We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
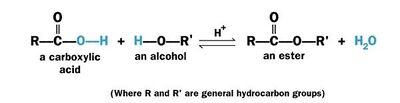
Esterification
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
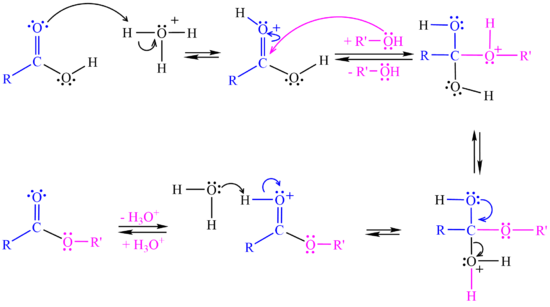
In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 11 19; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>second step</text></jmolLink></jmol> the alcohol attacks the protonated carbonyl group to create a tetrahedral intermediate structure. | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 11 19; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>second step</text></jmolLink></jmol> the alcohol attacks the protonated carbonyl group to create a tetrahedral intermediate structure. | ||
In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 20 41; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>third step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a proton is lost at one oxygen atom and bonds to another oxygen atom. | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 20 41; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>third step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a proton is lost at one oxygen atom and bonds to another oxygen atom. | ||
| - | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 41 50; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fourth step</text></jmolLink></jmol> water molecule leaves the structure. | + | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 41 50; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fourth step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a water molecule leaves the structure. |
| - | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range | + | In the <jmol><jmolLink><script>anim mode once; frame range 51 59; delay 0.5; frame play</script><text>fifth step</text></jmolLink></jmol> a proton (H+) leaves the carbonyl group, transfers to a base and '''ester''' is formed. |
| - | + | [[Image:Esterification Mechanism.png|550px]] <br> | |
| - | [[Image:Esterification | + | |
An animated example of this reaction is shown. Please click on the buttons below to '''animate''' the reaction with different representations. Use the '''popup''' button to enlarge the view and the '''quality''' button to turn on anti-aliasing. | An animated example of this reaction is shown. Please click on the buttons below to '''animate''' the reaction with different representations. Use the '''popup''' button to enlarge the view and the '''quality''' button to turn on anti-aliasing. | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
See also
SN1 reaction: Substitution of Cl− and tert-Butanol
SN2 reaction: substitution of Cl− and methanol