This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1789
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: {{Template:Sandbox_Reserved_Eric_Martz_3}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side...) |
|||
| (40 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {{ | + | {{BAMBED |
| - | == | + | |DATE=June 14, 2016 |
| - | + | |OLDID=2607465 | |
| - | + | |BAMBEDDOI=10.1002/bmb.21026 | |
| - | + | }} | |
| - | == Function == | ||
| - | == | + | ==SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS== |
| + | <StructureSection load='7UPI' size='340' side='right' caption='SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C'> | ||
| - | == | + | == Introduction == |
| - | == | + | <scene name='95/952717/Zoom_out/1'>SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS</scene> (SMP) is a ternary holophosphotase complex formed by the individual proteins: SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. The SMP complex is involved in signaling the initiation of [https://www.nature.com/articles/7290105. MAPK pathways], which is responsible for cellular growth and development, cell proliferation, and apoptosis <ref name="Hauseman">PMID:35830882</ref>. Formation of this complex begins with an extracellular signal binding to a membrane embedded receptor [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2536775/. tyrosine kinase receptor(RTK)] <ref name="Hauseman"/>. This causes membrane-bound MRAS to exchange GDP for GTP. Initiating the SMP complex formation at the plasma membrane consists of the SHOC2 and PP1C binding first. When the MRAS exchanges GDP to GTP, it then assembles with the combined SHOC2 and PP1C. Based on MRAS targeting, PP1C catalyzes the [https://www.cell.com/fulltext/S0092-8674(00)81356-2. dephosphorylation] of the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) on the [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3128629/. RAF complex] leading to the amplification of MAPK signaling <ref name="Hauseman"/>. In a normal cell, this would regulate cell proliferation but dysfunction in the ternary complex has shown signs to lead to tumor formation due to unregulated cell growth <ref name="Hauseman"/>. |
| - | This is a | + | [[Image:Mechanism.png|200px|center|thumb|Figure 1: Mechanism for Shoc2-MRAS-PP1C]] |
| + | [[Image:Phosphorylation.png|200px|center|thumb|Figure 2: PP1C phosphorylates Serine 259.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Overall Structure == | ||
| + | === SHOC2 === | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Shoc2/1'>SHOC2</scene> is a scaffold protein composed of 20 [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3901792/. leucine-rich repeat (LRR)] domains that form a solenoid structure <ref name="Hauseman"/>. The leucine rich region forms a concave hydrophobic core which is necessary for binding with PP1C and MRAS. SHOC2 is the crucial mediator for SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS complex formation <ref name="Hauseman"/>. The leucine rich domain is very important in creating selectivity for the PP1C protein, as that protein is used for so many other complex pathways <ref name="Hauseman"/>. The LRR domains are stabilized by an N-terminal flanking 𝝰-helix and a C-terminal helix-turn-helix <ref name="Kwon">PMID:35831509</ref>. Alongside the conserved leucine residues in the LRR domain, there is a group of conserved asparagine residues that creates a stabilizing [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7184636/. “asparagine ladder”] that is necessary for the LRR fold, giving the SHOC2 its concave structure <ref name="Kwon" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | SHOC2 is also capable of causing various forms of cancers and rasopathies. A common one is caused by a mutation known as p.S2G <ref name="Rauen">Rauen KA. The RASopathies. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2013;14:355-69. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153523 doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153523.]</ref>. This mutation causes the formation of an additional 14-carbon saturated fatty acid chain on the N-terminal glycine of SHOC2 <ref name="Rauen" />. This causes SHOC2 to become attached to the cell membrane, resulting in a prolonged dephosphorylation of RAF by PP1C <ref name="Rauen" />. With this abnormality, there is overexpression of the MAPK pathway and increased cell proliferation genes <ref name="Rauen" />. This can cause the formation of various tumors in the body. Other mutations of the SMP ternary structure as a whole can also lead to the development of Noonan syndrome <ref name="Hauseman"/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === PP1C === | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Pp1c/2'>PP1C</scene> is a phosphatase. After forming a ternary complex, the hydrophobic active site on PP1C interacts with Raf and dephosphorylate Ser 259. PP1C's active site is adjacent to a hydrophobic binding pocket that binds to the C-terminal phosphoserine, located on the N-terminus of RAF, the target for dephosphorylation. PP1C can act as a phosphatase in the absence of SHOC2 but PP1C lacks intrinsic substrate selectively. The SMP complex formation endows PP1C with specificity for RAF <ref name="Hauseman" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The mechanism that PP1C uses to catalyze the dephosphorylation is mainly through donating a hydrogen atom to a phosphate group on the C-terminal of a phosphoserine on Raf <ref name="Kubicek"/>. This makes the phosphate group a good leaving group and it breaks off <ref name="Kubicek"/>. This catalysis is done by the serine-threonine alpha catalytic site on PP1C <ref name="Kubicek"/>. In this catalytic site, there are two Manganese ions and one calcium ion <ref name="Kubicek"/>. These metal ions are necessary in stablizing this catalytic site and there are a lot of polar negative residues in this region <ref name="Kubicek"/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The catalytic site is also capable of causing various rasopathies if there is a mutation present <ref name="Rauen" />. Typically the mutation is centered around the catalytic site not being able to attach to the dephosphorylation site on Ras <ref name="Rauen" />. This causes an underproduction of cell proliferation pathways and leads to Rasopathies. RASopathy is a broad term used to describe developmental syndromes that stem from germline mutations of proteins along the RAS/MAPK pathway. These mutations can be either gain or loss of function. Rasopathies can also lead to cancer <ref name="Rauen" />. The mutation in PP1C can result in damages in growth and development in multiple areas of the body .<ref name="Rauen" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === MRAS === | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> is a monomeric GTPase. MRAS is membrane-bound due to post-translational lipidation which allows the protein to interact with the inner membrane leaflet. <ref name="Seabra">PMID:9607139</ref> MRAS localizes the SMP complex near RAF and other components of downstream signaling. The region of MRAS not directly bound to the membrane binds SHOC2 and PP1C to orient the complex such that PP1C’s active site faces the serine that will get dephosphorylated on RAF. MRAS also controls SMP complex formation in connection with extracellular signaling based on its dualistic switching between its inactive and active state. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by growth factors, the GDP is exchanged for GTP when a ligand binds to the RTK <ref name="Hauseman" />. The now <scene name='95/952718/Zoom_in_gtp/1'>GTP bound MRAS</scene> undergoes a conformational change of the <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>switch I and switch II regions</scene>. These regions are the major binding sites with SHOC2. This conformational change activates MRAS allowing it to bind with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. In its inactive GDP-bound state, MRAS is sterically occluded from binding SHOC2. For example, R83 of GDP-bound MRAS directly clashes with SHOC2 as shown in figure 2. In comparison to other RAS proteins such as H/K/NRAS, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex<ref name="Kubicek">Kubicek M, Pacher M, Abraham D, Podar K, Eulitz M, Baccarini M. Dephosphorylation of Ser-259 regulates Raf-1 membrane association. J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 8;277(10):7913-9. [http://10.1074/jbc.M108733200 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108733200.]</ref>. This indicates that the specific structure of MRAS is necessary for SMP function. While MRAS engages the SHOC2-PP1C complex to bring the complex to the membrane, an additional membrane-bound RAS binds RAF nearby. This binding is also stimulated by ligand binding to the RTK. This indicates that for full RAF activation and continuous signaling of Raf, two separate active RAS proteins are needed. Having two MRASs also help with the co-localization of PP1C to the NTpS region on RAF. To inactivate Raf signaling, MRAS uses its intrinsic GTPase to remove the activating gamma-phosphate on GTP. In the GDP-bound state, switch I and II move to the position shown in green in Figure 2. This inactivates SHOC2 binding due to steric clashing which causes the SMP structure to dissociate. | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952716/Gtp/1'>GTP-MRAS(full-image)</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952716/Gtp/1'>GTP-MRAS(zoomed-in)</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952716/Ras-swtich/2'>Switch I-II (full-image)</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>Switch I-II (zoomed-in)</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Key Ligand Interactions === | ||
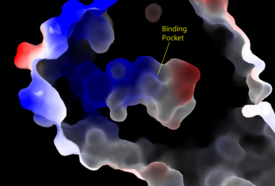
| + | [[Image:Amphbindingfinal.png|275 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 3''': Electrostatic illustration of the amphipathic binding pocket of the LPA<sub>1</sub> receptor. This binding pocket was revealed by cutting away the exterior or the protein. This binding pocket, located in the interior of the protein, has both polar and nonpolar regions. The blue and red coloration highlight the positively and negatively charged regions, respectively, and the white color shows the nonpolar region of the binding pocket.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === SHOC2 and PP1C === | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Shoc2_and_pp1c/1'>Shoc2-PP1C</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Shoc2_and_pp1c/2'>SHOC2-PP1C Binding Pocket</scene> | ||
| + | === SHOC2 and MRAS === | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952716/Scho2-mras-interactions/2'>SHOC2-MRAS(full-image)</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952716/Scho2-mras-interactions/1'>SHOC2-MRAS (residues)</scene> | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952716/Scho2-mras-interactions/3'>SHOC2-MRAS (surface)</scene> | ||
| + | === PP1C and MRAS === | ||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Mras_and_pp1c/1'>PP1C (blue) and MRAS (white)</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Mras_and_pp1c/4'>PP1C and MRAS residue interactions</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Signaling Pathway == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='95/952717/Pp1c_hydrophobic_patch/1'>PP1C Hydrophobic Patch and Active Site</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Disease Relevance == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Cancer === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === RASopathies=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Future Studies == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of lysophosphatidic acid receptor== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[4z34]], [[4z35]], [[4z36]] - hLPA1 + antagonist - human<br /> | ||
| + | [[2lq4]] – hLPA1 second extracellular loop – NMR<br /> | ||
| + | [[4p0c]] – hLPA2/NHERF2<br /> | ||
| + | [[5xsz]] – LPA6A (mutant) – zebra fish<br /> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | ==Proteopedia Resources== | ||
| + | [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Lysophosphatidic_acid_binding Category:Lysophosphatidic acid binding] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Lysophosphatidic_acid Category:Lysophosphatidic acid] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/User:R._Jeremy_Johnson/CH462:Biochemistry_II_Butler_University Butler University Proteopedia Pages] | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also: | ||
| + | *[[Receptor]] | ||
| + | *[[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
| + | *[[G protein-coupled receptors]] | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | ==Student Contributors== | ||
| + | Madeline Gilbert | ||
| + | Inaya Patel | ||
| + | Rushda Hussein | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Featured in BAMBED]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
This page, as it appeared on June 14, 2016, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS
| |||||||||||
Student Contributors
Madeline Gilbert Inaya Patel Rushda Hussein