Proteopedia:Featured EDU/7
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <table> <tr><td> <imagemap> Image:1bl8-epm-300pxsq.gif|center default Electrostatic_potential_maps </imagemap> </td></tr> <tr><td><div class="scrolling">'''Make Your Own Electrostatic ...) |
m (Protected "Proteopedia:Featured EDU/7" [edit=sysop:move=sysop]) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<tr><td> | <tr><td> | ||
<imagemap> | <imagemap> | ||
| - | Image: | + | Image:7pmx-y-morph-solid.gif|center |
| - | default [[ | + | default [[Drug and peptide transport in humans]] |
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
| - | <tr><td><div class="scrolling">''' | + | <tr><td><div class="scrolling">'''Transport of Drugs & Nutrients'''<br> |
| - | + | Above is a transmembrane protein that takes up, into your intestinal cells, orally consumed peptide nutrients and drugs. | |
| - | and | + | Its lumen-face (shown above) opens and binds |
| - | <b><span class="text- | + | <b><span class="text-magenta">peptide or drug</span></b>, |
| - | + | then closes, while its cytoplasmic face (opposite end from the above) opens to release its | |
| - | + | <b><span class="text-magenta">cargo</span></b> | |
| - | + | into the intestinal cell, which passes it on into the blood circulation. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | >>> [[ | + | >>> [[Drug and peptide transport in humans|See more animations and explanation]] >>> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
Current revision
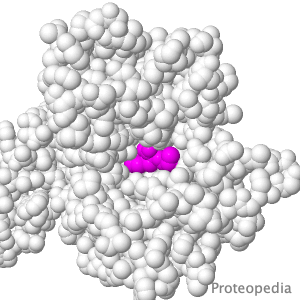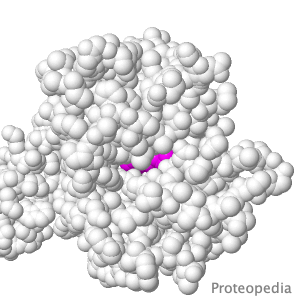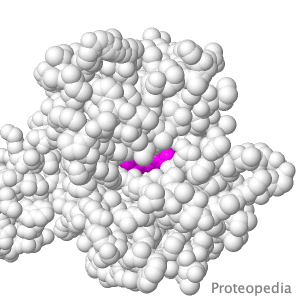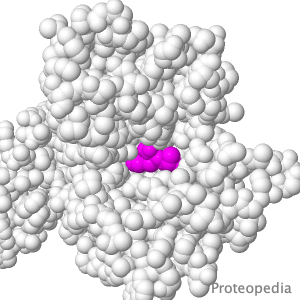
Transport of Drugs & Nutrients
Above is a transmembrane protein that takes up, into your intestinal cells, orally consumed peptide nutrients and drugs. Its lumen-face (shown above) opens and binds peptide or drug, then closes, while its cytoplasmic face (opposite end from the above) opens to release its cargo into the intestinal cell, which passes it on into the blood circulation. |