Sonic Hedgehog
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Sonic hedgehog''' (Shh) is a member of the Hedgehog (Hh) family of secreted extracellular signaling proteins, which serve important roles in regulating both short-range and long-range patterning processes in developing invertebrate and vertebrate tissues<ref>PMID: 7867057</ref>. First discovered in ''Drosophila'', where mutations of the single ''Hedgehog'' gene produces larvae that are covered in hedgehog-like denticles, Hh proteins are encoded by at least three genes in mammals - ''Sonic'', ''Desert'', and ''Indian hedgehog''<ref>PMID: 7916661</ref>. With the ability to control such fundamental processes as the anterioposterior patterning of vertebrate limb buds<ref name="limb">PMID: 8269518</ref>, the formation of motor neurons in the neural tube <ref name="neuron">PMID: 7736596</ref>, and the development and maintenance of tissues and organs<ref>PMID: 10980429</ref>, Shh is the most well-studied member of the Hh signaling proteins<ref name="papinsky">PMID: 10753901</ref>. Excessive signaling in adult cells has been implicated in the development of several human cancers<ref>PMID: 14737121</ref><ref name="Path">PMID: 12044012</ref>. Mutations in the ''Shh'' gene can also result in severe developmental consequences, including [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Holoprosencephaly holoprosencephaly] <ref>PMID: 8896572</ref>. | '''Sonic hedgehog''' (Shh) is a member of the Hedgehog (Hh) family of secreted extracellular signaling proteins, which serve important roles in regulating both short-range and long-range patterning processes in developing invertebrate and vertebrate tissues<ref>PMID: 7867057</ref>. First discovered in ''Drosophila'', where mutations of the single ''Hedgehog'' gene produces larvae that are covered in hedgehog-like denticles, Hh proteins are encoded by at least three genes in mammals - ''Sonic'', ''Desert'', and ''Indian hedgehog''<ref>PMID: 7916661</ref>. With the ability to control such fundamental processes as the anterioposterior patterning of vertebrate limb buds<ref name="limb">PMID: 8269518</ref>, the formation of motor neurons in the neural tube <ref name="neuron">PMID: 7736596</ref>, and the development and maintenance of tissues and organs<ref>PMID: 10980429</ref>, Shh is the most well-studied member of the Hh signaling proteins<ref name="papinsky">PMID: 10753901</ref>. Excessive signaling in adult cells has been implicated in the development of several human cancers<ref>PMID: 14737121</ref><ref name="Path">PMID: 12044012</ref>. Mutations in the ''Shh'' gene can also result in severe developmental consequences, including [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Holoprosencephaly holoprosencephaly] <ref>PMID: 8896572</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[Hedgehog signaling pathway]]. | ||
= Biosynthesis = | = Biosynthesis = | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Perrimon N. Hedgehog and beyond. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):517-20. PMID:7867057
- ↑ Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, Shen L, Mohler J, McMahon JA, McMahon AP. Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1417-30. PMID:7916661
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Riddle RD, Johnson RL, Laufer E, Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1401-16. PMID:8269518
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Roelink H, Porter JA, Chiang C, Tanabe Y, Chang DT, Beachy PA, Jessell TM. Floor plate and motor neuron induction by different concentrations of the amino-terminal cleavage product of sonic hedgehog autoproteolysis. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):445-55. PMID:7736596
- ↑ Chuang PT, Kornberg TB. On the range of hedgehog signaling. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000 Oct;10(5):515-22. PMID:10980429
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Pepinsky RB, Rayhorn P, Day ES, Dergay A, Williams KP, Galdes A, Taylor FR, Boriack-Sjodin PA, Garber EA. Mapping sonic hedgehog-receptor interactions by steric interference. J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 14;275(15):10995-1001. PMID:10753901
- ↑ Pasca di Magliano M, Hebrok M. Hedgehog signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003 Dec;3(12):903-11. PMID:14737121 doi:10.1038/nrc1229
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Ruiz i Altaba A, Sanchez P, Dahmane N. Gli and hedgehog in cancer: tumours, embryos and stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002 May;2(5):361-72. PMID:12044012 doi:10.1038/nrc796
- ↑ Roessler E, Belloni E, Gaudenz K, Jay P, Berta P, Scherer SW, Tsui LC, Muenke M. Mutations in the human Sonic Hedgehog gene cause holoprosencephaly. Nat Genet. 1996 Nov;14(3):357-60. PMID:8896572 doi:10.1038/ng1196-357
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Bumcrot DA, Takada R, McMahon AP. Proteolytic processing yields two secreted forms of sonic hedgehog. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):2294-303. PMID:7891723
- ↑ Porter JA, Young KE, Beachy PA. Cholesterol modification of hedgehog signaling proteins in animal development. Science. 1996 Oct 11;274(5285):255-9. PMID:8824192
- ↑ Pepinsky RB, Zeng C, Wen D, Rayhorn P, Baker DP, Williams KP, Bixler SA, Ambrose CM, Garber EA, Miatkowski K, Taylor FR, Wang EA, Galdes A. Identification of a palmitic acid-modified form of human Sonic hedgehog. J Biol Chem. 1998 May 29;273(22):14037-45. PMID:9593755
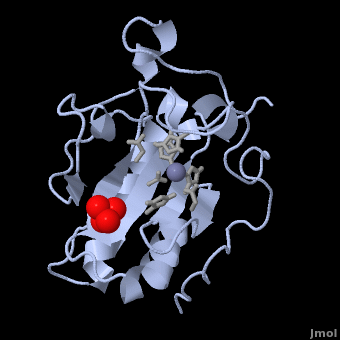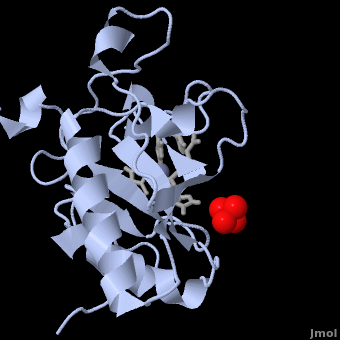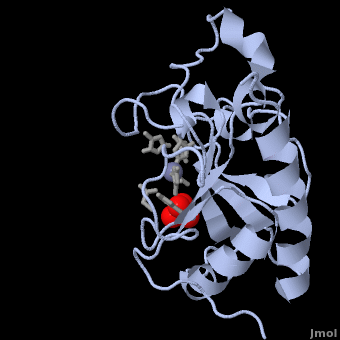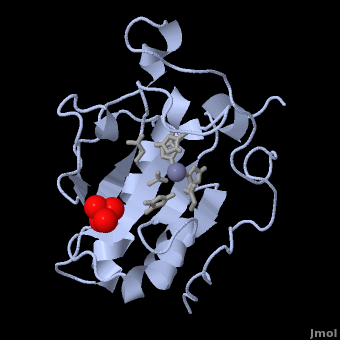
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 13.6 Hall TM, Porter JA, Beachy PA, Leahy DJ. A potential catalytic site revealed by the 1.7-A crystal structure of the amino-terminal signalling domain of Sonic hedgehog. Nature. 1995 Nov 9;378(6553):212-6. PMID:7477329 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/378212a0
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Bumcrot DA, McMahon AP. Sonic hedgehog: making the gradient. Chem Biol. 1996 Jan;3(1):13-6. PMID:8807822
- ↑ Placzek M, Jessell TM, Dodd J. Induction of floor plate differentiation by contact-dependent, homeogenetic signals. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):205-18. PMID:8223247
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Huangfu D, Anderson KV. Signaling from Smo to Ci/Gli: conservation and divergence of Hedgehog pathways from Drosophila to vertebrates. Development. 2006 Jan;133(1):3-14. PMID:16339192 doi:133/1/3
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Randi Woodbeck, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner, Riley Hicks, Andrea Gorrell, Alexander Berchansky
![Figure 2. Shh-N is released from the cell membrane for long-range signaling by zinc-dependent proteolysis. [Note: This figure is adapted from references and .]](/wiki/images/thumb/4/46/Short_and_Long-Range.jpg/180px-Short_and_Long-Range.jpg)
![Figure 3. The Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. In the absence of Shh, Patched inhibits Smo. Inhibition of Patched by Shh activates normal developmental processes. [Note: This figure is adapted from references and .]](/wiki/images/thumb/8/85/SHH_SIGNALING_PATHWAY.jpg/180px-SHH_SIGNALING_PATHWAY.jpg)
