Introduction
Before the emergence of the SARS-CoV, no research efforts were being directed toward the discovery of antiviral drugs against coronaviruses. The high infectivity and mortality rate established SARS as a significant global threat for which no efficacious therapy was available. Since the epidemic, which began in 2003, new insights into the genomics and pathogenisis of the SARS-CoV revealed several novel potential anti-coronavirus targets. Several proteins encoded by the SARS-CoV could be considered as targets for therapeutic intervention. The focus of this article is the SARS-CoV main protease. This protease is an essential enzyme for proteoplytic maturation of nonstructural proteins and is implicated as a potential antiviral drug target[1].
Coronaviruses
Coronaviruses are enveloped, positive-sense RNA viruses and are the second most prevalent cause of the common cold (rhinoviruses are the first). These viruses have the longest non-segmented RNA genomes currently known, ranging from 27 to 31 kb. Translation of the genome occurs in two phases: (1) the early phase where the viral replicase complex is assembled, and (2) the late phase, structural and nonstructural proteins are translated from a negative-sense RNA template. [2] The maturation of the RNA polymerase is achieved through extensive proteolytic processing by three cysteine peptidases. Two are papain-like proteases (PLpro) and the third is the main protease, also known as the 3C-like protease (3Clpro). [3]
SARS
The highly infectious severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) has caused one near pandemic to date, between the months of November 2002 and July 2003, with 8,096 known cases and 774 confirmed deaths (a fatality rate of nearly 10%). Genetic comparisons revealed this virus as a completely new coronavirus. [4] According to the World Health Organization's (WHO) April 2004 concluding report, China had the vast majority of cases, but Taiwan, Singapore, and Canada also had cases in the hundreds. [5] The virus spread to 37 countries, but the Global Alert and Response system as well as drastic action taken by the Chinese government effectively limited the spread of the disease. It has been established that the SARS virus can infect birds, livestock, and pets. [6] The re-emergence of SARS-CoV2 in late 2019/early 2020 led to a global pandemic [7].
The SARS Main Protease
Development of broad spectrum antivirals for coronaviruses is highly desirable as several new species have been recently discovered and the coronaviruses tend to have a wide host range . Thus the highly conserved Mpro is an ideal target for viral inhibition. The Mpro is necessary for cleaving at least 11 conserved sites containing a large hydrophobic residue (preferably Leu) in P2, a Gln in the P1 position, and a small aliphatic aa residue (Ser,Gly,Ala) in the P1’ position. [8]
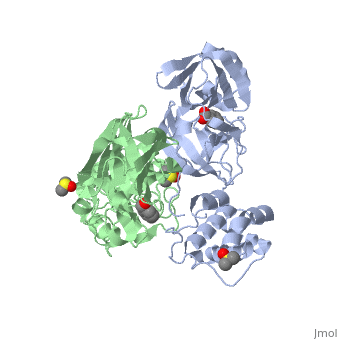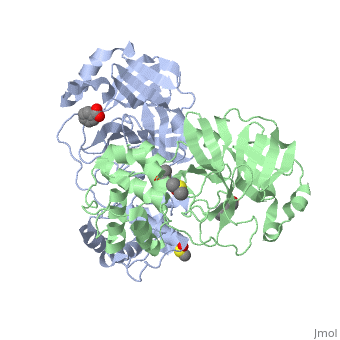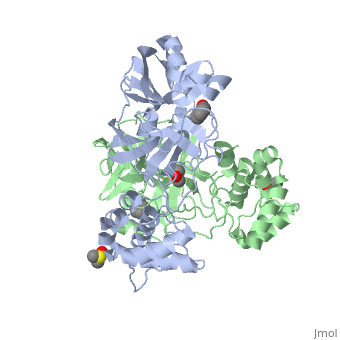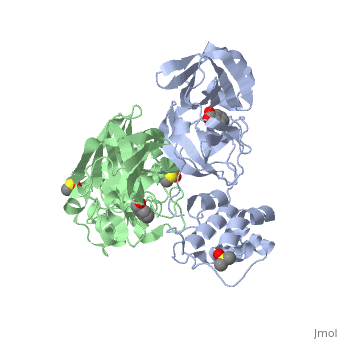
The SARS main protease, Mpro, is a 33.8 kDA protein belonging to the cysteine protease family. As in all coronaviruses, except infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), the enzyme is a homodimer. [9] It has been established that dimerization is essential for catalytic activity because the N-finger of one subunit is involved in organizing the substrate binding-pocket of the other. Furthermore, deletion of the N-finger also results in the inability of the monomers to dimerize.
Each monomer of the SARS Mpro consists of three domains. The two monomers are arranged perpendicular to each other and the active site is located at the connection between the first (residues 1-101) and second domain (residues 102-184). The catalytic dyad is composed of Histidine 41 and Cysteine 145. From the pH dependency of enzymatic activity, the pKa's have been determined as 6.4 for the histidine and 8.3 for the cysteine. The cysteine acts as the nucleophile in the proteolytic cleavage reaction. [10]
Peptidic inhibitors
A number of structures of MPro with candidate inhibitors have been determined, including , , , , , and 6WTT.
Mechanism of Inactivation by Benzotriazole Esters

A number of peptidic inhibitors have been derived from substrate cleavage consensus sequences, but until recently there have been only a small number of nonpeptidic inhibitors reported. Rather serendipitously, it was noticed that the intermediate benzotriazole esters, occurring during the synthesis of HIV proteinase inhibitors, were better inhibitors of the SARS Mpro than the end products themselves. These inhibitors have a reported Ki of 7.5 nM, among the highest levels of inhibition described so far. Spectrometric analyses suggested that the benzotriazole are mechanism based inhibitors which irreversibly acylate the active-site Cys145. Better visualization of the binding mode was observed through x-ray crystallography of the enzyme incubated with two benzotriazole ester compounds: 1-(benzoyloxy)-benzotriazole (compound XP-27) and 1-(4-dimethylaminobenzoyloxy)-benzotriazole (compound XP-59). Kinetic analysis found that XP-59 was more stable, and unlike XP-27, it showed a normal hyperbolic inhibition curve. XP-59 and its covalent Mpro product were more stable due to the electron donating nature of the p-dimethylamino group, which reduces the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon compared to XP-27. Addition of XP-27 to the enzyme led to rapid inactivation, however, after a few minutes the enzyme activity began to recover due to the instability of the thioester product. [11]
3D structures of SARS-Cov proteinase
See Virus protease 3D structures
References
- ↑ Takahashi D, Hiromasa Y, Kim Y, Anbanandam A, Yao X, Chang KO, Prakash O. Structural and dynamics characterization of norovirus protease. Protein Sci. 2013 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/pro.2215. PMID:23319456 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pro.2215
- ↑ Murray, Patrick R., Ken S. Rosenthal, and Michael A. Pfaller. "Coronaviruses and Noroviruses." Medical Microbiology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier, 2009. 565-68. Print.
- ↑ Ziebuhr, J., Herold,J., and Siddell, S.G. (1995). Characterization of a human coronavirus (strain 229E) 3C-like proteinase activity. J. Virol. 69, 4331-4338.
- ↑ Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1953-1966
- ↑ "Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003". WHO. Retrieved 2008-10-31.
- ↑ Li W, Shi Z, Yu M, et al. (2005). "Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses". Science (journal) 310 (5748): 676–9. doi:10.1126/science.1118391. PMID 16195424.
- ↑ Sharma A, Ahmad Farouk I, Lal SK. COVID-19: A Review on the Novel Coronavirus Disease Evolution, Transmission, Detection, Control and Prevention. Viruses. 2021 Jan 29;13(2):202. PMID:33572857 doi:10.3390/v13020202
- ↑ Ziebuhr, J., Snijder, E.J., and Gorbaleya, A.E. (2000). Virus-encoded proteinases and proteolytic processing in Nidovirales. J. Gen. Virol. 81, 853-879.
- ↑ Anad, K., Ziebhr, J., Wadhani, P., Mesters, J.R., and Hilgenfeld, R. (2003). Coronavirus main protease (3CLPro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science300, 1763-1767.
- ↑ Anad, K., Ziebhr, J., Wadhani, P., Mesters, J.R., and Hilgenfeld, R. (2003). Coronavirus main protease (3CLPro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science300, 1763-1767.
- ↑ Verschueren, Koen H.G., Ksenia Pumpor, Stefan Anemüller, Shuai Chen, Jeroen R. Mesters, and Rolf Hilgenfeld. "A Structural View of the Inactivation of the SARS Coronavirus Main Proteinase by Benzotriazole Esters." Chemistry & Biology 15.6 (2008): 597-606. Web. Oct. 2010.