|
The CD1 family
CD1 (Cluster of Differentiation 1) is a family of glycoproteins involved in the presentation of antigens on the surface of specific cells to NKT cells. CD1 molecules are notably expressed by splenic dendritic cells, marginal zone B cells and CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. The CD1 family is made of three groups. Group 1 is composed of CD1a, b and c proteins and group 2 is composed of CD1d proteins. The third group is the CD1e, which shares some partial characteristics from groups 1 and 2[1] [2].
Thus, the structure and function of such proteins in mice are akin to those of humans. Mice do not express group 1 CD1 molecules, but they have two kinds of CD1d molecules. Therefore, mice have been widely used to characterize the functions of CD1d and CD1d-dependent NKT cells in many diseases.
Function
 CD1d dependent lipid antigen presentation. Role in the immune system
CD1d protein is a molecule of the immune system, involved in the presentation of a lipid antigen to NKT cells, which are a subset of T cells. Indeed, these proteins are located on the plasma membrane of APC cells. When the recognition between the CD1d bound to its lipid ligand and the TCR of a NKT cell occurs, the lymphocyte turns out to be activated. Thus, the production of cytotoxic molecules such as interleukin-4 and IFN-gamma is triggered by this activation, leading to a Th2 or Th1 immune response respectively[3][4]. Therefore, CD1d proteins are precursors of the adaptive immune reaction. As a result, a deficiency of CD1d protein may lead to a deficiency of the NKT cells functioning and thus to autoimmune diseases and cancers.
Ligands presented by CD1d
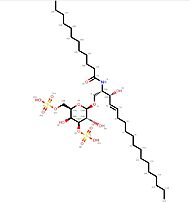
The ligands that can be presented by CD1d to NKT or other CD1d-restricted T cells are quite specific, because the recognition is based on a hydrophobic interaction between the ligand and the CD1d molecule. Thus, it limits the risk for other similar molecules to bind CD1d proteins and ensures that the immune response is accurate. Among these CD1d ligands, glycolipids from a marine sponge (alphagalactosylceramide or α-GalCer), bacterial glycolipids, normal endogenous glycolipids, tumor-derived phospholipids and glycolipids, and nonlipidic molecules have been described[5].
Structure of mouse CD1d
is made of 2 chains [6]:
- - an (T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1d1) of 287 amino acids
- - a of 99 amino acids.
The alpha chain is made of three domains: alpha 1, alpha 2 and alpha 3. The association of alpha 1 and alpha 2 is composed of two beta-sheets and a set of 2 alpha helixes. Each beta-sheet contains four antiparallel strands. The ligand binds between the two alpha 1 and 2 helices. The alpha 3 domain is non-covalently bound with beta-2-microglobulin domain.
Additionally, there are five [6] bound to the alpha chain via N-glycosylations, three of which have been clearly identified [7]. The total molecular weight of the alpha chain is 33 kDa when not associated to any oligosaccharide and 55 kDa when oligosaccharides are associated to the chain [3].
CD1d molecules are structurally similar to Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I, but present lipid antigens as opposed to peptides. Thus the cleft where the ligand can bind is different between MHC molecules and CD1d molecules. Indeed, the hydrophobic cleft of CD1d has a narrow opening.The recognition between the protein and its ligand occurs at a specific hydrophobic spot which creates an appropriate environment for the interaction to happen. This is located at the A' and F' pockets in the region of the alpha helices[8].
Impact of ligand-binding
Conformational variation
The stability of the CD1d-glycolipid complexes has an impact on the cytokine release (cell signaling). Conformational variations that would stabilize the F’-pocket (primary site of interaction with the T cell receptor, NKT TCR) might increase CD1d affinity for the NKT TCR[4][8].
The binding of a ligand (such as C12-di-sulfatide) leads to of CD1d molecule (The moving molecules are the oligosaccharides molecules ; the ligand is not represented).
CD1d affinity
CD1d proteins lipid recognition is based on the interaction of the protein with its ligand. Nevertheless, the interaction relies on two recognitions. The first one is the recognition of the head of the lipid and the second one is the recognition of the length of the molecule. Because there are more than one condition to fill in order to interact with CD1d proteins, the affinity for a lipid depends itself on a plurality of parameters which modulates it[4][8][9].
Applications
Immunotherapeutic tool
The presentation of several kinds of ligands can have immunopotentiating effects, such as serving as an adjuvant in malaria vaccine or resulting in a more rapid clearance of certain virus infections. They can also be protective in autoimmune diseases or cancer[4][5][10].
The orientation of the immune pathway (Th1 or Th2) due to the cytokines secretion by NKT cells is dependant of the affinity of the ligand for CD1d molecule. The design of agonists with a higher or lower affinity for CD1d could also lead to therapeutic effects, due to the possibility of specifically directing the immune response towards the Th1 or Th2 pathway [8] [11].
NKT cells marker
CD1 molecules can also be used as NKT cell markers. Indeed, a CD1 molecule can be engineered to become fluorescent by binding a fluorescent-potent molecule to it. When the engineered complex interacts with a NKT cell, the fluorescent signal is emitted and therefore the NKT cells can be spotted[12].
See Also
References
- ↑ Jullien, D.; Afanassieff, M.; Claudy, A.; Nicolas, J.; Kaiserlian, D. CD1 : une nouvelle famille de molécules présentatrices d’antigènes aux caractéristiques singulières. Med Sci (Paris) 1999, 15 (1), 7. https://doi.org/10.4267/10608/1190.
- ↑ Angenieux C, Salamero J, Fricker D, Cazenave JP, Goud B, Hanau D, de La Salle H. Characterization of CD1e, a third type of CD1 molecule expressed in dendritic cells. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 1;275(48):37757-64. http://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M007082200 PMID: 10948205.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Joyce, S. CD1d and Natural T Cells: How Their Properties Jump-Start the Immune System. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58 (3), 442–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000869.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Rossjohn, J., Pellicci, D. G., Patel, O., Gapin, L., & Godfrey, D. I. (2012). Recognition of CD1d-restricted antigens by natural killer T cells. Nature reviews. Immunology, 12(12), 845–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3328.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Brutkiewicz, R. R. CD1d Ligands: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. The Journal of Immunology 2006, 177 (2), 769–775. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.769.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Information, N. C. for B.; Pike, U. S. N. L. of M. R.; BethesdaMD; 20894USA. 3GMQ: Structure of mouse CD1d expressed in SF9 cells, no ligand added https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/3GMQ (accessed Dec 5, 2020).
- ↑ Sriram, V., Willard, C.A., Liu, J., & Brutkiewicz, R.R.(2008). Importance of N-linked glycosylation in the functional expression of murine CD1d1. Immunology, 123:272–281.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2433293/
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Schiefner, A.; Fujio, M.; Wu, D.; Wong, C.-H.; Wilson, I. A. Structural Evaluation of Potent NKT-Cell Agonists: Implications for Design of Novel Stimulatory Ligands. J Mol Biol 2009, 394 (1), 71–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.08.061
- ↑ McCarthy, C.; Shepherd, D.; Fleire, S.; Stronge, V. S.; Koch, M.; Illarionov, P. A.; Bossi, G.; Salio, M.; Denkberg, G.; Reddington, F.; Tarlton, A.; Reddy, B. G.; Schmidt, R. R.; Reiter, Y.; Griffiths, G. M.; van der Merwe, P. A.; Besra, G. S.; Jones, E. Y.; Batista, F. D.; Cerundolo, V. The Length of Lipids Bound to Human CD1d Molecules Modulates the Affinity of NKT Cell TCR and the Threshold of NKT Cell Activation. J Exp Med 2007, 204 (5), 1131–1144. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20062342.
- ↑ Sköld, M.; Behar, S. M. Role of CD1d-Restricted NKT Cells in Microbial Immunity. Infect Immun 2003, 71 (10), 5447–5455. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.71.10.5447-5455.2003.
- ↑ Kishi J, Inuki S, Hirata N, Kashiwabara E, Yoshidome D, Ichihara O, Fujimoto Y. Structure-activity relationship studies of Bz amide-containing α-GalCer derivatives as natural killer T cell modulators. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Apr 15;29(8):970-973. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.02.018. Epub 2019 Feb 18. PMID: 30824201.
- ↑ Benlagha, K., Weiss, A., Beavis, A., Teyton, L., & Bendelac, A. (2000). In vivo identification of glycolipid antigen-specific T cells using fluorescent CD1d tetramers. The Journal of experimental medicine, 191(11), 1895–1903. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.191.11.1895
|