User:Kylie Blake/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Kylie Blake(Difference between revisions)
| (23 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<ref name="7TYF">PMID:35324283</ref> | <ref name="7TYF">PMID:35324283</ref> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1037496/C-term_amide/ | + | <scene name='10/1037496/C-term_amide/3'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> |
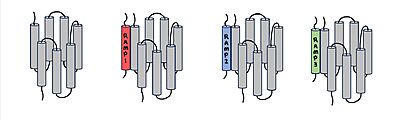
<scene name='10/1037496/Overlay_of_ramps/1'>Overlay of RAMPs</scene> | <scene name='10/1037496/Overlay_of_ramps/1'>Overlay of RAMPs</scene> | ||
<scene name='10/1037496/Overlay_of_ligands/1'>Overlay of Ligands</scene> | <scene name='10/1037496/Overlay_of_ligands/1'>Overlay of Ligands</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1037496/Ligand_in_membrane/2'>Ligand in membrane</scene> | ||
<scene name='10/1037496/G_protein_interaction/1'>Arg 180 and Gln 390 interaction</scene> | <scene name='10/1037496/G_protein_interaction/1'>Arg 180 and Gln 390 interaction</scene> | ||
<scene name='10/1037496/H2ophobic_interactions/1'>Hydrophobic interactions in G protein activation</scene> | <scene name='10/1037496/H2ophobic_interactions/1'>Hydrophobic interactions in G protein activation</scene> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| + | [[Image:bio role.jpg|500 px|right|thumb|Figure number]] | ||
| + | |||
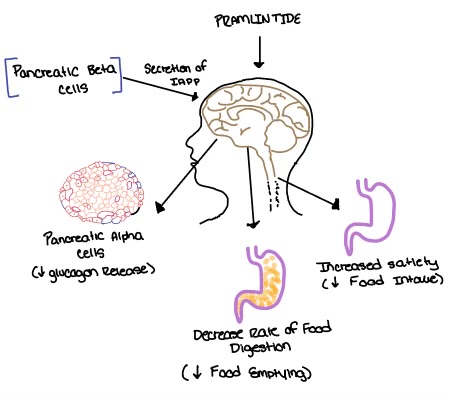
| + | [[Image:Pramlintide.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|Figure number]] | ||
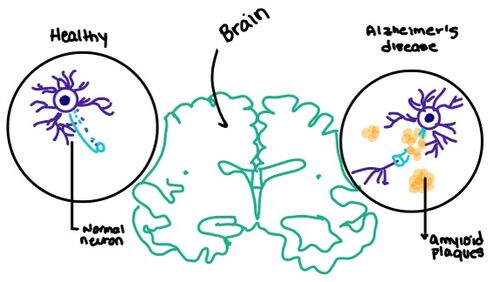
| + | [[Image:Amylin brain.jpeg|500 px|right|thumb|Figure number]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Overlay of RAMPs.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure number]] | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | <ref name=" | + | |
| + | <ref name="Hay">PMID:26071095</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Grizzanti">PMID:30282360</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Mathiesen">PMID:33488526</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="Thapa">Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. ''How Synthetic Drugs Work.'' 95-122. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1 DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Press"> Press, M., Jung, T., Konig, J., Grune, T., & Hohn, A. (2019). Protein aggregates and proteostasis in aging: Amylin and β-cell function. ''Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 3,'' 46-54. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010 DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010 | ||
| + | |||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
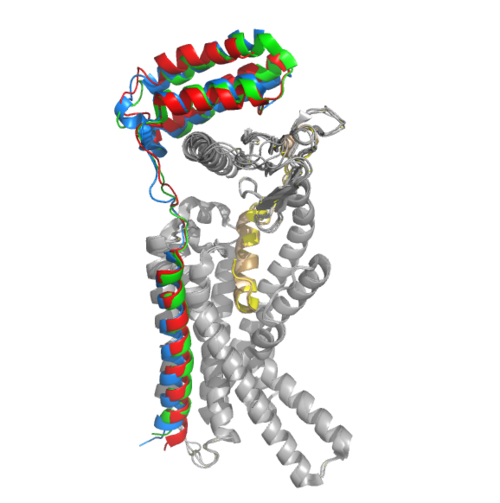
| - | [[Image:Amylin Receptors with ramp 1, 2, 3.png|400px|right|thumb|Figure 1.]] | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | <scene name='10/1037494/Transmembrane/4'>Transmembrane</scene> |
| + | <scene name='10/1037495/Amylin_disulfide_bond2/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:RAMP_diagram.jpg|400px|right|thumb|Figure 2.]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 45: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | <ref name="Ransey"/> | ||
<ref name="7TYF"/> | <ref name="7TYF"/> | ||
| + | <ref name="Hay"> | ||
| + | <ref name="Grizzanti"> | ||
| + | <ref name="Cao"> | ||
| + | <ref name="Mathiesen"> | ||
| + | <ref name="Thapa"> | ||
| + | <ref name="Press"> | ||
| + | |||
==Student Contributors== | ==Student Contributors== | ||
Current revision
Amylin Receptor, AMYr, Protein
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. PMID:26071095 doi:10.1124/pr.115.010629
- ↑ Grizzanti J, Corrigan R, Casadesus G. Neuroprotective Effects of Amylin Analogues on Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(1):11-23. PMID:30282360 doi:10.3233/JAD-180433
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609
- ↑ Mathiesen DS, Lund A, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK, Bagger JI. Amylin and Calcitonin: Potential Therapeutic Strategies to Reduce Body Weight and Liver Fat. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 8;11:617400. PMID:33488526 doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.617400
- ↑ Thapa, G., Kumari, A., Dasgupta, D., Bandyopadhy, S., Sarkar, N., Roy, K., Karunakaran, G., Kazmi, I., Karmakar, S., & Chakraborty, M. (2023). Chapter 5- Insight into the mechanism of action of anti-diabetic drugs. How Synthetic Drugs Work. 95-122. DOI:10.1016/B978-0-323-99855-0.00005-1
- ↑ Press, M., Jung, T., Konig, J., Grune, T., & Hohn, A. (2019). Protein aggregates and proteostasis in aging: Amylin and β-cell function. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 3, 46-54. DOI:10.1016/j.mad.2018.03.010