Sandbox Reserved 1765
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <scene name='95/952693/Shoc2_gtp_bound_vs_gdp_bound/7'>Text To Be Displayed</scene>{{Template:CH462_Biochemistry_II_2023}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | |
| - | {{Template:CH462_Biochemistry_II_2023}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | + | |
=SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS= | =SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS= | ||
<StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C Holophosphatase Complex' scene='95/952694/Overall_image/2'> | <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' side='right' caption='SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C Holophosphatase Complex' scene='95/952694/Overall_image/2'> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
In all images and animations, {{Font color|cyan|SHOC2}} will be shown as cyan blue, {{Font color|lime|MRAS}} as lime, and {{Font color|violet|PP1C}} as violet. Other important components involved in the function of the SMP complex include the {{Font color|salmon|14-3-3}} dimer and {{Font color|slate-blue|Raf}}, which will be shown in salmon and slate-blue, respectively. | In all images and animations, {{Font color|cyan|SHOC2}} will be shown as cyan blue, {{Font color|lime|MRAS}} as lime, and {{Font color|violet|PP1C}} as violet. Other important components involved in the function of the SMP complex include the {{Font color|salmon|14-3-3}} dimer and {{Font color|slate-blue|Raf}}, which will be shown in salmon and slate-blue, respectively. | ||
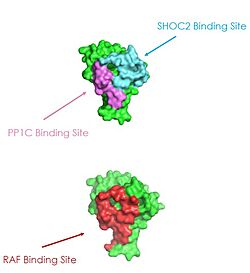
| + | [[Image:RASRAF.png|250 px|right|thumb|Figure 2: MRAS binding sites with SHOC2, PP1C, and RAF (PDB 7DSO).<ref name="Liau">PMID: 35768504</ref>.]] | ||
| - | + | <scene name='95/952693/Shoc2_gtp_bound_vs_gdp_bound/7'>6° conformational change</scene> | |
== Structure of Subunits == | == Structure of Subunits == | ||
=== SHOC2 === | === SHOC2 === | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
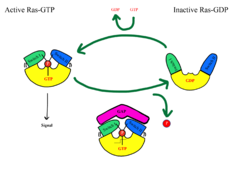
The Ras-Raf signaling cascade will be inhibited without the dephosphorylation of Raf at Ser259. There is a <scene name='95/952695/14-3-3/1'>14-3-3</scene> dimer present in the cytoplasm that interacts with Raf through hydrogen bonds between R129 of 14-3-3 and Ser259 of Raf when Ser259 is phosphorylated. This interaction causes an <scene name='95/952695/Autoinhibited_confirmation/7'>autoinhibited confirmation</scene> as 14-3-3 restricts Raf to the cytoplasm and sterically inhibits Raf from binding with activated Ras. This interaction is crucial in regulating cell proliferation, as it prevents cell growth in the absence of a signal. Extracellular growth factors trigger GTP to bind to MRAS, which triggers SMP formation. Upon SMP complex formation, PP1C is brought into close proximity of Ras, leading to the dephosphorylation of Ser259 of Raf by the active site of PP1C. Once dephosphorylated, Raf is in the <scene name='95/952695/Non-inhibited_confirmation/9'>active confirmation</scene>, allowing for the interaction of Ras and Raf, and the initiation of the signaling cascade.<ref name="Young">PMID: 30348783</ref> | The Ras-Raf signaling cascade will be inhibited without the dephosphorylation of Raf at Ser259. There is a <scene name='95/952695/14-3-3/1'>14-3-3</scene> dimer present in the cytoplasm that interacts with Raf through hydrogen bonds between R129 of 14-3-3 and Ser259 of Raf when Ser259 is phosphorylated. This interaction causes an <scene name='95/952695/Autoinhibited_confirmation/7'>autoinhibited confirmation</scene> as 14-3-3 restricts Raf to the cytoplasm and sterically inhibits Raf from binding with activated Ras. This interaction is crucial in regulating cell proliferation, as it prevents cell growth in the absence of a signal. Extracellular growth factors trigger GTP to bind to MRAS, which triggers SMP formation. Upon SMP complex formation, PP1C is brought into close proximity of Ras, leading to the dephosphorylation of Ser259 of Raf by the active site of PP1C. Once dephosphorylated, Raf is in the <scene name='95/952695/Non-inhibited_confirmation/9'>active confirmation</scene>, allowing for the interaction of Ras and Raf, and the initiation of the signaling cascade.<ref name="Young">PMID: 30348783</ref> | ||
| + | [[Image:pic3.jpg|250 px|right|thumb|Figure 2: MRAS binding sites with SHOC2, PP1C, and RAF (PDB 7DSO).<ref name="Liau">PMID: 35768504</ref>.]] | ||
=== Switch I and Switch II === | === Switch I and Switch II === | ||
Current revision
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS
| |||||||||||
Protopedia Resources
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Kwon JJ, Hajian B, Bian Y, Young LC, Amor AJ, Fuller JR, Fraley CV, Sykes AM, So J, Pan J, Baker L, Lee SJ, Wheeler DB, Mayhew DL, Persky NS, Yang X, Root DE, Barsotti AM, Stamford AW, Perry CK, Burgin A, McCormick F, Lemke CT, Hahn WC, Aguirre AJ. Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. PMID:35831509 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Hauseman ZJ, Fodor M, Dhembi A, Viscomi J, Egli D, Bleu M, Katz S, Park E, Jang DM, Porter KA, Meili F, Guo H, Kerr G, Molle S, Velez-Vega C, Beyer KS, Galli GG, Maira SM, Stams T, Clark K, Eck MJ, Tordella L, Thoma CR, King DA. Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. PMID:35830882 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3
- ↑ Hurley TD, Yang J, Zhang L, Goodwin KD, Zou Q, Cortese M, Dunker AK, DePaoli-Roach AA. Structural basis for regulation of protein phosphatase 1 by inhibitor-2. J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28874-83. Epub 2007 Jul 18. PMID:17636256 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M703472200
- ↑ Young LC, Hartig N, Boned Del Río I, Sari S, Ringham-Terry B, Wainwright JR, Jones GG, McCormick F, Rodriguez-Viciana P. SHOC2-MRAS-PP1 complex positively regulates RAF activity and contributes to Noonan syndrome pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10576-E10585. PMID:30348783 doi:10.1073/pnas.1720352115
- ↑ Lavoie H, Therrien M. Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signalling pathway. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. PMID:35970881 doi:10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7
1. Hauseman ZJ, Fodor M, Dhembi A, Viscomi J, Egli D, Bleu M, Katz S, Park E, Jang DM, Porter KA, Meili F, Guo H, Kerr G, Mollé S, Velez-Vega C, Beyer KS, Galli GG, Maira SM, Stams T, Clark K, Eck MJ, Tordella L, Thoma CR, King DA. Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):416-423. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. Epub 2022 Jul 13. PMID: 35830882; PMCID: PMC9452295.[1].
2. Hurley TD, Yang J, Zhang L, Goodwin KD, Zou Q, Cortese M, Dunker AK, DePaoli-Roach AA. Structural basis for regulation of protein phosphatase 1 by inhibitor-2. J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28874-28883. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703472200. Epub 2007 Jul 18. PMID: 17636256.[2].
3. Kwon JJ, Hajian B, Bian Y, Young LC, Amor AJ, Fuller JR, Fraley CV, Sykes AM, So J, Pan J, Baker L, Lee SJ, Wheeler DB, Mayhew DL, Persky NS, Yang X, Root DE, Barsotti AM, Stamford AW, Perry CK, Burgin A, McCormick F, Lemke CT, Hahn WC, Aguirre AJ. Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):408-415. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. Epub 2022 Jul 13. PMID: 35831509; PMCID: PMC9694338.[3].
4. Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):400-407. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. Epub 2022 Jun 29. PMID: 35768504; PMCID: PMC9452301.[4].
5. Lavoie H, Therrien M. Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signalling pathway. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. PMID: 35970881.[5].
6. Young LC, Hartig N, Boned Del Río I, Sari S, Ringham-Terry B, Wainwright JR, Jones GG, McCormick F, Rodriguez-Viciana P. SHOC2-MRAS-PP1 complex positively regulates RAF activity and contributes to Noonan syndrome pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10576-E10585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720352115. Epub 2018 Oct 22. PMID: 30348783; PMCID: PMC6233131.[6].
Student Contributors
- Sloan August
- Rosa Trippel
- Kayla Wilhoite