User:Natalia de Araujo./Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Natalia de Araujo.(Difference between revisions)
| (55 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==CEP170 | + | ==Centrosomal protein of 170kDa (CEP170)== |
| - | <StructureSection load='4jon' size='350' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='4jon' size='350' side='right' caption='[[4jon]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.15Å' scene=''> |
| - | + | '''The first structure''', displayed on the left-hand side of the screen, corresponds to [[4jon]], the Crystal structure of CEP170's transcript variant beta, from Homo sapiens. 4jon is a <scene name='89/897701/4jon_5_chain_structure/1'>5 chain structure</scene> obtained by ''X-ray Crystallography'' [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_crystallography#:~:text=X%2Dray%20crystallography%20is%20the,diffract%20into%20many%20specific%20directions.&text=In%20a%20single%2Dcrystal%20X,is%20mounted%20on%20a%20goniometer.] and represents the first 126 residues of CEP170's N-termini region. | |
| - | + | '''The second structure''' available for CEP170 is <scene name='89/897701/Q5sw79/1'>Q5SW79</scene>, a ''predicted'' 3D model representing its full lenght (1-1584). You can compare the Q5SW79 <scene name='89/897701/Q5sw79_-_4jon/1'>N-termini regoin</scene> corresponding to <scene name='89/897701/4jon_a_chain/1'>4jon</scene>. | |
| - | + | Here we are going to focus on the Q5SW79 model due to its full sequence, allowing us to highlight residues and regions important for the understanding of CEP170's functions and interactions. | |
| - | == | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'> |
| + | </td></tr><tr id=' Available 3D models'><td class="sblockLbl"><b> Available 3D models:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[4jon]], <scene name='89/897701/Q5sw79/1'>Q5SW79</scene> </td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='Specie:'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Specie:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">Human</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">CEP170, FAM68A, KAB, KIAA0470, NM_001042404 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='Splice variants'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Splice Variants</b></td><td class="sblockDat">CEP170α, CEP170β, and CEP170γ</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='RefSeq (mRNA):'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>RefSeq (mRNA):</b></td><td class="sblockDat">CEP170α: NM_014812[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_014812], CEP170β: NM_001042404 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_001042404], CEP170γ: NM_001042405[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_001042405]</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='RefSeq (protein):'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>RefSeq (protein):</b></td><td class="sblockDat">CEP170α: NP_055627[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_055627], CEP170β: NP_001035863[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001035863], CEP170γ: NP_001035864[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001035864]</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='UniProt'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>UniProt:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>Q5SW79[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q5SW79]</span></td></tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
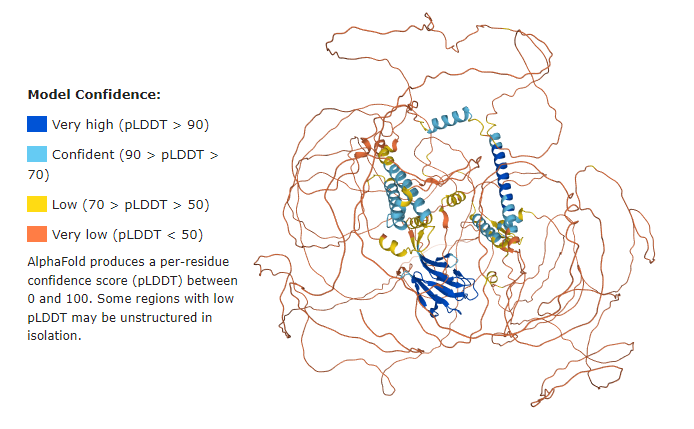
| - | == | + | == Q5SW79 Confidence Model == |
| - | + | Before getting started, it is important to have in mind that the majority of the Q5SW79 structure has {{Font color|orange|very low confidence}}. | |
| - | + | You can read more about the predicted aligned error at Alphafold[https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q5SW79]. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | < | + | <imagemap> |
| - | + | Image:Q5SW79 Model confidence.png|700px | |
| - | < | + | default [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q5SW79] |
| + | </imagemap> | ||
| + | == CEP170 gene == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The CEP170 gene (OMIM*613023[https://omim.org/entry/613023]) spans over 131,369 bases at 1q43, contains 30 exons, and encodes the Centrosomal Protein of 170 kDa (CEP170)[https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=CEP170]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <imagemap> | ||
| + | Image:CEP170-gene.png|700px | ||
| + | default [https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=CEP170] | ||
| + | </imagemap> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bulk RNA-seq of CEP170 [https://gtexportal.org/home/gene/CEP170](average expression of the gene) shows that CEP170 is expressed in a variety of tissues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == CEP170 protein == | ||
| + | CEP170 is a pericentriolar protein that associates with the mother-centriole during interphase and with the spindle apparatus during mitosis<ref>PMID: 15616186</ref>, showing a dynamic behavior throughout the cell cycle. CEP170 is a phosphoprotein heavily phosphorylated during mitosis<ref>PMID:23087211</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Function''' | ||
| + | CEP170 plays an important role in microtubule organization, microtubule nucleation, and the proper dynamics of the mitotic spindle.<ref>PMID:15616186</ref><ref>PMID:23087211</ref><ref>PMID:30354798</ref><ref>PMID:26656453</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Subcellular localization''' | ||
| + | Centrosome, Centriole, and Mitotic Spindle. | ||
| + | At the centrosome, CEP170 binds specifically to the subdistal appendages of the mother-centriole.<ref>PMID:15616186</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Protein-Protein Interactions == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''CHEK1 and circCHEK1_246aa''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Through Co-IP [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunoprecipitation#Protein_complex_immunoprecipitation_(Co-IP)]and MS[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass_spectrometry] CEP170 was identified as a putative interactor with CHEK1, further confirmed with Co-IP in cells overexpressing CHEK1<ref>DOI 10.1186/s12943-021-01380-0</ref>. | ||
| + | CHEK and circCHEK1_246aa (isoform from a cRNA) phosphorylate the <scene name='89/897701/Ser_1260/4'>Ser1260</scene> residue of CEP170, which results in chromosomal instability seen in multiple myeloid cells. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''PLK1''' | ||
| + | Through yeast two-hybrid screen[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two-hybrid_screening] CEP170 was identified as a putative interactor with PLK1, further confirmed with Reciprocal Co-IP in vivo. | ||
| + | PLK1 phosphorylates the C-termini region (<scene name='89/897701/Plk1_substrate_aa_755-1460/1'>assayed fragment aa 755-1460</scene>) of CEP170. <ref>PMID:15616186</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''KIF2B''' | ||
| + | Through affinity purifications [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Affinity_chromatography] of GFP-Kifc3 CEP170 was identified and confirmed as a KIF2B interactor.<ref>PMID:23087211</ref> | ||
| + | CEP170 targets KIF2B to the mitotic spindle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''TBK1''' | ||
| + | Proximity ligation assay (PLA)[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proximity_ligation_assay] showed co-localization of TBK1 and CEP170 and the interaction was further confirmed with Co-IP experiments. | ||
| + | In vitro kinase assays showed that TBK1 phosphorylates 12 serine residues and 1 threonine residue of CEP170 (see Structural highlights-phosphoresidues).<ref>PMID:26656453</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''CCDC68 and CCDC120''' | ||
| + | CCDC120 co-fractionated with CEP170 and interaction was confirmed with immunoprecipitation. CCDC120 binds to the the C terminus(<scene name='89/897701/Ccdc120_binding_region/1'>1,015–1,460 aa</scene>) of CEP170. | ||
| + | to CCDC120<ref>PMID:28422092</ref>. | ||
| + | Through MS CCDC68 was identified as a CEP170 interactor, further confirmed by immunoprecipitation<ref>PMID:28422092</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''CCDC61''' | ||
| + | Through proximity-dependent biotin identification (BioID) and MS CEP170 was identified in possible interaction with CCDC61, further confirmed with immunoprecipitation. | ||
| + | CCDC61 plays a role as a mediator of the interaction between TBK1 and CEP170.<ref>PMID:30354798</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''WDR62''' | ||
| + | Though Co-IP and iTRAQ MS CEP170 was identified as a putative interactor with WDR622, further confirmed with Co-IP experiment in cells overexpressing WDR62 or CEP170.<ref>PMID:31533924</ref> | ||
| - | ==Crystal structure of a centrosomal protein 170kDa, transcript variant beta (CEP170) from Homo sapiens at 2.15 A resolution (PSI Community Target, Sundstrom)== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='4jon' size='340' side='right' caption='[[4jon]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.15Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | < | + | |
| - | </td></tr><tr id=' | + | All three splice variants harbor an N-terminal forkhead-associated (FHA) domain and a serine-rich domain and a short coiled-coil region in the C-terminal half.<ref>PMID:15616186</ref> |
| - | <tr id=' | + | |
| - | <tr id=' | + | *'''Forkhead-associated (FHA) domain''' |
| + | FHA is a phosphopeptide recognition domain that displays specificity for phosphothreonine-containing epitopes but will also recognize phosphotyrosine with relatively high affinity[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forkhead-associated_domain]. CEP170's FHA domain is located at the N-terminal region composed of the residues <scene name='89/897701/Fha_domain/1'>22–73</scene><ref>PMID:15616186</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Serine-rich region''' | ||
| + | <scene name='89/897701/Serine-rich_region/1'>968-1228aa</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Phosphoresidues''' | ||
| + | As shown previously, CEP170 is a phosphoprotein, phosphorylated probably by PLK1, TBK1, CHEK1 and circCHEK1_246aa. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'> | ||
| + | </td></tr><tr id=' Phosphoserine'><td class="sblockLbl"><b> Phosphoserine:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='89/897701/Ser_138/1'>138</scene>; <scene name='89/897701/Ser_141/1'>141</scene>; 356; 359; 446; 466; 497; 571; 580; 630; 633; 636; 667; 725; 838; 879; 881; 930; 933; 958; 1019; 1059; 1112; 1114; 1132; 1133; 1145; 1160; 1165; 1198; 1205; 1210; 1239; 1241; 1251; 1270; 1280; 1362; 1521; 1522</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='Phosphotyrosine'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Phosphotyrosine:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">364</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='Phosphothreonine'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Phosphothreonine:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">501; 667; 760; 914; 920; 1023; 1058</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='Mashup'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Mashup:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='89/897701/All_phosphoresidues/1'>All Phosphoresidues</scene></td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='Proteins'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Proteins:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">PLK1, TBK1, CHEK1, and circCHEK1_246aa</td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| - | == | + | |
| - | [ | + | *'''Targeting to microtubules''' |
| + | The C-terminus region contains 2 microtubule binding domains, located at <scene name='89/897701/Mt_domain/2'>709–1009aa</scene> and <scene name='89/897701/Mt_domain2/2'>1010–1200aa</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Coiled-coil domain''' | ||
| + | Type of secondary structure composed of alpha-helices [https://www.uniprot.org/keywords/KW-0175]. Located at <scene name='89/897701/Coiled-coil_domain/1'>1467–1495</scene> <ref>PMID:15616186</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | __TOC__ | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: Human]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Structural genomic]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Fha domain]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Jcsg]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Pf00498]] | ||
| - | [[Category: PSI, Protein structure initiative]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Psi-biology]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Putative protein-protein recognition]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Unknown function]] | ||
Current revision
Centrosomal protein of 170kDa (CEP170)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA. The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1095-107. Epub 2004 Dec 22. PMID:15616186 doi:E04-10-0939
- ↑ Welburn JP, Cheeseman IM. The microtubule-binding protein Cep170 promotes the targeting of the kinesin-13 depolymerase Kif2b to the mitotic spindle. Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Dec;23(24):4786-95. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0214. Epub 2012, Oct 19. PMID:23087211 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0214
- ↑ Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA. The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1095-107. Epub 2004 Dec 22. PMID:15616186 doi:E04-10-0939
- ↑ Welburn JP, Cheeseman IM. The microtubule-binding protein Cep170 promotes the targeting of the kinesin-13 depolymerase Kif2b to the mitotic spindle. Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Dec;23(24):4786-95. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0214. Epub 2012, Oct 19. PMID:23087211 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0214
- ↑ Barenz F, Kschonsak YT, Meyer A, Jafarpour A, Lorenz H, Hoffmann I. Ccdc61 controls centrosomal localization of Cep170 and is required for spindle assembly and symmetry. Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Dec 15;29(26):3105-3118. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0115. Epub, 2018 Oct 24. PMID:30354798 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0115
- ↑ Pillai S, Nguyen J, Johnson J, Haura E, Coppola D, Chellappan S. Tank binding kinase 1 is a centrosome-associated kinase necessary for microtubule dynamics and mitosis. Nat Commun. 2015 Dec 10;6:10072. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10072. PMID:26656453 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10072
- ↑ Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA. The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1095-107. Epub 2004 Dec 22. PMID:15616186 doi:E04-10-0939
- ↑ Gu C, Wang W, Tang X, Xu T, Zhang Y, Guo M, Wei R, Wang Y, Jurczyszyn A, Janz S, Beksac M, Zhan F, Seckinger A, Hose D, Pan J, Yang Y. CHEK1 and circCHEK1_246aa evoke chromosomal instability and induce bone lesion formation in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer. 2021 Jun 5;20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01380-0. PMID:34090465 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01380-0
- ↑ Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA. The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1095-107. Epub 2004 Dec 22. PMID:15616186 doi:E04-10-0939
- ↑ Welburn JP, Cheeseman IM. The microtubule-binding protein Cep170 promotes the targeting of the kinesin-13 depolymerase Kif2b to the mitotic spindle. Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Dec;23(24):4786-95. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0214. Epub 2012, Oct 19. PMID:23087211 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0214
- ↑ Pillai S, Nguyen J, Johnson J, Haura E, Coppola D, Chellappan S. Tank binding kinase 1 is a centrosome-associated kinase necessary for microtubule dynamics and mitosis. Nat Commun. 2015 Dec 10;6:10072. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10072. PMID:26656453 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10072
- ↑ Huang N, Xia Y, Zhang D, Wang S, Bao Y, He R, Teng J, Chen J. Hierarchical assembly of centriole subdistal appendages via centrosome binding proteins CCDC120 and CCDC68. Nat Commun. 2017 Apr 19;8:15057. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15057. PMID:28422092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15057
- ↑ Huang N, Xia Y, Zhang D, Wang S, Bao Y, He R, Teng J, Chen J. Hierarchical assembly of centriole subdistal appendages via centrosome binding proteins CCDC120 and CCDC68. Nat Commun. 2017 Apr 19;8:15057. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15057. PMID:28422092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15057
- ↑ Barenz F, Kschonsak YT, Meyer A, Jafarpour A, Lorenz H, Hoffmann I. Ccdc61 controls centrosomal localization of Cep170 and is required for spindle assembly and symmetry. Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Dec 15;29(26):3105-3118. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0115. Epub, 2018 Oct 24. PMID:30354798 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0115
- ↑ Qin Y, Zhou Y, Shen Z, Xu B, Chen M, Li Y, Chen M, Behrens A, Zhou J, Qi X, Meng W, Wang Y, Gao F. WDR62 is involved in spindle assembly by interacting with CEP170 in spermatogenesis. Development. 2019 Oct 21;146(20). pii: dev.174128. doi: 10.1242/dev.174128. PMID:31533924 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/dev.174128
- ↑ Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA. The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1095-107. Epub 2004 Dec 22. PMID:15616186 doi:E04-10-0939
- ↑ Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA. The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1095-107. Epub 2004 Dec 22. PMID:15616186 doi:E04-10-0939
- ↑ Guarguaglini G, Duncan PI, Stierhof YD, Holmstrom T, Duensing S, Nigg EA. The forkhead-associated domain protein Cep170 interacts with Polo-like kinase 1 and serves as a marker for mature centrioles. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1095-107. Epub 2004 Dec 22. PMID:15616186 doi:E04-10-0939