reg phenotype. <ref> PMID: 21839265 </ref> When acting upon T-reg cells, RA acts as the ligand for the Retinoic Acid Receptor-α (RARα) / Retinoid X Receptor-α (RXRα) heterodimer. This heterodimer is of the [[Nuclear receptors|nuclear receptor family]], and each chain consists of the same three part structure: a Ligand binding domain (LBD), a DNA binding domain (DBD), and a hinge region connecting the two binding domains. <ref> PMID: 10406480 </ref> | T-regulatory cells (T-regs) are a small subset of CD4+ T-cells that exhibit strong down regulation of immune system activity in their local environment. They are distinguished from other CD4+ T-cells by the expression of FOXP3, a gene regulator. <ref> PMID: 19410687 </ref> The exact mechanisms used by T-regs to down regulate the immune system has not yet been clearly elucidated. These cells have been shown to differentiate from CD4+ T-helper cells upon activation and exposure to the following cytokines: tumor growth factor β (TGF-β), Interleukin-2 (IL-2) and retinoic acid (RA). <ref> PMID: 21839265 </ref> Both TGF-β and IL-2 are used in other immune system differentiation, however, RA has been shown to bias T-cells to the T-reg phenotype. <ref> PMID: 21839265 </ref> When acting upon T-reg cells, RA acts as the ligand for the Retinoic Acid Receptor-α (RARα) / Retinoid X Receptor-α (RXRα) heterodimer. This heterodimer is of the [[Nuclear receptors|nuclear receptor family]], and each chain consists of the same three part structure: a Ligand binding domain (LBD), a DNA binding domain (DBD), and a hinge region connecting the two binding domains. <ref> PMID: 10406480 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Intracellular receptors]] | ||
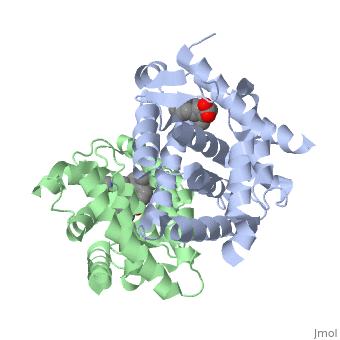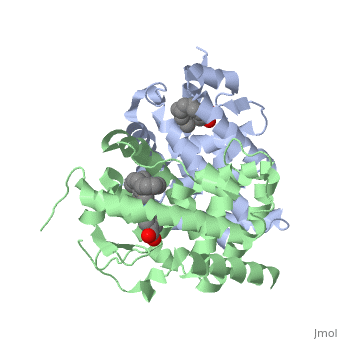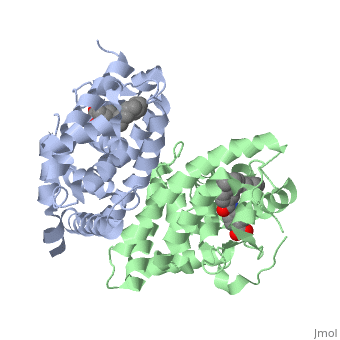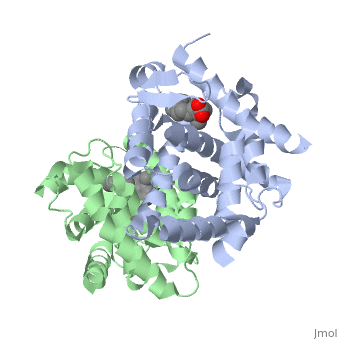
==Ligand Binding Domain== | ==Ligand Binding Domain== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ochs HD, Oukka M, Torgerson TR. TH17 cells and regulatory T cells in primary immunodeficiency diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009 May;123(5):977-83; quiz 984-5. PMID:19410687 doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.03.030
- ↑ Moore C, Fuentes C, Sauma D, Morales J, Bono MR, Rosemblatt M, Fierro JA. Retinoic acid generates regulatory T cells in experimental transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2011 Jul-Aug;43(6):2334-7. PMID:21839265 doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.06.057
- ↑ Moore C, Fuentes C, Sauma D, Morales J, Bono MR, Rosemblatt M, Fierro JA. Retinoic acid generates regulatory T cells in experimental transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2011 Jul-Aug;43(6):2334-7. PMID:21839265 doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.06.057
- ↑ Kumar R, Thompson EB. The structure of the nuclear hormone receptors. Steroids. 1999 May;64(5):310-9. PMID:10406480
- ↑ Bourguet W, Vivat V, Wurtz JM, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D. Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains. Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):289-98. PMID:10882070
- ↑ Bourguet W, Vivat V, Wurtz JM, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D. Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains. Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):289-98. PMID:10882070
- ↑ Bourguet W, Vivat V, Wurtz JM, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D. Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains. Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):289-98. PMID:10882070
- ↑ Zhao Q, Chasse SA, Devarakonda S, Sierk ML, Ahvazi B, Rastinejad F. Structural basis of RXR-DNA interactions. J Mol Biol. 2000 Feb 18;296(2):509-20. PMID:10669605 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3457
- ↑ Zhao Q, Chasse SA, Devarakonda S, Sierk ML, Ahvazi B, Rastinejad F. Structural basis of RXR-DNA interactions. J Mol Biol. 2000 Feb 18;296(2):509-20. PMID:10669605 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3457
- ↑ Umesono K, Murakami KK, Thompson CC, Evans RM. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255-66. PMID:1648450
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
William Bailey, Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky