User:Maria Carolina Boer Copstein/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Introduction == | ==Introduction == | ||
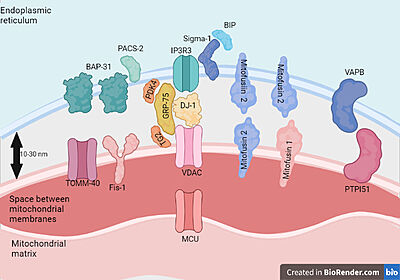
| - | Three different isoforms of VDAC have been identified, VDAC1, VDAC2, and VDAC3. VDAC1 has been best studied, whereas only limited information regarding the cellular functions of VDAC2 and VDAC3 is available .VDAC1 is a protein present in the outer mitochondrial membrane(OMM) and in other cellular compartments such as the plasma membrane.VDAC1 controls the metabolic and energy cross-talk between mitochondria and the rest of the cell, mediating the fluxes of ions, nucleotides, and other metabolites across the OMM . This protein is involved in several cellular processes.[[Image:MAM.jpg|400px|left|thumb| Proteins present in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum membranes | + | Three different isoforms of VDAC have been identified, VDAC1, VDAC2, and VDAC3. VDAC1 has been best studied, whereas only limited information regarding the cellular functions of VDAC2 and VDAC3 is available .VDAC1 is a protein present in the outer mitochondrial membrane(OMM) and in other cellular compartments such as the plasma membrane.VDAC1 controls the metabolic and energy cross-talk between mitochondria and the rest of the cell, mediating the fluxes of ions, nucleotides, and other metabolites across the OMM . This protein is involved in several cellular processes.[[Image:MAM.jpg|400px|left|thumb| Proteins present in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum membranes that interact with each other.Feito com Biorender.com]]VDAC1 has been shown to be a regulator of OMM permeability to Ca2+.Mitochondria play a major role in different events beyond theircritical bioenergetics function of supplying ATP, such as in cellsignaling events, inter-organellar communication, aging, cell pro-liferation, disease, and apoptosis. Apart from their metabolic role,mitochondria are also a major hub of cellular Ca2+homeostasis thatis fundamental for a wide range of cellular activities, such as controlof oxidative phosphorylation, modulation of cytosolic Ca2+signals,cell death, secretion, and the production of reactive oxygen species(ROS) |
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | As VDAC1 is a mitochondrial membrane protein, it is involved in cell metabolism in addition to mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis processes and regulates calcium homeostasis and oxidative stress.VDAC1 is highly Ca2+-permeable and modulates Ca2+ access to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Intramitochondrial Ca2+ controls energy metabolism by enhancing the rate of NADH production via modulating critical enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation. Mitochondrial [Ca2+] is regarded as an important determinant of cell sensitivity to apoptotic stimuli and was proposed to act as a “priming signal,” sensitizing the organelle and promoting the release of pro-apoptotic proteins.Intracellular Ca2+concentration ([Ca2+]i) regulates a number of cellular and intercellular events, such as the cell cycle, proliferation, gene transcription, and cell death pathways, as well as processes like muscle contractility and neuronal processing and transmission | + | As VDAC1 is a mitochondrial membrane protein, it is involved in cell metabolism in addition to mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis processes and regulates calcium homeostasis and oxidative stress.VDAC1 is highly Ca2+-permeable and modulates Ca2+ access to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Intramitochondrial Ca2+ controls energy metabolism by enhancing the rate of NADH production via modulating critical enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation. Mitochondrial [Ca2+] is regarded as an important determinant of cell sensitivity to apoptotic stimuli and was proposed to act as a “priming signal,” sensitizing the organelle and promoting the release of pro-apoptotic proteins.Intracellular Ca2+concentration ([Ca2+]i) regulates a number of cellular and intercellular events, such as the cell cycle, proliferation, gene transcription, and cell death pathways, as well as processes like muscle contractility and neuronal processing and transmission. The alteration of Ca2+ homeostasis is closely related with various cancer hallmarks, including proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, invasion abilities, and resistance to cell death.VDAC1 has also been recognized as a key protein in mitochondria-mediated apo-ptosis, contributing to the release of apoptotic proteins located in the inter-membranal space (IMS) andregulating apoptosis via association with pro- and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family of pro-teins and hexokinase. |
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== Neurodegenerative disease == | == Neurodegenerative disease == | ||
| - | [[Image:ALS dysfunctions.png|500px|right|thumb| | + | [[Image:ALS dysfunctions.png|500px|right|thumb| Alterations in VDAC1 observed in ALS[2].]] |
Several studies have already observed the participation of VDAC1 in mitochondrial dysfunctions observed in several neurodegenerative diseases and constitutes a point of accumulation of protein aggregates with Tau,β amyloid,SOD1 that are present in these pathologies. Due to the involvement of VDAC1 in metabolism and processes of apoptosis this protein becomes a possible therapeutic target of these diseases.The Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) associates with about 20% of familial ALS (fALS) cases and over 180 mutant forms of enzymatically active or inactive SOD1 have been characterized in humans (http://alsod.iop.kcl.ac.uk). In affected tissues, toxic effects of SOD1 mutants are related to the formation of misfolded SOD1 aggregates upon the mitochondrial surface, leading to morphological degeneration and malfunctioning of the organelle.In the spinal cord from ALS patients, voltage dependent anion selective channel isoform 1 (VDAC1) represents the docking site on the outer mitochondrial membrane for ALS-linked SOD1 mutants.In ALS, the VDAC1-SOD1 mutant interaction strongly affects the functional properties of VDAC1 | Several studies have already observed the participation of VDAC1 in mitochondrial dysfunctions observed in several neurodegenerative diseases and constitutes a point of accumulation of protein aggregates with Tau,β amyloid,SOD1 that are present in these pathologies. Due to the involvement of VDAC1 in metabolism and processes of apoptosis this protein becomes a possible therapeutic target of these diseases.The Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) associates with about 20% of familial ALS (fALS) cases and over 180 mutant forms of enzymatically active or inactive SOD1 have been characterized in humans (http://alsod.iop.kcl.ac.uk). In affected tissues, toxic effects of SOD1 mutants are related to the formation of misfolded SOD1 aggregates upon the mitochondrial surface, leading to morphological degeneration and malfunctioning of the organelle.In the spinal cord from ALS patients, voltage dependent anion selective channel isoform 1 (VDAC1) represents the docking site on the outer mitochondrial membrane for ALS-linked SOD1 mutants.In ALS, the VDAC1-SOD1 mutant interaction strongly affects the functional properties of VDAC1 | ||
channel suggesting a role in the impairment of the bioenergetics metabolism and oxidative stress of | channel suggesting a role in the impairment of the bioenergetics metabolism and oxidative stress of | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
Magri Andrea ,Messina Angela, “Interactions of VDAC with Proteins Involved in Neurodegenerative Aggregation: An Opportunity for Advancement on Therapeutic Molecules”, Current Medicinal Chemistry 2017; 24(40) . https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170601073920
Hosaka T, Okazaki M, Kimura-Someya T, et al. Crystal structural characterization reveals novel oligomeric interactions of human voltage-dependent anion channel 1. Protein Sci. 2017;26(9):1749-1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121218
Pittalà, M.G.G.; Reina, S.; Cubisino, S.A.M.; Cucina, A.; Formicola, B.; Cunsolo, V.; Foti, S.; Saletti, R.; Messina, A. Post-Translational Modification Analysis of VDAC1 in ALS-SOD1 Model Cells Reveals Specific Asparagine and Glutamine Deamidation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121218
![Alterations in VDAC1 observed in ALS[2].](/wiki/images/thumb/e/e1/ALS_dysfunctions.png/500px-ALS_dysfunctions.png)
