This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Esterification
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | == | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Esterification of fatty acid with ethanol' scene='88/887592/Esterification_with_fifth_step/1'> |
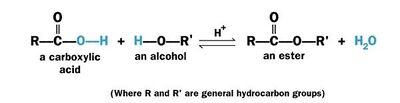
Esterification is a chemical reaction of an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acid acid] with an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alcohol alcohol] (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR'). | Esterification is a chemical reaction of an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acid acid] with an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alcohol alcohol] (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR'). | ||
Usually esterification refers to reaction between an organic (carboxylic) acid (RCOOH) with an alcohol (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR') and water and called '''Fischer esterification'''. | Usually esterification refers to reaction between an organic (carboxylic) acid (RCOOH) with an alcohol (R'OH) to form an ester (RCOOR') and water and called '''Fischer esterification'''. | ||
The chemical reaction for Fischer esterification is given below: | The chemical reaction for Fischer esterification is given below: | ||
[[Image:Esterformation2.jpg|400px]] | [[Image:Esterformation2.jpg|400px]] | ||
| - | ==Esterification of fatty acid with ethanol== | ||
| - | |||
| - | <jmol><jmolApplet> | ||
| - | <float>right</float> | ||
| - | <color>gainsboro</color> | ||
| - | <uploadedFileContents>Esterification.xyz</uploadedFileContents> | ||
| - | <script>dots off; wireframe 30; spacefill 90; label off;</script> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <script>rotate x 25; zoom 0; zoom 95.; spacefill on; dots off; spacefill 25%; set antialiasDisplay ON</script> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <script> | ||
| - | connect @4 @8 SINGLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.1 and @4) (1.1 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.2 and @4) (1.2 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.3 and @4) (1.3 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.4 and @4) (1.4 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.5 and @4) (1.5 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.6 and @4) (1.6 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.7 and @4) (1.7 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | |||
| - | connect (1.43 and @4) (1.43 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.44 and @4) (1.44 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.45 and @4) (1.45 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.46 and @4) (1.46 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.47 and @4) (1.47 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.48 and @4) (1.48 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.49 and @4) (1.49 and @8) DOUBLE; | ||
| - | connect (1.50 and @4) (1.50 and @8) DOUBLE</script> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <caption>Esterification of fatty acid with ethanol</caption> | ||
| - | <controls>spin quality popup labels</controls> | ||
| - | </jmolApplet></jmol> | ||
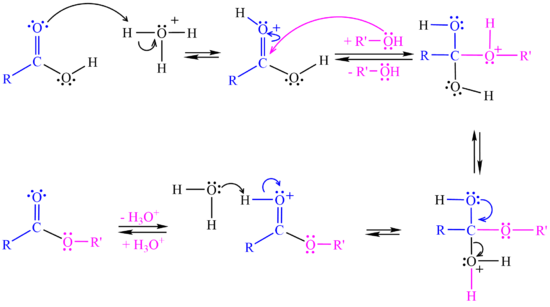
The <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 1 10; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>reaction starts</text></jmolLink></jmol> when the carboxylic acid accepts a proton from the strong acid catalyst. | The <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 1 10; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>reaction starts</text></jmolLink></jmol> when the carboxylic acid accepts a proton from the strong acid catalyst. | ||
In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 11 19; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>second step</text></jmolLink></jmol> the alcohol attacks the protonated carbonyl group to create a tetrahedral intermediate structure. | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 11 19; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>second step</text></jmolLink></jmol> the alcohol attacks the protonated carbonyl group to create a tetrahedral intermediate structure. | ||
In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 20 41; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>third step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a proton is lost at one oxygen atom and bonds to another oxygen atom. | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 20 41; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>third step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a proton is lost at one oxygen atom and bonds to another oxygen atom. | ||
| - | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 41 50; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fourth step</text></jmolLink></jmol> water molecule leaves the structure. | + | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 41 50; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fourth step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a water molecule leaves the structure. |
| - | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range | + | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 51 59; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fifth step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a proton (H+) leaves the carbonyl group, transfers to a base and '''ester''' is formed. |
| - | + | [[Image:Esterification Mechanism.png|550px]] <br> | |
| - | [[Image:Esterification | + | |
An animated example of this reaction is shown. Please click on the buttons below to '''animate''' the reaction with different representations. Use the '''popup''' button to enlarge the view and the '''quality''' button to turn on anti-aliasing. | An animated example of this reaction is shown. Please click on the buttons below to '''animate''' the reaction with different representations. Use the '''popup''' button to enlarge the view and the '''quality''' button to turn on anti-aliasing. | ||
| Line 70: | Line 37: | ||
and [[User:Veronika Pelekhov | Veronika Pelekhov]]. | and [[User:Veronika Pelekhov | Veronika Pelekhov]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
===See also=== | ===See also=== | ||
[[SN1_reaction|S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction: Substitution of Cl<sup>−</sup> and ''tert''-Butanol ]]<br> | [[SN1_reaction|S<sub>N</sub>1 reaction: Substitution of Cl<sup>−</sup> and ''tert''-Butanol ]]<br> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
See also
SN1 reaction: Substitution of Cl− and tert-Butanol
SN2 reaction: substitution of Cl− and methanol