Emily Berkman/Sandbox 2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==amylin images== | ==amylin images== | ||
<StructureSection load='7tzf' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='7tzf' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | <scene name='10/1038871/Rat_pram_19/2'>residue 19 changes</scene> | |
| - | <scene name='10/1038871/Rat_pram_19/ | + | <scene name='10/1037520/Y37_and_e74_ramp3/2'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> |
| + | <scene name='10/1037516/R18/4'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Starting in 1900, amylin deposits were first discovered in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatic_islets pancreatic islet] cells in diabetic patients. Later in 1943, more characterization was done and it was determined that these amylin deposits were [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid amyloid] in nature. More research was done over the years and by the 1980s, amylin was properly identified and the 37 amino acid sequence was identified. By 1995, the first analog of amylin, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pramlintide pramlintide], was synthesized. In the late 1990s, it was discovered through [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryogenic_electron_microscopy cryogenic electron microscopy] that the amylin receptor was made of the calcitonin receptor core. The calcitonin heterodimerizes with a receptor-activating modifying protein, or RAMP, to form different amylin receptors.<ref name="Bower">PMID:27061187</ref> | Starting in 1900, amylin deposits were first discovered in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatic_islets pancreatic islet] cells in diabetic patients. Later in 1943, more characterization was done and it was determined that these amylin deposits were [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid amyloid] in nature. More research was done over the years and by the 1980s, amylin was properly identified and the 37 amino acid sequence was identified. By 1995, the first analog of amylin, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pramlintide pramlintide], was synthesized. In the late 1990s, it was discovered through [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryogenic_electron_microscopy cryogenic electron microscopy] that the amylin receptor was made of the calcitonin receptor core. The calcitonin heterodimerizes with a receptor-activating modifying protein, or RAMP, to form different amylin receptors.<ref name="Bower">PMID:27061187</ref> | ||
| - | [[Image:conserved residues.png|400 px|left|thumb|Figure 1. Sequence alignment comparing the amylin residues across species.]] | + | [[Image:conserved residues.png|400 px|left|thumb|Figure 1. Sequence alignment comparing the amylin residues across species. <ref name="Bower">PMID:27061187</ref>]] |
==Amylin== | ==Amylin== | ||
| - | Amylin is extremely conserved among species, in order to maintain proper structure and function. Some of the main <scene name='10/1038871/Conserved_residues/ | + | Amylin is extremely conserved among species, in order to maintain proper structure and function. Some of the main <scene name='10/1038871/Conserved_residues/5'>conserved residues</scene> are Lysine 1, Cysteine 2, Alanine 5, Threonine 6, and Cysteine 7. All of the conserved residues exhibit extensive hydrogen bonding networks between either other residues or surrounding water molecules. There is also a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disulfide disulfide bond] between <scene name='10/1038871/Disulfide/4'>C2 and C7</scene> that is conserved across almost every species. This disulfide causes the N-terminus of amylin to wrap around. <ref name="Bower">PMID:27061187</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 20: | Line 25: | ||
==T9== | ==T9== | ||
| - | Threonine 9 is an essential residue for the stabilization of amylin in the receptor. Threonine side chains are polar which allows them to hydrogen bond with other nearby polar groups, which can lead to extensive networks of interactions. This is seen in amylin at T9. T9 interacts with the <scene name='10/1038871/T9_main_chain/ | + | Threonine 9 is an essential residue for the stabilization of amylin in the receptor. Threonine side chains are polar which allows them to hydrogen bond with other nearby polar groups, which can lead to extensive networks of interactions. This is seen in amylin at T9. T9 interacts with the <scene name='10/1038871/T9_main_chain/8'>main chain atoms</scene> of Y191, M230, I380, and H381 of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitonin_receptor calcitonin receptor] and many surrounding water molecules, but it also interacts with the <scene name='10/1038871/T9_network/4'>side chain atoms</scene> of S159, N194, S195, H226, N233, and Q383. All of these interactions create a very strong interaction between amylin and the receptor. The water network also helps stabilize the active receptor conformation. <ref name="Cao">PMID:35324283</ref> |
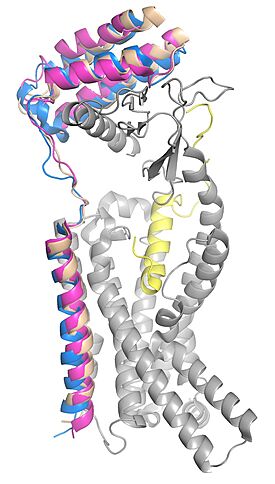
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Superimposed_ramps3.jpg|275 px|left|thumb|Figure 2. RAMP 1, 2, and 3 superimposed in the calcitonin receptor. RAMP 1 is in pink, RAMP 2 is in tan, RAMP 3 is in blue, calcitonin receptor is in grey, and amylin is in yellow. pdb: 7TYF (RAMP 1), 7TYX (RAMP 2), 7TZF (RAMP 3).]] |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
amylin images
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Bower RL, Hay DL. Amylin structure-function relationships and receptor pharmacology: implications for amylin mimetic drug development. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;173(12):1883-98. PMID:27061187 doi:10.1111/bph.13496
- ↑ Cao J, Belousoff MJ, Liang YL, Johnson RM, Josephs TM, Fletcher MM, Christopoulos A, Hay DL, Danev R, Wootten D, Sexton PM. A structural basis for amylin receptor phenotype. Science. 2022 Mar 25;375(6587):eabm9609. PMID:35324283 doi:10.1126/science.abm9609