Beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex updated
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='3sn6' size='340' side='right' caption='Adrenergic receptor (blue) complex with G protein α subunit (grey), β subunit (green), γ-2 subunit (gold), antibody fragme...) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
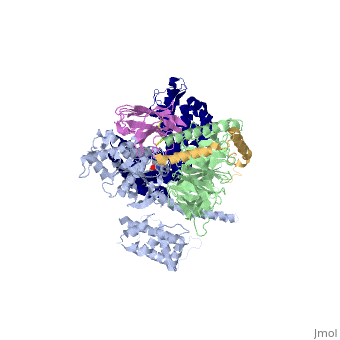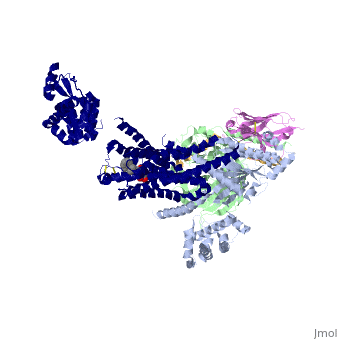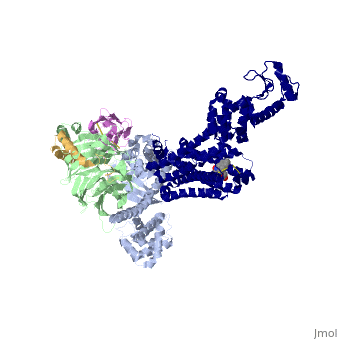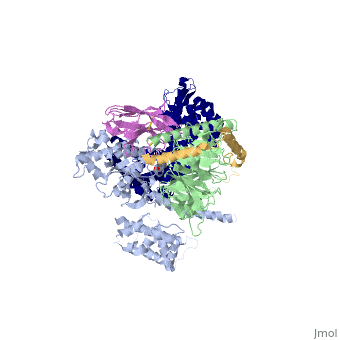
<StructureSection load='3sn6' size='340' side='right' caption='Adrenergic receptor (blue) complex with G protein α subunit (grey), β subunit (green), γ-2 subunit (gold), antibody fragment (Orchid) and benzoxazin derivative [[3sn6]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.20Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3sn6' size='340' side='right' caption='Adrenergic receptor (blue) complex with G protein α subunit (grey), β subunit (green), γ-2 subunit (gold), antibody fragment (Orchid) and benzoxazin derivative [[3sn6]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.20Å' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | Created by [[User:Wayne Decatur]] | |
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
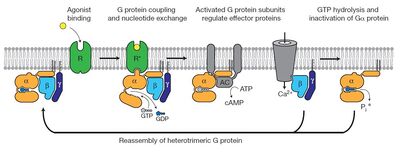
[[G protein-coupled receptors]] (GPCRs) are a large family of protein receptors, which have seven-transmembrane helices and are found over a large array of eukaryotic cells. These receptors take a major part in a multitude of signal transduction pathways, including amongst others responses to hormones and neurotransmitters, sensing light, taste and smell, and many more. These receptors are also involved in many different types of diseases and are the target of almost 50% of current medical drugs. | [[G protein-coupled receptors]] (GPCRs) are a large family of protein receptors, which have seven-transmembrane helices and are found over a large array of eukaryotic cells. These receptors take a major part in a multitude of signal transduction pathways, including amongst others responses to hormones and neurotransmitters, sensing light, taste and smell, and many more. These receptors are also involved in many different types of diseases and are the target of almost 50% of current medical drugs. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
*[[User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012|User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012]] | *[[User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012|User:Wayne Decatur/UNH BCHEM833 Structural Proteomics Introductory Lecture Fall 2012]] | ||
*[[3sn6|3SN6]] | *[[3sn6|3SN6]] | ||
| + | *[[Receptor]] | ||
| + | *[[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | Created by [[User:Wayne Decatur]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GTPase
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_GTPase
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heterotrimeric_G_protein
- ↑ Hurowitz EH, Melnyk JM, Chen YJ, Kouros-Mehr H, Simon MI, Shizuya H. Genomic characterization of the human heterotrimeric G protein alpha, beta, and gamma subunit genes. DNA Res. 2000 Apr 28;7(2):111-20. doi: 10.1093/dnares/7.2.111. PMID:10819326 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/dnares/7.2.111
- ↑ Rasmussen SG, DeVree BT, Zou Y, Kruse AC, Chung KY, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Chae PS, Pardon E, Calinski D, Mathiesen JM, Shah ST, Lyons JA, Caffrey M, Gellman SH, Steyaert J, Skiniotis G, Weis WI, Sunahara RK, Kobilka BK. Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature. 2011 Jul 19;477(7366):549-55. doi: 10.1038/nature10361. PMID:21772288 doi:10.1038/nature10361
Created by User:Wayne Decatur