We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Renin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
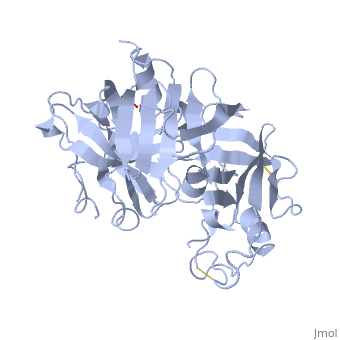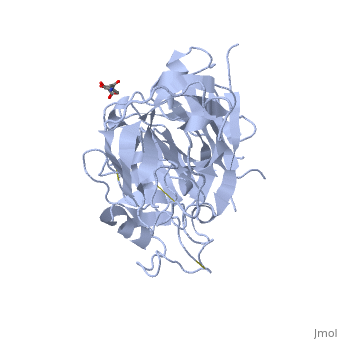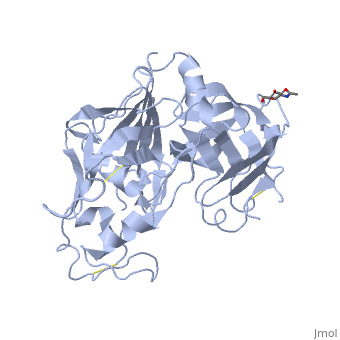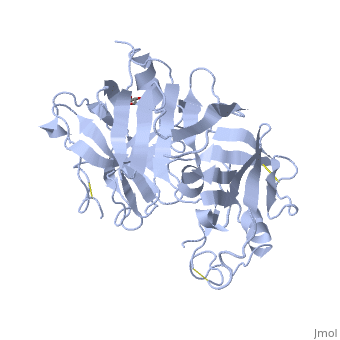
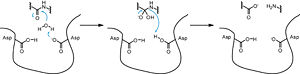
| - | The precursor of renin is a 406 amino acid residue protein. <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Signal_domain/1'>Residues 1-23</scene> are a signal peptide sequence and residues 24-66 are cleaved to produce the mature 340 amino acid residue <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Mature_renin/1'>mature renin</scene>. The secondary structural elements of renin include 29 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Betasheetscolors/1'> antiparallel β sheets</scene>, 3 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Betabridges/1'> β bridges</scene>, 4 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Alphahelixes/1'> α helices</scene>, <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/310heleices/1'> 2 </scene>3<sub>10</sub><scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/310heleices/1'> helices</scene>, and <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Turns/1'>18 turns</scene>. The most impressive structural feature of renin is the antiparallel <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Betasheetspiral/1'> β sheet</scene> that forms the two similar lobes of renin. <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Hydrophobichydrophillic/1'>Hydrophilic (blue) and hydrophobic (red) residues</scene> are located primarily on the outside and inside portions of renin respectively. The most important structure is the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Hydrophobicactivesite/1'>hydrophobic pocket</scene> located in the active site that allows substrate binding. The active site of renin contains two essential <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Activesiteasps2/2'>aspartate residues</scene>. Renin has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Catalyticmotifs/1'>two catalytic motifs</scene> after each of the two aspartate residues. Renin also uses a <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Activesiteflap/1'>active site flap</scene>, a β hairpin structure, that open and closes to uncover or cover the active site. | + | The precursor of renin '''prorenin''' is a 406 amino acid residue protein. <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Signal_domain/1'>Residues 1-23</scene> are a signal peptide sequence and residues 24-66 are cleaved to produce the mature 340 amino acid residue <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Mature_renin/1'>mature renin</scene>. The secondary structural elements of renin include 29 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Betasheetscolors/1'> antiparallel β sheets</scene>, 3 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Betabridges/1'> β bridges</scene>, 4 <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Alphahelixes/1'> α helices</scene>, <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/310heleices/1'> 2 </scene>3<sub>10</sub><scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/310heleices/1'> helices</scene>, and <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Turns/1'>18 turns</scene>. The most impressive structural feature of renin is the antiparallel <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Betasheetspiral/1'> β sheet</scene> that forms the two similar lobes of renin. <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Hydrophobichydrophillic/1'>Hydrophilic (blue) and hydrophobic (red) residues</scene> are located primarily on the outside and inside portions of renin respectively. The most important structure is the <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Hydrophobicactivesite/1'>hydrophobic pocket</scene> located in the active site that allows substrate binding. The active site of renin contains two essential <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Activesiteasps2/2'>aspartate residues</scene>. Renin has <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Catalyticmotifs/1'>two catalytic motifs</scene> after each of the two aspartate residues. Renin also uses a <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Activesiteflap/1'>active site flap</scene>, a β hairpin structure, that open and closes to uncover or cover the active site. |
Post translational modifications of renin include; precursor cleavage of propetide to produce active mature renin, disulfide bond formation, and glycosylation of certain residues. Disulfide bonds are formed to connect serine residues <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Disulfidebond1/2'>51 to 58</scene>, <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Disulfidebond2/2'>217 to 221</scene>, and <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Disulfidebond3/2'>259 to 296</scene>. <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Glycosylated/2'>Two asparagine residues</scene> at positions 14 and 75 can be glycosylated. The asparagine residue at postion 75 is glycosylated (2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-A-D-glucopyranose) in mature renin whereas the residue at postion 14 is not glycosylated.<ref>Margrane M. and the UnitProt consortium, '''Uniprot Knowledgebase: a hub of integrated protein data''', Database, 2012: bar009 (2011). Public Accession Number P00797 </ref> | Post translational modifications of renin include; precursor cleavage of propetide to produce active mature renin, disulfide bond formation, and glycosylation of certain residues. Disulfide bonds are formed to connect serine residues <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Disulfidebond1/2'>51 to 58</scene>, <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Disulfidebond2/2'>217 to 221</scene>, and <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Disulfidebond3/2'>259 to 296</scene>. <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_489/Glycosylated/2'>Two asparagine residues</scene> at positions 14 and 75 can be glycosylated. The asparagine residue at postion 75 is glycosylated (2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-A-D-glucopyranose) in mature renin whereas the residue at postion 14 is not glycosylated.<ref>Margrane M. and the UnitProt consortium, '''Uniprot Knowledgebase: a hub of integrated protein data''', Database, 2012: bar009 (2011). Public Accession Number P00797 </ref> | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
==3D structures of renin== | ==3D structures of renin== | ||
| + | [[Renin 3D structures]] | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | [[1bbs]], [[2ren]] – hRen – human<br /> | ||
| - | [[1rne]] – hRen + transition state analog inhibitor <br /> | ||
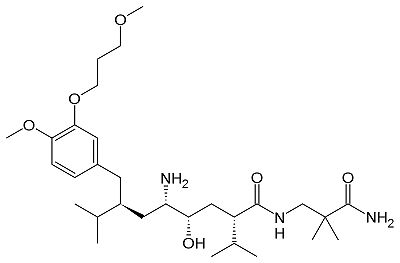
| - | [[1hrn]], [[1bil]], [[1bim]], [[2bks]], [[2bkt]], [[2fs4]], [[2g1n]], [[2g1o]], [[2g1r]], [[2g1s]], [[2g1y]], [[2g21]], [[2g22]], [[2g24]], [[2g26]], [[2g27]], [[2g20]], [[2i4q]], [[2iko]], [[2iku]], [[2il2]], [[2v0z]], [[2v10]], [[2v11]], [[3d91]], [[2v13]], [[2v16]], [[3gw5]], [[3g6z]], [[3g70]], [[3g72]], [[3km4]], [[3k1w]], [[3oqf]], [[3oot]], [[3oqk]], [[3oad]], [[3oag]], [[3own]], [[3o9l]], [[3q3t]], [[3sfc]], [[3q4b]], [[3q5h]], [[3vsw]], [[3vsx]], [[2v12]], [[3vuc]], [[3vyd]], [[3vye]], [[3vyf]], [[4gj5]], [[4gj6]], [[4gj7]], [[4gj8]], [[4gj9]], [[4gja]], [[4gjb]], [[4gjc]], [[4gjd]], [[4pyv]], [[4q1n]], [[4ryc]], [[4ryg]], [[4rz1]], [[4s1g]], [[4xx3]], [[4xx4]], [[5kod]], [[5kos]], [[5kot]], [[5t4s]], [[5sxn]], [[5sy2]], [[5sy3]], [[5sz9]], [[5koq]], [[5tmg]], [[5tmk]], [[5v8v]], [[5vpm]], [[5vrp]], [[7xgk]], [[7xgo]], [[7xgp]] - hRen + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[2x0b]] – hRen + angiotensinogen<br /> | ||
| - | [[6i3f]] – hRen (mutant) + angiotensinogen<br /> | ||
| - | [[5mkt]] – mRen-1 – mouse<br /> | ||
| - | [[1smr]] - mRen + peptide inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[5mlg]] – Ren – rat<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[3vcm]], [[4amt]] – hProrenin | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||