Journal:Acta Cryst F:S2053230X19001213
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
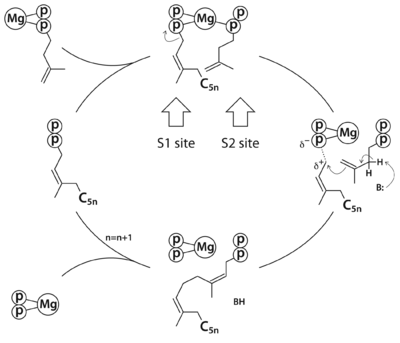
Rv1086 produces Ω-''E,Z''-farnesyl diphosphate (''EZ''-FPP, C15) from geranyl diphosphate (GPP, C10) and isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP, C5) that is used by Rv2361c for further elongation to form decaprenyl diphosphate (DPP, C50). In this structure we have substrate analogues of GPP and IPP as well as the essential Mg ion bound to Rv2361 (''i.e.'' MtDPPS) in a productive mode. GPP binds to S1 site and IPP binds to S2 site. The hydrocarbon chains are joined head-to-tail to form a 5-carbon longer product. Meanwhile, we also have the GPP analogue bound in alternate conformations. The varying interactions of this substrate with Asp76 from one subunit and Arg292 from another may account for the transition pathway from S2 site to S1 site after each cycle of elongation reaction. So the enzyme can proceed to the next cycle of catalysis. | Rv1086 produces Ω-''E,Z''-farnesyl diphosphate (''EZ''-FPP, C15) from geranyl diphosphate (GPP, C10) and isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP, C5) that is used by Rv2361c for further elongation to form decaprenyl diphosphate (DPP, C50). In this structure we have substrate analogues of GPP and IPP as well as the essential Mg ion bound to Rv2361 (''i.e.'' MtDPPS) in a productive mode. GPP binds to S1 site and IPP binds to S2 site. The hydrocarbon chains are joined head-to-tail to form a 5-carbon longer product. Meanwhile, we also have the GPP analogue bound in alternate conformations. The varying interactions of this substrate with Asp76 from one subunit and Arg292 from another may account for the transition pathway from S2 site to S1 site after each cycle of elongation reaction. So the enzyme can proceed to the next cycle of catalysis. | ||
| - | <scene name='80/806392/Cv/8'>Overall structure of MtDPPS</scene> | + | <scene name='80/806392/Cv/8'>Overall structure of MtDPPS</scene>. The two monomers in an asymmetric unit of the MtDPPS crystal are shown as ribbon diagrams. The β-strands are named A-F and the α-helices numbered 1-7 from N to C terminus. They are colored yellow/red for one subunit and magenta/cyan for the other. |
The reaction catalyzed by Rv2361c (or ''M. tuberculosis'' DPP synthase, MtDPPS) is very similar to that of undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase (UPPS), except for the chain length of the final product (C<sub>50</sub> vs C<sub>55</sub>) and the starting allylic substrate (''EZ''-FPP vs ''EE''-FPP). In fact, most ''cis''-PTs share a common dimeric architecture, and the conserved S1 and S2 sites for substrate binding are located near the subunit interface. The starting allylic substrate is bound to the S1 site and the homoallylic substrate to be incorporated is bound to the S2 site. An invariant aspartate residue plays a central role in the catalysis by coordinating the Mg2+-bound substrates. The head-to-tail coupling reaction of ''cis''-PT proceeds through a concerted pathway similar to the ionization-condensation-elimination mechanism of ''trans''-PT. After the new C-C bond formation, the pyrophosphate leaves the S1 site along with Mg2+, and the resulting prenyl diphosphate switches from the S2 site to the S1 site (see static image below). | The reaction catalyzed by Rv2361c (or ''M. tuberculosis'' DPP synthase, MtDPPS) is very similar to that of undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase (UPPS), except for the chain length of the final product (C<sub>50</sub> vs C<sub>55</sub>) and the starting allylic substrate (''EZ''-FPP vs ''EE''-FPP). In fact, most ''cis''-PTs share a common dimeric architecture, and the conserved S1 and S2 sites for substrate binding are located near the subunit interface. The starting allylic substrate is bound to the S1 site and the homoallylic substrate to be incorporated is bound to the S2 site. An invariant aspartate residue plays a central role in the catalysis by coordinating the Mg2+-bound substrates. The head-to-tail coupling reaction of ''cis''-PT proceeds through a concerted pathway similar to the ionization-condensation-elimination mechanism of ''trans''-PT. After the new C-C bond formation, the pyrophosphate leaves the S1 site along with Mg2+, and the resulting prenyl diphosphate switches from the S2 site to the S1 site (see static image below). | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | PDB reference: Rv2361c, [[6ime]]. | + | '''PDB reference: Rv2361c, [[6ime]].''' |
<b>References</b><br> | <b>References</b><br> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.