We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
RMSD between structures
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The root mean square deviation (RMSD) "is a measure of the average deviation in distance between aligned Cα atoms in 3D superimposition. For sequences sharing 50% identity, this should be around 1.0 [Å]."<ref name="holm-using">PMID:32006276</ref>. | The root mean square deviation (RMSD) "is a measure of the average deviation in distance between aligned Cα atoms in 3D superimposition. For sequences sharing 50% identity, this should be around 1.0 [Å]."<ref name="holm-using">PMID:32006276</ref>. | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | For N deviations ''d'' <ref name="equation">since <math> is not implemented in Proteopedia, I generated this equation in Wikipedia on a scratch page, and then took a snapshot. Code in wikipedia: | ||
| + | <nowiki>:<math>\operatorname{RMSD}= \sqrt{\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{N} (d_{i})^2}{N}}</math></nowiki></ref>,<br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Rmsd-equation.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The RMSD between two independently-determined [[X-ray crystallography]] structures of the same protein is typically about 1.0 Å. Larger values of the RMSD indicate less similarity between the two structures. | ||
| + | |||
| + | RMSD is useful for structures with substantial similarity, but less useful when the structures diverge more. [[Calculating GDT TS|GDT TS]] has been used in the [[CASP]] competitions to detect more remote similarities. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Current revision
The root mean square deviation (RMSD) "is a measure of the average deviation in distance between aligned Cα atoms in 3D superimposition. For sequences sharing 50% identity, this should be around 1.0 [Å]."[1].
For N deviations d [2],
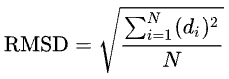
The RMSD between two independently-determined X-ray crystallography structures of the same protein is typically about 1.0 Å. Larger values of the RMSD indicate less similarity between the two structures.
RMSD is useful for structures with substantial similarity, but less useful when the structures diverge more. GDT TS has been used in the CASP competitions to detect more remote similarities.
See Also
- Structure superposition tools
- Calculating GDT TS, the comparison used in the CASP competitions.
References
- ↑ Holm L. Using Dali for Protein Structure Comparison. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2112:29-42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0270-6_3. PMID:32006276 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0270-6_3
- ↑ since <math> is not implemented in Proteopedia, I generated this equation in Wikipedia on a scratch page, and then took a snapshot. Code in wikipedia:
- <math>\operatorname{RMSD}= \sqrt{\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{N} (d_{i})^2}{N}}</math>
