User:Marcos Vinícius Caetano/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Marcos Vinícius Caetano(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
*'''Insert 2''' (<scene name='97/973101/774-812_orange/2'>Pro774-Tyr812</scene>) - it redirects the lever arm towards the minus end. It also contains a new calmodulin-binding motif. | *'''Insert 2''' (<scene name='97/973101/774-812_orange/2'>Pro774-Tyr812</scene>) - it redirects the lever arm towards the minus end. It also contains a new calmodulin-binding motif. | ||
*'''<scene name='97/973101/Iq_motif/1'>IQ motif</scene>''' - Constitute the binding sites for Calcium-free, Calcium-calmodulin (CaM) or Apocalmodulin (apo-CaM). | *'''<scene name='97/973101/Iq_motif/1'>IQ motif</scene>''' - Constitute the binding sites for Calcium-free, Calcium-calmodulin (CaM) or Apocalmodulin (apo-CaM). | ||
| - | *'''<scene name='97/973101/P_loop_switch_i_and_ii/1'>P-loop, switch I and switch II</scene>''': <span style="color:blue">'''P-loop'''</span>, <span style="color:magenta">'''Switch I'''</span> and <span style="color:green">'''Switch II'''</span> are nucleotide-binding elements, participating in nucleotide-binding in different stages of the kinetic cycle. More specifically, | + | *'''<scene name='97/973101/P_loop_switch_i_and_ii/1'>P-loop, switch I and switch II</scene>''': <span style="color:blue">'''P-loop'''</span>, <span style="color:magenta">'''Switch I'''</span> and <span style="color:green">'''Switch II'''</span> are nucleotide-binding elements, participating in nucleotide-binding in different stages of the kinetic cycle. More specifically, <span style="color:magenta">'''Switch I'''</span> binds both the Mg<sup>2+</sup> ion and the γ-phosphate of ATP in the active site, therefore, it controls the nucleotide release from the motor and binding to the motor. The <scene name='97/973101/P_loop_switch_i_and_ii/2'>spacefill representation</scene> shows a better view where the nucleotides binds and how tightly this process may be regulated. |
| - | The '''motor domain''' contains '''two inserts''' that are unique in the myosin superfamily: | + | The '''motor domain''' of myosin VI contains '''two inserts''' that are unique in the myosin superfamily: |
'''Insert 1: <scene name='97/973101/278_303_purple/1'>Cys278-Ala303</scene>.''' | '''Insert 1: <scene name='97/973101/278_303_purple/1'>Cys278-Ala303</scene>.''' | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
*'''Function''': This insert provides unique kinetic characteristics: it modulates nucleotide binding and Switch I flexibility, therefore, it slows ADP release and ATP-induced dissociation of the motor from actin (at saturating ATP concentrations). | *'''Function''': This insert provides unique kinetic characteristics: it modulates nucleotide binding and Switch I flexibility, therefore, it slows ADP release and ATP-induced dissociation of the motor from actin (at saturating ATP concentrations). | ||
| - | *'''Mechanism''': As also seen in all other myosins, the conformation of Switch I relative to the U50kDa subdomain is not altered by the presence of insert 1. However, the small loop (<scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop/1'>Gly304-Asp313</scene> - in <span style="color:grey">'''grey'''</span>) that follows this insert, is repositioned, standing out in the nucleotide-binding pocket (decreasing nucleotide accessibility by steric impediment) and strongly interacting with Switch I by the residues: <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/1'>L306, D308, L310, L311</scene> (in <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span>). Also, <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/1'>C278 and F282</scene> (in <span style="color:green">'''green'''</span>) of insert 1 interacts with <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/3'>Switch I</scene> (in <span style="color:magenta">'''magenta'''</span>). <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/2'>Leucine 310</scene> (highlighted in <span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span>) is specifically important because its position selectively interferes with ATP binding, while having little or no effect on ADP binding. Mutation of | + | *'''Mechanism''': As also seen in all other myosins, the conformation of Switch I relative to the U50kDa subdomain is not altered by the presence of insert 1. However, the small loop (<scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop/1'>Gly304-Asp313</scene> - in <span style="color:grey">'''grey'''</span>) that follows this insert, is repositioned, standing out in the nucleotide-binding pocket (decreasing nucleotide accessibility by steric impediment) and strongly interacting with Switch I by the residues: <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/1'>L306, D308, L310, L311</scene> (in <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span>). Also, <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/1'>C278 and F282</scene> (in <span style="color:green">'''green'''</span>) of insert 1 interacts with <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/3'>Switch I</scene> (in <span style="color:magenta">'''magenta'''</span>). <scene name='97/973101/Insert_1_and_small_loop_key/2'>Leucine 310</scene> (highlighted in <span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span>) is specifically important because its position selectively interferes with ATP binding, while having little or no effect on ADP binding. Mutation of Leucine 310 to Glycine removes all influence of insert 1 on ATP binding <ref>Pylypenko, O., Song, L., Squires, G., Liu, X., Zong, A. B., Houdusse, A., & Sweeney, H. L. (2011). Role of insert-1 of myosin VI in modulating nucleotide affinity. The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(13), 11716–11723. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.200626</ref>. |
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
*'''Function''': Redirectionare the lever arm and contains a new CaM-binding motif. | *'''Function''': Redirectionare the lever arm and contains a new CaM-binding motif. | ||
| - | *'''Mechanism''': The proximal part of insert 2 (<scene name='97/973101/774_812_distal_and_proximal/3'>Pro774-Trp787</scene> - in <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span>) wraps around the <scene name='97/973101/774_812_distal_and_proximal/4'>converter</scene> (in <span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span>), while the distal part (<scene name='97/973101/774_812_distal_and_proximal/3'>Trp787-Tyr812</scene> - in <span style="color:green">'''green'''</span>) forms a CaM-binding motif. The insert 2 and its associated CaM molecule (with 4Ca<sup>2+</sup>), make specific interactions with the converter, many involving a variable loop (<scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/1'>Lys719-Pro731</scene>- in <span style="color:magenta">'''magenta'''</span>). In addiction, there is '''apolar interactions''' that stabilize the proximal part of insert 2 on the surface of the converter, where <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/3'>hidrophofobic side chains</scene> from the amino acids <span style="color:gold">'''F763, F766, M770'''</span> stabilize the orientation of the last helix <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/4'>(representation with cartoon and stick)</scene>. Also, there is <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full_salt_bridges/2'>salt-bridge interactions</scene> between the converter and both lobes of CaM, throghout the amino acids: <span style="color:orange">''' D730, E114, K795, R792'''</span>; <span style="color:blue">'''K736, E14, R732'''</span>; and <span style="color:gold">'''R728, E120'''</span>. The result of <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/2'>interactions</scene> is that <scene name='97/973101/Iq_helix_emerge/1'>IQ helix</scene> | + | *'''Mechanism''': The proximal part of insert 2 (<scene name='97/973101/774_812_distal_and_proximal/3'>Pro774-Trp787</scene> - in <span style="color:red">'''red'''</span>) wraps around the <scene name='97/973101/774_812_distal_and_proximal/4'>converter</scene> (in <span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span>), while the distal part (<scene name='97/973101/774_812_distal_and_proximal/3'>Trp787-Tyr812</scene> - in <span style="color:green">'''green'''</span>) forms a CaM-binding motif. The insert 2 and its associated CaM molecule (with 4Ca<sup>2+</sup>), make specific interactions with the converter, many involving a variable loop (<scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/1'>Lys719-Pro731</scene>- in <span style="color:magenta">'''magenta'''</span>). In addiction, there is '''apolar interactions''' that stabilize the proximal part of insert 2 on the surface of the converter, where <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/3'>hidrophofobic side chains</scene> from the amino acids <span style="color:gold">'''F763, F766, M770'''</span> stabilize the orientation of the last helix <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/4'>(representation with cartoon and stick)</scene>. Also, there is <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full_salt_bridges/2'>salt-bridge interactions</scene> between the converter and both lobes of CaM, throghout the amino acids: <span style="color:orange">''' D730, E114, K795, R792'''</span>; <span style="color:blue">'''K736, E14, R732'''</span>; and <span style="color:gold">'''R728, E120'''</span>. The result of <scene name='97/973101/Insert_2_full/2'>interactions</scene> is that <scene name='97/973101/Iq_helix_emerge/1'>IQ helix</scene> (in <span style="color:green">'''green'''</span>) '''emerges ~120°''' from the position that it emerges in all other myosins, '''redirecting the IQ helix''' and the CaM towards the '''minus-end''' of the actin filament. '''This is what makes myosin VI unique'''. |
The figure below compare the orientation of the last helix of the converter in myosin VI (<span style="color:green">'''green'''</span>) with myosin V (<span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span>), and it shows a '''difference of 19°''', that combined with the apolar and salt-bridges interactions, makes the emerge of the IQ helix 120° from the position that it emerges in all other myosins. | The figure below compare the orientation of the last helix of the converter in myosin VI (<span style="color:green">'''green'''</span>) with myosin V (<span style="color:blue">'''blue'''</span>), and it shows a '''difference of 19°''', that combined with the apolar and salt-bridges interactions, makes the emerge of the IQ helix 120° from the position that it emerges in all other myosins. | ||
Current revision
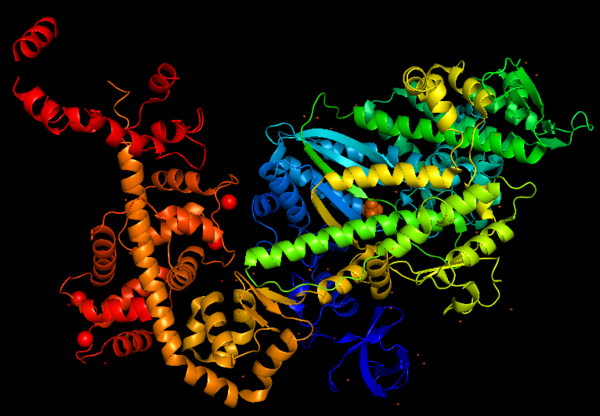
Myosin VI nucleotide-free (MDinsert2-IQ) crystal structure (2BKI)
| |||||||||||