| 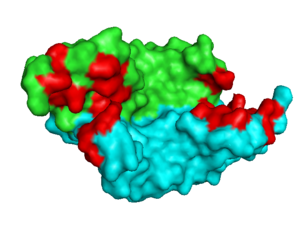 VEGF-A highlighting 2 monomers and binding sites in red, 1vpf Introduction
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors (VEGFs) are a class of proteins that regulate vascular development in embryos and angiogenesis in adult mammals after sustaining an injury or notably in cancerous tumors. A number of structural studies have been conducted on VEGF and its receptors (VEGFRs) to better understand the VEGF-VEGFR interaction and how the signal cascade originating from this interaction leads to a number of biological features. VEGF and its receptors have been closely looked at for their potential use as targets for pharmaceutical medicine with some success. The VEGF family contains:
- VEGF-A which mediates increased vascular permeability[1].
- VEGF-B which is a growth factor [2].
- VEGF-C and VEGF-D are active in angiogenesis[3],[4].
- VEGF-E is found in viruses[5]
- VEGF-F found in snake venom[6].
For additional information see:
VEGFR
VEGF IN COMPLEX WITH A NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY
Autocrine signaling
VEGF signaling pathway.
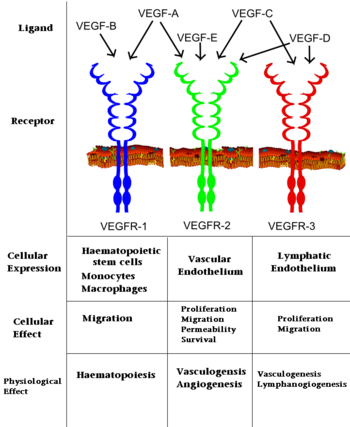 Interaction of VEGFs with VEGFRs. History and Biological Function
VEGF-A was first described by Senger et al. in 1983 as a tumor secreted “vascular-permeability factor (VPF). [7] In 1989, Henzel and Ferrara reported the isolation of an endothelial cell mitogen they named VEGF which also mediated vascular permeability in vivo. Subsequent sequencing revealed that VPF and VEGF were identical, with the VEGF moniker sticking. [8]. VEGF represents a family of homodimeric glycoprotins which are essential for vasculogenesis (embryonic development of blood vessels), Lymphangiogenesis (lymphatic system development) and angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones). [9] VEGF-A, arguably the most important member of the VEGF family, belongs to a gene family that includes placenta growth factor (PIGF) and VEGF’s B, C, D, E (Viral), and F (found in snake toxin) [10].
VEGF is produced by a range of cells including tumor cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, and macrophages. The VEGF-A gene contains a hypoxia responsive element, and hypoxia induces rapid production of VEGF-mRNA[11].The biological function of VEGFs is predicated upon binding to three receptor tyrosine kinases, VEGFR-1-3, that are typically localized on the surface of endothelial cells, bone marrow derived hematopoetic precursor cells, and some malignant cells. [12] VEGF identity determines which of the VEGFRs it binds with high affinity (See Image at the left). VEGF binding of a VEGFR begins a cascade reaction which ultimately leads to angiogenesis, vasculogenesis or haematopoiesis. The biological importance of VEGFs, especially VEGF-A, is highlighted by the fact that VEGF-A -/- knockout mice exhibit severe defects in vascular development and die at E9.5-10.5 [13]. Additionally, loss of just a single VEGF-A allele leads to vascular defects and death by E11-12 [14].
Structure of VEGF-A & its Biology
is a homodimer composed of two 23 kDa subunits. VEGF-A exists in a number of different isoforms following alternative splicing of its precursor mRNA [15]. In humans, 6 variants have been found: VEGF-A-121, VEGF-A-145, VEGF-A-165, VEGF-A-183, VEGF-A-189, and VEGF-A-206, with VEGF-A-165 the most abundantly expressed. All VEGF-A isoforms bind to VEGFR-1 and -2.
The amino acids determined to be are D63, L66, and E67. VEGF-A binding by VEGFR-1 leads to cellular proliferation, migration, and increased cellular permeability resulting in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Those residues are I43, I46, Q79, I83, K84 and P85.[16] Binding of VEGF-A to VEGFR-2 results in similar Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, but also lymphangiogenesis in embryos. The remainder of the is formed by D34, S50, E64, and F36. It is upon binding of VEGFR by VEGF that the subsequent signal cascade is initiated leading to angiogenesis, etc.[17]
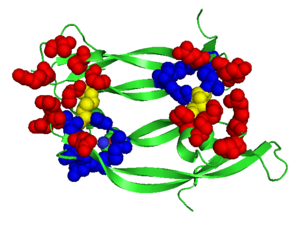 Structure of VEGF-E. Red Highlights Binding sites, Blue Highlights the Cysteine Knot, Yellow Highlights the intermolecular Dislufide bonds, 2gnn Structure of VEGF-E as a Model
Although VEGF-E is only found in viral sources and thus is of less importance than VEGF-A, analysis of its structure is informative because it is the only member of the VEGF family that binds exclusively to VEGFR-2, the most essential VEGF receptor. Further, VEGF-E shares significant homology to VEGF-A, and thus can serve as an effective model. [18]
consists of a homodimer that is covalently linked by two intermolecular disulfide bonds between .
Each monomer contains a central antiparallel beta sheet, with the canonical found in other VEGFs. [19] The knot consists of an eight residue ring formed by the backbone of residues 57-61 and 102-104 and intramolecular disulfide bridges Cys57-Cys102 and Cys61-Cys104, and a third bridge, Cys26-Cys68, that passes perpendicularly through the ring. Each VEGF-E monomer contains an amino terminal alpha helix and three solvent accessible loop regions, L2, .
are able to form a complex hydrogen bond network as well as extensive hydrophobic contacts with VEGFR making these loops ideal receptor specificity determinants. Residues: P34, S36, T43, P50, R46, D63, E64, and E67 make up the and are critical for binding to VEGFR-2 as determined by alanine mutagenesis.[20] Further, the salt bridge between is believed to be the source of VEGF-E’s VEGFR-2 specificity by preventing binding to VEGFR-1. [21]
 Image of a blood vessel with an erythrocyte (E) within its lumen and endothelial cells form its its tunica intima Medical Implications
VEGF has received significant attention from the pharmaceutical industry in the hopes of correcting impaired vessel function. Such impaired vessel function accompanies many pathologies including atherosclerosis, arthritis, some neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS, and malignant cell growth such as cancerous tumors. [22] In fact, numerous studies highlighted the increased expression of VEGF in cancer cells resulting in tumoral angiogenesis, providing the tumor with the network of blood vessels need to grow and expand. VEGF expression is stimulated by hypoxia, a common characteristic of most newly formed tumors, and genetic mutations such as K-ras and p53, extremely common mutations present in a majority of cancers. [23] Since angiogenesis in typical adults is infrequent while extremely common in tumors, VEGF serves as a selective therapeutic target for cancer. A number of drugs, like Bevacizumab (a monoclonal antibody better known as Avastin) have been developed to interrupt the VEGF-VEGFR connection, with some success. Avastin binds to and inhibits all VEGF-A isoforms and has achieved megablockbuster status by earning over $5 billion in 2009 for Roche. [24]
3D Structures of VEGF
VEGF 3D Structures
Additional Resources
For additional information, see:
References
- ↑ Wiszniak S, Schwarz Q. Exploring the Intracrine Functions of VEGF-A. Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 19;11(1):128. PMID:33478167 doi:10.3390/biom11010128
- ↑ Li X, Lee C, Tang Z, Zhang F, Arjunan P, Li Y, Hou X, Kumar A, Dong L. VEGF-B: a survival, or an angiogenic factor? Cell Adh Migr. 2009 Oct-Dec;3(4):322-7. PMID:19684473 doi:10.4161/cam.3.4.9459
- ↑ Witzenbichler B, Asahara T, Murohara T, Silver M, Spyridopoulos I, Magner M, Principe N, Kearney M, Hu JS, Isner JM. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C/VEGF-2) promotes angiogenesis in the setting of tissue ischemia. Am J Pathol. 1998 Aug;153(2):381-94. PMID:9708799 doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65582-4
- ↑ Bokhari SMZ, Hamar P. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-D (VEGF-D): An Angiogenesis Bypass in Malignant Tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 28;24(17):13317. PMID:37686121 doi:10.3390/ijms241713317
- ↑ Wise LM, Inder MK, Real NC, Stuart GS, Fleming SB, Mercer AA. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-E encoded by orf virus regulates keratinocyte proliferation and migration and promotes epidermal regeneration. Cell Microbiol. 2012 Sep;14(9):1376-90. PMID:22507661 doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01802.x
- ↑ Suto K, Yamazaki Y, Morita T, Mizuno H. Crystal structures of novel vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) from snake venoms: insight into selective VEGF binding to kinase insert domain-containing receptor but not to fms-like tyrosine kinase-1. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 21;280(3):2126-31. Epub 2004 Nov 12. PMID:15542594 doi:10.1074/jbc.M411395200
- ↑ Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):983-5. PMID:6823562
- ↑ Ferrara N, Henzel WJ. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851-8. PMID:2735925
- ↑ Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004 Aug;25(4):581-611. PMID:15294883 doi:10.1210/er.2003-0027
- ↑ Suto K, Yamazaki Y, Morita T, Mizuno H. Crystal structures of novel vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) from snake venoms: insight into selective VEGF binding to kinase insert domain-containing receptor but not to fms-like tyrosine kinase-1. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 21;280(3):2126-31. Epub 2004 Nov 12. PMID:15542594 doi:10.1074/jbc.M411395200
- ↑ Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):843-5. PMID:1279431 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/359843a0
- ↑ Ferrara N, Davis-Smyth T. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1997 Feb;18(1):4-25. PMID:9034784
- ↑ Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, Fahrig M, Vandenhoeck A, Harpal K, Eberhardt C, Declercq C, Pawling J, Moons L, Collen D, Risau W, Nagy A. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature. 1996 Apr 4;380(6573):435-9. PMID:8602241 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/380435a0
- ↑ Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, Fahrig M, Vandenhoeck A, Harpal K, Eberhardt C, Declercq C, Pawling J, Moons L, Collen D, Risau W, Nagy A. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature. 1996 Apr 4;380(6573):435-9. PMID:8602241 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/380435a0
- ↑ Robinson CJ, Stringer SE. The splice variants of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors. J Cell Sci. 2001 Mar;114(Pt 5):853-65. PMID:11181169
- ↑ Muller YA, Li B, Christinger HW, Wells JA, Cunningham BC, de Vos AM. Vascular endothelial growth factor: crystal structure and functional mapping of the kinase domain receptor binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jul 8;94(14):7192-7. PMID:9207067
- ↑ Keyt BA, Nguyen HV, Berleau LT, Duarte CM, Park J, Chen H, Ferrara N. Identification of vascular endothelial growth factor determinants for binding KDR and FLT-1 receptors. Generation of receptor-selective VEGF variants by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 8;271(10):5638-46. PMID:8621427
- ↑ Pieren M, Prota AE, Ruch C, Kostrewa D, Wagner A, Biedermann K, Winkler FK, Ballmer-Hofer K. Crystal structure of the Orf virus NZ2 variant of vascular endothelial growth factor-E. Implications for receptor specificity. J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 14;281(28):19578-87. Epub 2006 May 3. PMID:16672228 doi:10.1074/jbc.M601842200
- ↑ Oefner C, D'Arcy A, Winkler FK, Eggimann B, Hosang M. Crystal structure of human platelet-derived growth factor BB. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3921-6. PMID:1396586
- ↑ Pieren M, Prota AE, Ruch C, Kostrewa D, Wagner A, Biedermann K, Winkler FK, Ballmer-Hofer K. Crystal structure of the Orf virus NZ2 variant of vascular endothelial growth factor-E. Implications for receptor specificity. J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 14;281(28):19578-87. Epub 2006 May 3. PMID:16672228 doi:10.1074/jbc.M601842200
- ↑ Errico M, Riccioni T, Iyer S, Pisano C, Acharya KR, Persico MG, De Falco S. Identification of placenta growth factor determinants for binding and activation of Flt-1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 15;279(42):43929-39. Epub 2004 Jul 21. PMID:15272021 doi:10.1074/jbc.M401418200
- ↑ Brockington A, Lewis C, Wharton S, Shaw PJ. Vascular endothelial growth factor and the nervous system. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2004 Oct;30(5):427-46. PMID:15488020 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2004.00600.x
- ↑ Doyle B, Morton JP, Delaney DW, Ridgway RA, Wilkins JA, Sansom OJ. p53 mutation and loss have different effects on tumourigenesis in a novel mouse model of pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma. J Pathol. 2010 Jun 17. PMID:20662002 doi:10.1002/path.2748
- ↑ http://www.foxbusiness.com/story/markets/industries/technology/roche-increased-avastin-sales-efforts-doubles-force/
|