Testgp
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== G-Protein Activation Cycle == | == G-Protein Activation Cycle == | ||
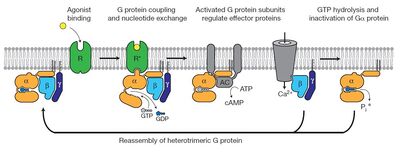
| - | [[Image:Img.JPG| | + | [[Image:Img.JPG|400px|G protein cycle for the β2AR–Gs complex. Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd on behalf of Cancer Research UK: Nature 477, 549–555, copyright 2011]] |
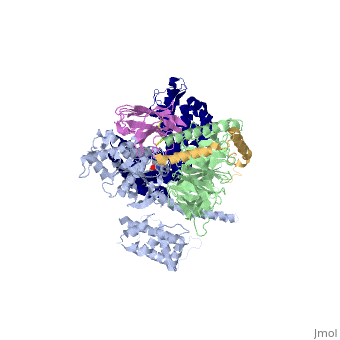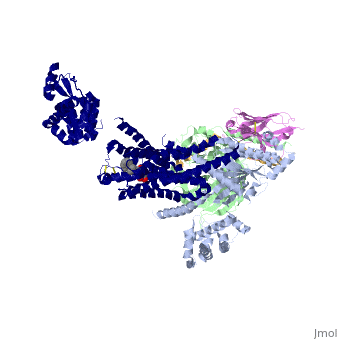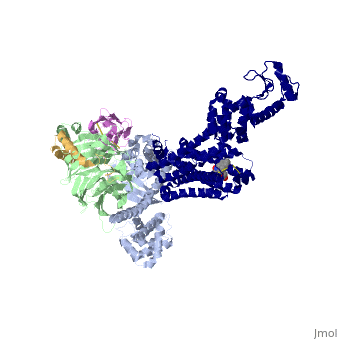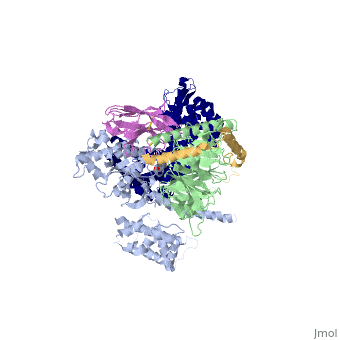
The figure shows the G Protein cycle<ref>doi:10.1038/nature10361</ref> - an extracellular agonist binding to the β2AR leads to <scene name='70/701430/Receptor_morphing_animation/2'>conformational rearrangements</scene> of the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane segments that enable the Gs heterotrimer to bind the receptor. GDP is released from the α subunit upon formation of β2AR–Gs complex. The GTP binds to the nucleotide-free α subunit resulting in dissociation of the α and βγ subunits from the receptor. The subunits regulate their respective effector proteins adenylyl cyclase (AC) and Ca2+ channels. The Gs heterotrimer reassembles from α and βγ subunits following hydrolysis of GTP to GDP in the α subunit. | The figure shows the G Protein cycle<ref>doi:10.1038/nature10361</ref> - an extracellular agonist binding to the β2AR leads to <scene name='70/701430/Receptor_morphing_animation/2'>conformational rearrangements</scene> of the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane segments that enable the Gs heterotrimer to bind the receptor. GDP is released from the α subunit upon formation of β2AR–Gs complex. The GTP binds to the nucleotide-free α subunit resulting in dissociation of the α and βγ subunits from the receptor. The subunits regulate their respective effector proteins adenylyl cyclase (AC) and Ca2+ channels. The Gs heterotrimer reassembles from α and βγ subunits following hydrolysis of GTP to GDP in the α subunit. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{Template:Button Toggle Animation2}} | {{Template:Button Toggle Animation2}} | ||
| - | A previous structure of a GTPγS bound (i.e. active, "turned on") Gαs protein showed that both domains are involved in nucleotide binding, as the nucleotide-binding pocket of the Gαs subunit is formed by the interface between GαsRas and GαsAH<ref>doi:10.1126/science.278.5345.1943</ref>. It was also previously known that the GsαAH domain has a variable position relative to the GsαRas domain between this GTP bound (active) state and the nucleotide free state<ref>DOI:10.1126/science.8266082</ref><ref>doi:10.1073/pnas.1105810108</ref><ref>doi:10.1073/pnas.1113645108</ref><ref>doi:10.1038/nature10488</ref>. However, the β2AR–Gs complex structure of the receptor attached to the empty (no guanosine phosphate attached) G protein enabled comparing it to the active (GTP bound) structure and by that showing <scene name='70/701430/Gamorph/2'>how large this displacement is</scene> - this is probably the most surprising observation arising from the β2AR–Gs complex. | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Template:Button Toggle Animation2}} | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GTPase
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_GTPase
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heterotrimeric_G_protein
- ↑ Hurowitz EH, Melnyk JM, Chen YJ, Kouros-Mehr H, Simon MI, Shizuya H. Genomic characterization of the human heterotrimeric G protein alpha, beta, and gamma subunit genes. DNA Res. 2000 Apr 28;7(2):111-20. doi: 10.1093/dnares/7.2.111. PMID:10819326 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/dnares/7.2.111
- ↑ Rasmussen SG, DeVree BT, Zou Y, Kruse AC, Chung KY, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Chae PS, Pardon E, Calinski D, Mathiesen JM, Shah ST, Lyons JA, Caffrey M, Gellman SH, Steyaert J, Skiniotis G, Weis WI, Sunahara RK, Kobilka BK. Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature. 2011 Jul 19;477(7366):549-55. doi: 10.1038/nature10361. PMID:21772288 doi:10.1038/nature10361